+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7aod | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
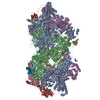
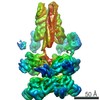
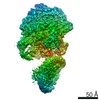
| Title | Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA polymerase I (dimer) | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA polymerase II, holoenzyme / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter ...RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA polymerase II, holoenzyme / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / mRNA Capping / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / DNA-templated transcription elongation / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter / transcription by RNA polymerase III / RNA polymerase I complex / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / RNA polymerase III complex / RNA polymerase II, core complex / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / transcription by RNA polymerase I / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / nucleic acid binding / transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein dimerization activity / nucleolus / mitochondrion / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Heiss, F. / Daiss, J. / Becker, P. / Engel, C. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2items Germany, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Conserved strategies of RNA polymerase I hibernation and activation. Authors: Florian B Heiss / Julia L Daiß / Philipp Becker / Christoph Engel /  Abstract: RNA polymerase (Pol) I transcribes the ribosomal RNA precursor in all eukaryotes. The mechanisms 'activation by cleft contraction' and 'hibernation by dimerization' are unique to the regulation of ...RNA polymerase (Pol) I transcribes the ribosomal RNA precursor in all eukaryotes. The mechanisms 'activation by cleft contraction' and 'hibernation by dimerization' are unique to the regulation of this enzyme, but structure-function analysis is limited to baker's yeast. To understand whether regulation by such strategies is specific to this model organism or conserved among species, we solve three cryo-EM structures of Pol I from Schizosaccharomyces pombe in different functional states. Comparative analysis of structural models derived from high-resolution reconstructions shows that activation is accomplished by a conserved contraction of the active center cleft. In contrast to current beliefs, we find that dimerization of the S. pombe polymerase is also possible. This dimerization is achieved independent of the 'connector' domain but relies on two previously undescribed interfaces. Our analyses highlight the divergent nature of Pol I transcription systems from their counterparts and suggest conservation of regulatory mechanisms among organisms. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7aod.cif.gz 7aod.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7aod.ent.gz pdb7aod.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7aod.json.gz 7aod.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7aod_validation.pdf.gz 7aod_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7aod_full_validation.pdf.gz 7aod_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7aod_validation.xml.gz 7aod_validation.xml.gz | 222.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7aod_validation.cif.gz 7aod_validation.cif.gz | 328.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ao/7aod https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ao/7aod ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ao/7aod ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ao/7aod | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  11841MC  7aocC  7aoeC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase I subunit ... , 4 types, 8 molecules AMDPGSIU
| #1: Protein | Mass: 189489.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: P15398, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #4: Protein | Mass: 17008.439 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: Q9P7P1 #7: Protein | Mass: 19406.354 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: O43036 #9: Protein | Mass: 13127.667 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: O94703 |
|---|
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I and III subunit ... , 2 types, 4 molecules COKW
| #3: Protein | Mass: 39205.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: O94616 #11: Protein | Mass: 13734.478 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: Q09177 |
|---|
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit ... , 5 types, 10 molecules EQFRHTJVLX
| #5: Protein | Mass: 23954.504 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: Q09191 #6: Protein | Mass: 15742.497 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: P36595 #8: Protein | Mass: 14317.318 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: Q92399 #10: Protein | Mass: 8286.801 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: O13877 #12: Protein | Mass: 7216.495 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: P48011 |
|---|
-Protein / Non-polymers , 2 types, 14 molecules BN

| #13: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #2: Protein | Mass: 131854.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / References: UniProt: Q9P7X8, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: S. pombe RNA polymerase I / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#12 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 86.5 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 17102 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 108.25 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj





