+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
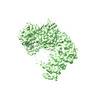
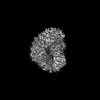
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Kap114 bound to Gsp1 (RanGTP) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | sharpened | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Karyopherin Beta / Nuclear Transport / GTPase / PROTEIN TRANSPORT-NUCLEAR PROTEIN complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of cell cycle phase transition / regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport / exonucleolytic trimming to generate mature 3'-end of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / Postmitotic nuclear pore complex (NPC) reformation / NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus / nuclear import signal receptor activity / poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus / nucleus organization / mRNA transport / nuclear pore ...regulation of cell cycle phase transition / regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport / exonucleolytic trimming to generate mature 3'-end of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / Postmitotic nuclear pore complex (NPC) reformation / NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus / nuclear import signal receptor activity / poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus / nucleus organization / mRNA transport / nuclear pore / ribosomal subunit export from nucleus / small GTPase binding / protein import into nucleus / nuclear envelope / GTPase activity / GTP binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.49 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jiou J / Chook YM | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023Title: Mechanism of RanGTP priming H2A-H2B release from Kap114 in an atypical RanGTP•Kap114•H2A-H2B complex. Authors: Jenny Jiou / Joy M Shaffer / Natalia E Bernades / Ho Yee Joyce Fung / Juliana Kikumoto Dias / Sheena D'Arcy / Yuh Min Chook /  Abstract: Previously, we showed that the nuclear import receptor Importin-9 wraps around the H2A-H2B core to chaperone and transport it from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. However, unlike most nuclear import ...Previously, we showed that the nuclear import receptor Importin-9 wraps around the H2A-H2B core to chaperone and transport it from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. However, unlike most nuclear import systems where RanGTP dissociates cargoes from their importins, RanGTP binds stably to the Importin-9•H2A-H2B complex, and formation of the ternary RanGTP•Importin-9•H2A-H2B complex facilitates H2A-H2B release to the assembling nucleosome. It was unclear how RanGTP and the cargo H2A-H2B can bind simultaneously to an importin, and how interactions of the three components position H2A-H2B for release. Here, we show cryo-EM structures of Importin-9•RanGTP and of its yeast homolog Kap114, including Kap114•RanGTP, Kap114•H2A-H2B, and RanGTP•Kap114•H2A-H2B, to explain how the conserved Kap114 binds H2A-H2B and RanGTP simultaneously and how the GTPase primes histone transfer to the nucleosome. In the ternary complex, RanGTP binds to the N-terminal repeats of Kap114 in the same manner as in the Kap114/Importin-9•RanGTP complex, and H2A-H2B binds via its acidic patch to the Kap114 C-terminal repeats much like in the Kap114/Importin-9•H2A-H2B complex. Ran binds to a different conformation of Kap114 in the ternary RanGTP•Kap114•H2A-H2B complex. Here, Kap114 no longer contacts the H2A-H2B surface proximal to the H2A docking domain that drives nucleosome assembly, positioning it for transfer to the assembling nucleosome or to dedicated H2A-H2B chaperones in the nucleus. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28788.map.gz emd_28788.map.gz | 15.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28788-v30.xml emd-28788-v30.xml emd-28788.xml emd-28788.xml | 21.3 KB 21.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
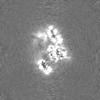
| Images |  emd_28788.png emd_28788.png | 78.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28788.cif.gz emd-28788.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28788_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28788_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28788_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28788_half_map_2.map.gz | 28.3 MB 28.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28788 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28788 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28788 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28788 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8f19MC  8f0xC  8f1eC  8f7aC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28788.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28788.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | sharpened | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
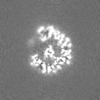
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.059 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
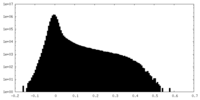
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: half-A
| File | emd_28788_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-A | ||||||||||||
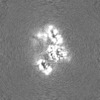
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
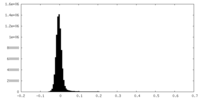
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-B
| File | emd_28788_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
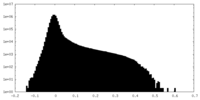
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of Kap114 bound to Gsp1 (RanGTP)
| Entire | Name: Complex of Kap114 bound to Gsp1 (RanGTP) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of Kap114 bound to Gsp1 (RanGTP)
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of Kap114 bound to Gsp1 (RanGTP) / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Importin subunit beta-5
| Macromolecule | Name: Importin subunit beta-5 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 114.019695 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDINELIIGA QSADKHTREV AETQLLQWCD SDASQVFKAL ANVALQHEAS LESRQFALLS LRKLITMYWS PGFESYRSTS NVEIDVKDF IREVLLKLCL NDNENTKIKN GASYCIVQIS AVDFPDQWPQ LLTVIYDAIS HQHSLNAMSL LNEIYDDVVS E EMFFEGGI ...String: MDINELIIGA QSADKHTREV AETQLLQWCD SDASQVFKAL ANVALQHEAS LESRQFALLS LRKLITMYWS PGFESYRSTS NVEIDVKDF IREVLLKLCL NDNENTKIKN GASYCIVQIS AVDFPDQWPQ LLTVIYDAIS HQHSLNAMSL LNEIYDDVVS E EMFFEGGI GLATMEIVFK VLNTETSTLI AKIAALKLLK ACLLQMSSHN EYDEASRKSF VSQCLATSLQ ILGQLLTLNF GN VDVISQL KFKSIIYENL VFIKNDFSRK HFSSELQKQF KIMAIQDLEN VTHINANVET TESEPLLETV HDCSIYIVEF LTS VCTLQF SVEEMNKIIT SLTILCQLSS ETREIWTSDF NTFVSKETGL AASYNVRDQA NEFFTSLPNP QLSLIFKVVS NDIE HSTCN YSTLESLLYL LQCILLNDDE ITGENIDQSL QILIKTLENI LVSQEIPELI LARAILTIPR VLDKFIDALP DIKPL TSAF LAKSLNLALK SDKELIKSAT LIAFTYYCYF AELDSVLGPE VCSETQEKVI RIINQVSSDA EEDTNGALME VLSQVI SYN PKEPHSRKEI LQAEFHLVFT ISSEDPANVQ VVVQSQECLE KLLDNINMDN YKNYIELCLP SFINVLDSNN ANNYRYS PL LSLVLEFITV FLKKKPNDGF LPDEINQYLF EPLAKVLAFS TEDETLQLAT EAFSYLIFNT DTRAMEPRLM DIMKVLER L LSLEVSDSAA MNVGPLVVAI FTRFSKEIQP LIGRILEAVV VRLIKTQNIS TEQNLLSVLC FLTCNDPKQT VDFLSSFQI DNTDALTLVM RKWIEAFEVI RGEKRIKENI VALSNLFFLN DKRLQKVVVN GNLIPYEGDL IITRSMAKKM PDRYVQVPLY TKIIKLFVS ELSFQSKQPN PEQLITSDIK QEVVNANKDD DNDDWEDVDD VLDYDKLKEY IDDDVDEEAD DDSDDITGLM D VKESVVQL LVRFFKEVAS KDVSGFHCIY ETLSDSERKV LSEALL UniProtKB: Importin subunit beta-5 |
-Macromolecule #2: GTP-binding nuclear protein GSP1/CNR1
| Macromolecule | Name: GTP-binding nuclear protein GSP1/CNR1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 20.41759 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSAPAANGEV PTFKLVLVGD GGTGKTTFVK RHLTGEFEKK YIATIGVEVH PLSFYTNFGE IKFDVWDTAG LEKFGGLRDG YYINAQCAI IMFDVTSRIT YKNVPNWHRD LVRVCENIPI VLCGNKVDVK ERKVKAKTIT FHRKKNLQYY DISAKSNYNF E KPFLWLAR KLAGNPQLEF V UniProtKB: GTP-binding nuclear protein GSP1/CNR1 |
-Macromolecule #3: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: GTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.18 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GTP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4.0 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: 20 mM Tris pH 7.5, 300 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM TCEP, and 0.1% NP-40 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 4 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | ||||||||||||||||||
| Details | 1 Kap114 to 1.2 Gsp1 (RanGTP) ratio |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)