[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-26578: Human Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex in an intermediate state, tran... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex in an intermediate state, transmembrane region | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | potassium channel complex / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationKv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex / A-type (transient outward) potassium channel activity / Phase 1 - inactivation of fast Na+ channels / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / membrane repolarization / Voltage gated Potassium channels / anchoring junction / postsynaptic specialization membrane / neuronal cell body membrane / locomotor rhythm ...Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex / A-type (transient outward) potassium channel activity / Phase 1 - inactivation of fast Na+ channels / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / membrane repolarization / Voltage gated Potassium channels / anchoring junction / postsynaptic specialization membrane / neuronal cell body membrane / locomotor rhythm / regulation of heart contraction / action potential / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / plasma membrane raft / neuronal action potential / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / sensory perception of pain / muscle contraction / protein homooligomerization / GABA-ergic synapse / cellular response to hypoxia / perikaryon / dendritic spine / chemical synaptic transmission / postsynaptic membrane / neuronal cell body / glutamatergic synapse / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.01 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao H / Dai Y / Lee CH | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022Title: Activation and closed-state inactivation mechanisms of the human voltage-gated K4 channel complexes. Authors: Wenlei Ye / Hongtu Zhao / Yaxin Dai / Yingdi Wang / Yu-Hua Lo / Lily Yeh Jan / Chia-Hsueh Lee /  Abstract: The voltage-gated ion channel activity depends on both activation (transition from the resting state to the open state) and inactivation. Inactivation is a self-restraint mechanism to limit ion ...The voltage-gated ion channel activity depends on both activation (transition from the resting state to the open state) and inactivation. Inactivation is a self-restraint mechanism to limit ion conduction and is as crucial to membrane excitability as activation. Inactivation can occur when the channel is open or closed. Although open-state inactivation is well understood, the molecular basis of closed-state inactivation has remained elusive. We report cryo-EM structures of human K4.2 channel complexes in inactivated, open, and closed states. Closed-state inactivation of K4 involves an unprecedented symmetry breakdown for pore closure by only two of the four S4-S5 linkers, distinct from known mechanisms of open-state inactivation. We further capture K4 in a putative resting state, revealing how voltage sensor movements control the pore. Moreover, our structures provide insights regarding channel modulation by KChIP2 and DPP6 auxiliary subunits. Our findings elucidate mechanisms of closed-state inactivation and voltage-dependent activation of the K4 channel. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_26578.map.gz emd_26578.map.gz | 156.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-26578-v30.xml emd-26578-v30.xml emd-26578.xml emd-26578.xml | 14.5 KB 14.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_26578.png emd_26578.png | 90.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-26578.cif.gz emd-26578.cif.gz | 5.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_26578_half_map_1.map.gz emd_26578_half_map_1.map.gz emd_26578_half_map_2.map.gz emd_26578_half_map_2.map.gz | 154 MB 154 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26578 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26578 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26578 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26578 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7ukeMC  7uk5C  7ukcC  7ukdC  7ukfC  7ukgC  7ukhC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_26578.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_26578.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
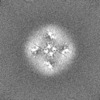
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.826 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_26578_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
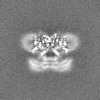
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
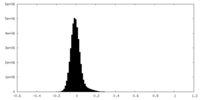
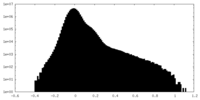
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_26578_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
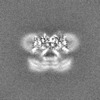
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex in an intermediate state, tran...
| Entire | Name: Human Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex in an intermediate state, transmembrane region |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex in an intermediate state, tran...
| Supramolecule | Name: Human Kv4.2-KChIP2 channel complex in an intermediate state, transmembrane region type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 59.049332 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAAGVAAWLP FARAAAIGWM PVASGPMPAP PRQERKRTQD ALIVLNVSGT RFQTWQDTLE RYPDTLLGSS ERDFFYHPET QQYFFDRDP DIFRHILNFY RTGKLHYPRH ECISAYDEEL AFFGLIPEII GDCCYEEYKD RRRENAERLQ DDADTDTAGE S ALPTMTAR ...String: MAAGVAAWLP FARAAAIGWM PVASGPMPAP PRQERKRTQD ALIVLNVSGT RFQTWQDTLE RYPDTLLGSS ERDFFYHPET QQYFFDRDP DIFRHILNFY RTGKLHYPRH ECISAYDEEL AFFGLIPEII GDCCYEEYKD RRRENAERLQ DDADTDTAGE S ALPTMTAR QRVWRAFENP HTSTMALVFY YVTGFFIAVS VIANVVETVP CGSSPGHIKE LPCGERYAVA FFCLDTACVM IF TVEYLLR LAAAPSRYRF VRSVMSIIDV VAILPYYIGL VMTDNEDVSG AFVTLRVFRV FRIFKFSRHS QGLRILGYTL KSC ASELGF LLFSLTMAII IFATVMFYAE KGSSASKFTS IPAAFWYTIV TMTTLGYGDM VPKTIAGKIF GSICSLSGVL VIAL PVPVI VSNFSRIYHQ NQRADKRRAQ KKARLARIRA AKSGSANAYM QSKRNGLLSN QLQSSEDEQA FVSKSGSSFE TQHHH LLHC LEKTTNHEFV DEQVFEESCM EVATVNRPSS HSPSLSSQQG UniProtKB: A-type voltage-gated potassium channel KCND2 |
-Macromolecule #2: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 76.4 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.01 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 199309 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)