+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8f0x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
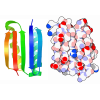
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Kap114 bound to H2A-H2B | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN TRANSPORT/STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Karyopherin Beta Nuclear Transport Histone Histone Chaperone / PROTEIN TRANSPORT-STRUCTURAL PROTEIN complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHATs acetylate histones / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / : / : / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / HDACs deacetylate histones / NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / RMTs methylate histone arginines ...HATs acetylate histones / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / : / : / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / HDACs deacetylate histones / NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / RMTs methylate histone arginines / nuclear import signal receptor activity / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / mRNA transport / Ub-specific processing proteases / nuclear pore / small GTPase binding / protein import into nucleus / structural constituent of chromatin / nuclear envelope / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / chromatin organization / protein heterodimerization activity / DNA repair / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.21 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jiou, J. / Chook, Y.M. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023Title: Mechanism of RanGTP priming H2A-H2B release from Kap114 in an atypical RanGTP•Kap114•H2A-H2B complex. Authors: Jenny Jiou / Joy M Shaffer / Natalia E Bernades / Ho Yee Joyce Fung / Juliana Kikumoto Dias / Sheena D'Arcy / Yuh Min Chook /  Abstract: Previously, we showed that the nuclear import receptor Importin-9 wraps around the H2A-H2B core to chaperone and transport it from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. However, unlike most nuclear import ...Previously, we showed that the nuclear import receptor Importin-9 wraps around the H2A-H2B core to chaperone and transport it from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. However, unlike most nuclear import systems where RanGTP dissociates cargoes from their importins, RanGTP binds stably to the Importin-9•H2A-H2B complex, and formation of the ternary RanGTP•Importin-9•H2A-H2B complex facilitates H2A-H2B release to the assembling nucleosome. It was unclear how RanGTP and the cargo H2A-H2B can bind simultaneously to an importin, and how interactions of the three components position H2A-H2B for release. Here, we show cryo-EM structures of Importin-9•RanGTP and of its yeast homolog Kap114, including Kap114•RanGTP, Kap114•H2A-H2B, and RanGTP•Kap114•H2A-H2B, to explain how the conserved Kap114 binds H2A-H2B and RanGTP simultaneously and how the GTPase primes histone transfer to the nucleosome. In the ternary complex, RanGTP binds to the N-terminal repeats of Kap114 in the same manner as in the Kap114/Importin-9•RanGTP complex, and H2A-H2B binds via its acidic patch to the Kap114 C-terminal repeats much like in the Kap114/Importin-9•H2A-H2B complex. Ran binds to a different conformation of Kap114 in the ternary RanGTP•Kap114•H2A-H2B complex. Here, Kap114 no longer contacts the H2A-H2B surface proximal to the H2A docking domain that drives nucleosome assembly, positioning it for transfer to the assembling nucleosome or to dedicated H2A-H2B chaperones in the nucleus. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8f0x.cif.gz 8f0x.cif.gz | 208.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8f0x.ent.gz pdb8f0x.ent.gz | 161.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8f0x.json.gz 8f0x.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f0/8f0x https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f0/8f0x ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f0/8f0x ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f0/8f0x | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  28782MC  8f19C  8f1eC  8f7aC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 114019.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Production host:  References: UniProt: P53067 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 13881.980 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 14133.145 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of Kap114 bound to H2A-H2B dimer / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: 20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 300 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM TCEP, and 0.1% NP-40 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: 1 Kap114 to 1.2 H2A-H2B ratio | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 4 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.1_4122: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.21 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 554529 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj