[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
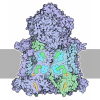
Yorodumi- PDB-7zc5: Complex I from E. coli, DDM/LMNG-purified, under Turnover at pH 8... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7zc5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Complex I from E. coli, DDM/LMNG-purified, under Turnover at pH 8, Resting state | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTON TRANSPORT / Complex I / NADH / Quinone | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTranslocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions / NADH dehydrogenase (quinone) (non-electrogenic) activity / NADH dehydrogenase complex / oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor / ubiquinone binding / electron transport coupled proton transport / NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity / quinone binding / ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / endomembrane system ...Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions / NADH dehydrogenase (quinone) (non-electrogenic) activity / NADH dehydrogenase complex / oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor / ubiquinone binding / electron transport coupled proton transport / NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity / quinone binding / ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / endomembrane system / aerobic respiration / 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding / NAD binding / FMN binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / oxidoreductase activity / iron ion binding / metal ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kravchuk, V. / Kampjut, D. / Sazanov, L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Austria, 1items Austria, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: A universal coupling mechanism of respiratory complex I. Authors: Vladyslav Kravchuk / Olga Petrova / Domen Kampjut / Anna Wojciechowska-Bason / Zara Breese / Leonid Sazanov /    Abstract: Complex I is the first enzyme in the respiratory chain, which is responsible for energy production in mitochondria and bacteria. Complex I couples the transfer of two electrons from NADH to quinone ...Complex I is the first enzyme in the respiratory chain, which is responsible for energy production in mitochondria and bacteria. Complex I couples the transfer of two electrons from NADH to quinone and the translocation of four protons across the membrane, but the coupling mechanism remains contentious. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of Escherichia coli complex I (EcCI) in different redox states, including catalytic turnover. EcCI exists mostly in the open state, in which the quinone cavity is exposed to the cytosol, allowing access for water molecules, which enable quinone movements. Unlike the mammalian paralogues, EcCI can convert to the closed state only during turnover, showing that closed and open states are genuine turnover intermediates. The open-to-closed transition results in the tightly engulfed quinone cavity being connected to the central axis of the membrane arm, a source of substrate protons. Consistently, the proportion of the closed state increases with increasing pH. We propose a detailed but straightforward and robust mechanism comprising a 'domino effect' series of proton transfers and electrostatic interactions: the forward wave ('dominoes stacking') primes the pump, and the reverse wave ('dominoes falling') results in the ejection of all pumped protons from the distal subunit NuoL. This mechanism explains why protons exit exclusively from the NuoL subunit and is supported by our mutagenesis data. We contend that this is a universal coupling mechanism of complex I and related enzymes. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7zc5.cif.gz 7zc5.cif.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7zc5.ent.gz pdb7zc5.ent.gz | 746.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7zc5.json.gz 7zc5.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zc/7zc5 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zc/7zc5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zc/7zc5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zc/7zc5 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14620MC  7p61C  7p62C  7p63C  7p64C  7p69C  7p7cC  7p7eC  7p7jC  7p7kC  7p7lC  7p7mC  7z7rC  7z7sC  7z7tC  7z7vC  7z80C  7z83C  7z84C  7zciC  7zd6C 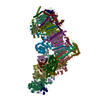 7zdhC 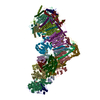 7zdjC 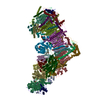 7zdmC 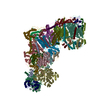 7zdpC 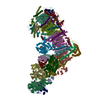 7zebC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit ... , 10 types, 10 molecules FCBIHALNKJ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 49352.332 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: A0A037YNA7, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 68810.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 25081.809 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: E7T2M5, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 20562.771 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: A0A4V1DR98, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 36240.922 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: E6BKM7, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 16474.283 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: A0A358FP87, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 66513.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: A0A1V3W1N5, NADH dehydrogenase (quinone) |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 52072.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: E2QPD7, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 10852.961 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: A0A7U9LRT0, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 19889.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: A0A0H3MIP2, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
-NADH dehydrogenase I subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules EM
| #2: Protein | Mass: 18614.049 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #10: Protein | Mass: 56560.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules G
| #3: Protein | Mass: 100349.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: A0A8A5GYF0, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of protons; Linked to oxidoreductase reactions |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 7 types, 23 molecules 








| #14: Chemical | ChemComp-SF4 / #15: Chemical | ChemComp-FMN / | #16: Chemical | ChemComp-NAI / | #17: Chemical | #18: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / | #19: Chemical | ChemComp-LFA / #20: Chemical | ChemComp-3PE / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex I / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#13 / Source: NATURAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.16 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid type: Quantifoil R0.6/1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 288 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 80 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 8659 |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1648181 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 82734 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: ML | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 66.01 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








































































 PDBj
PDBj