+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6shq | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
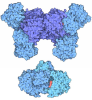
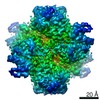
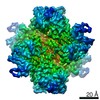
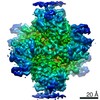
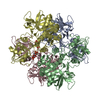
| Title | Escherichia coli AGPase in complex with AMP. Symmetry C2 | ||||||
 Components Components | Glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase | ||||||
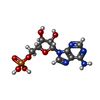
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / ADP-glucose pyrophosphorilase Complex with AMP inhibitor | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase complex / glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase / glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase activity / glycogen biosynthetic process / AMP binding / protein homotetramerization / magnesium ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Cifuente, J.O. / Comino, N. / D'Angelo, C. / Marina, A. / Gil-Carton, D. / Albesa-Jove, D. / Guerin, M.E. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Spain, 1items Spain, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Curr Res Struct Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Curr Res Struct Biol / Year: 2020Title: The allosteric control mechanism of bacterial glycogen biosynthesis disclosed by cryoEM. Authors: Javier O Cifuente / Natalia Comino / Cecilia D'Angelo / Alberto Marina / David Gil-Carton / David Albesa-Jové / Marcelo E Guerin /  Abstract: Glycogen and starch are the major carbon and energy reserve polysaccharides in nature, providing living organisms with a survival advantage. The evolution of the enzymatic machinery responsible for ...Glycogen and starch are the major carbon and energy reserve polysaccharides in nature, providing living organisms with a survival advantage. The evolution of the enzymatic machinery responsible for the biosynthesis and degradation of such polysaccharides, led the development of mechanisms to control the assembly and disassembly rate, to store and recover glucose according to cell energy demands. The tetrameric enzyme ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGPase) catalyzes and regulates the initial step in the biosynthesis of both α-polyglucans. AGPase displays cooperativity and allosteric regulation by sensing metabolites from the cell energy flux. The understanding of the allosteric signal transduction mechanisms in AGPase arises as a long-standing challenge. In this work, we disclose the cryoEM structures of the paradigmatic homotetrameric AGPase from (AGPase), in complex with either positive or negative physiological allosteric regulators, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) and AMP respectively, both at 3.0 Å resolution. Strikingly, the structures reveal that FBP binds deeply into the allosteric cleft and overlaps the AMP site. As a consequence, FBP promotes a concerted conformational switch of a regulatory loop, RL2, from a "locked" to a "free" state, modulating ATP binding and activating the enzyme. This notion is strongly supported by our complementary biophysical and bioinformatics evidence, and a careful analysis of vast enzyme kinetics data on single-point mutants of AGPase. The cryoEM structures uncover the residue interaction networks (RIN) between the allosteric and the catalytic components of the enzyme, providing unique details on how the signaling information is transmitted across the tetramer, from which cooperativity emerges. Altogether, the conformational states visualized by cryoEM reveal the regulatory mechanism of AGPase, laying the foundations to understand the allosteric control of bacterial glycogen biosynthesis at the molecular level of detail. #1:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2020 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2020Title: The allosteric control mechanism of bacterial glycogen biosynthesis disclosed by cryoEM Authors: Cifuente, J.O. / Comino, N. / D'Angelo, C. / Marina, A. / Gil-Carton, D. / Albesa-Jove, D. / Guerin, M.E. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6shq.cif.gz 6shq.cif.gz | 551.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6shq.ent.gz pdb6shq.ent.gz | 461 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6shq.json.gz 6shq.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sh/6shq https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sh/6shq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sh/6shq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sh/6shq | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 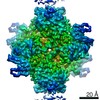 10203MC  6shjC  6shnC  6si8C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 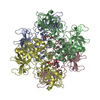
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 48758.590 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   References: UniProt: P0A6V1, glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase #2: Chemical | ChemComp-AMP / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ADP.glucose pyrophosphorylase in complex with the inhibitor AMP Type: COMPLEX / Details: Homotetrameric enzyme / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.194 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.35 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Sample with single particles and some linear chains of particles | ||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Details: Titan Krios I - Ebic - Diamond Light Source |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 80 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.14_3260: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 94769 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5L6V Accession code: 5L6V / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj