[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
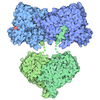
Yorodumi- PDB-7ukf: Human Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex in a putative resting state, t... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ukf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex in a putative resting state, transmembrane region | ||||||
 Components Components | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 2 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / potassium channel complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationKv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex / A-type (transient outward) potassium channel activity / Phase 1 - inactivation of fast Na+ channels / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / membrane repolarization / Voltage gated Potassium channels / anchoring junction / neuronal cell body membrane / postsynaptic specialization membrane / regulation of heart contraction ...Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex / A-type (transient outward) potassium channel activity / Phase 1 - inactivation of fast Na+ channels / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / membrane repolarization / Voltage gated Potassium channels / anchoring junction / neuronal cell body membrane / postsynaptic specialization membrane / regulation of heart contraction / locomotor rhythm / action potential / plasma membrane raft / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / neuronal action potential / muscle contraction / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / sensory perception of pain / GABA-ergic synapse / protein homooligomerization / cellular response to hypoxia / chemical synaptic transmission / dendritic spine / perikaryon / postsynaptic membrane / neuronal cell body / glutamatergic synapse / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.02 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao, H. / Dai, Y. / Lee, C.H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022Title: Activation and closed-state inactivation mechanisms of the human voltage-gated K4 channel complexes. Authors: Wenlei Ye / Hongtu Zhao / Yaxin Dai / Yingdi Wang / Yu-Hua Lo / Lily Yeh Jan / Chia-Hsueh Lee /  Abstract: The voltage-gated ion channel activity depends on both activation (transition from the resting state to the open state) and inactivation. Inactivation is a self-restraint mechanism to limit ion ...The voltage-gated ion channel activity depends on both activation (transition from the resting state to the open state) and inactivation. Inactivation is a self-restraint mechanism to limit ion conduction and is as crucial to membrane excitability as activation. Inactivation can occur when the channel is open or closed. Although open-state inactivation is well understood, the molecular basis of closed-state inactivation has remained elusive. We report cryo-EM structures of human K4.2 channel complexes in inactivated, open, and closed states. Closed-state inactivation of K4 involves an unprecedented symmetry breakdown for pore closure by only two of the four S4-S5 linkers, distinct from known mechanisms of open-state inactivation. We further capture K4 in a putative resting state, revealing how voltage sensor movements control the pore. Moreover, our structures provide insights regarding channel modulation by KChIP2 and DPP6 auxiliary subunits. Our findings elucidate mechanisms of closed-state inactivation and voltage-dependent activation of the K4 channel. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ukf.cif.gz 7ukf.cif.gz | 196.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ukf.ent.gz pdb7ukf.ent.gz | 151.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ukf.json.gz 7ukf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uk/7ukf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uk/7ukf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uk/7ukf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uk/7ukf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  26579MC  7uk5C  7ukcC  7ukdC  7ukeC  7ukgC  7ukhC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 59053.340 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCND2, KIAA1044 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCND2, KIAA1044 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NZV8 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9NZV8#2: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-HG / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex in a putative resting state, transmembrane region Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 69.6 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.02 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 486681 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj