[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8g6y: Structure of WT E.coli ribosome 50S subunit with complexed with m... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8g6y | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of WT E.coli ribosome 50S subunit with complexed with mRNA, P-site fMet-NH-tRNAfMet and A-site 3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylic acid charged NH-tRNAPhe | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / non-natural monomers / aminobenzoic acids / unnatural monomers | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / DnaA-L2 complex / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / cytosolic ribosome assembly / ribosome assembly / regulation of cell growth / translational initiation / large ribosomal subunit ...negative regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / DnaA-L2 complex / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / cytosolic ribosome assembly / ribosome assembly / regulation of cell growth / translational initiation / large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosome binding / 5S rRNA binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / response to antibiotic / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.09 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Majumdar, C. / Cate, J.H.D. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: ACS Cent Sci / Year: 2023 Journal: ACS Cent Sci / Year: 2023Title: Aminobenzoic Acid Derivatives Obstruct Induced Fit in the Catalytic Center of the Ribosome. Authors: Chandrima Majumdar / Joshua A Walker / Matthew B Francis / Alanna Schepartz / Jamie H D Cate /  Abstract: The () ribosome can incorporate a variety of non-l-α-amino acid monomers into polypeptide chains but with poor efficiency. Although these monomers span a diverse set of compounds, there exists no ...The () ribosome can incorporate a variety of non-l-α-amino acid monomers into polypeptide chains but with poor efficiency. Although these monomers span a diverse set of compounds, there exists no high-resolution structural information regarding their positioning within the catalytic center of the ribosome, the peptidyl transferase center (PTC). Thus, details regarding the mechanism of amide bond formation and the structural basis for differences and defects in incorporation efficiency remain unknown. Within a set of three aminobenzoic acid derivatives-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylic acid (Apy), aminobenzoic acid (ABZ), and aminobenzoic acid (ABZ)-the ribosome incorporates Apy into polypeptide chains with the highest efficiency, followed by ABZ and then ABZ, a trend that does not track with the nucleophilicity of the reactive amines. Here, we report high-resolution cryo-EM structures of the ribosome with each of these three aminobenzoic acid derivatives charged on tRNA bound in the aminoacyl-tRNA site (A-site). The structures reveal how the aromatic ring of each monomer sterically blocks the positioning of nucleotide U2506, thereby preventing rearrangement of nucleotide U2585 and the resulting induced fit in the PTC required for efficient amide bond formation. They also reveal disruptions to the bound water network that is believed to facilitate formation and breakdown of the tetrahedral intermediate. Together, the cryo-EM structures reported here provide a mechanistic rationale for differences in reactivity of aminobenzoic acid derivatives relative to l-α-amino acids and each other and identify stereochemical constraints on the size and geometry of non-monomers that can be accepted efficiently by wild-type ribosomes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8g6y.cif.gz 8g6y.cif.gz | 2.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8g6y.ent.gz pdb8g6y.ent.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8g6y.json.gz 8g6y.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g6/8g6y https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g6/8g6y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g6/8g6y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g6/8g6y | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 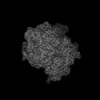 29788MC  8g6wC  8g6xC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 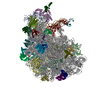
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 28 types, 28 molecules 01234cdefghijklmnoprstuvwxyz
-RNA chain , 5 types, 5 molecules XYZab
| #6: RNA chain | Mass: 9036.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
|---|---|
| #7: RNA chain | Mass: 24485.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
| #8: RNA chain | Mass: 24513.604 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
| #9: RNA chain | Mass: 941811.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #10: RNA chain | Mass: 38790.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules q
| #25: Protein | Mass: 11586.374 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 7 types, 3711 molecules 
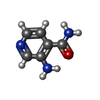
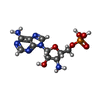
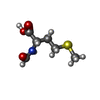









| #35: Chemical | | #36: Chemical | ChemComp-YRW / | #37: Chemical | ChemComp-8AN / | #38: Chemical | ChemComp-FME / | #39: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #40: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #41: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: 50S subunit of E.coli ribosome / Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: #1-#6, #9-#34 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.09 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 288552 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj



































