+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6lhv | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
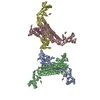
| Title | Structure of FANCA and FANCG Complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA REPAIR / nuclear localization / fanconi anemia core protein / fanconi anemia complementation group a / fanconi anemia complementation group g / interstrand crosslink repair | |||||||||
| Biological species | ||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.59 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jeong, E. / Lee, S. / Shin, J. / Kim, Y. / Scharer, O. / Kim, Y. / Kim, H. / Cho, Y. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Korea, Republic Of, 2items Korea, Republic Of, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2020 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis of the fanconi anemia-associated mutations within the FANCA and FANCG complex. Authors: Eunyoung Jeong / Seong-Gyu Lee / Hyun-Suk Kim / Jihyeon Yang / Jinwoo Shin / Youngran Kim / Jihan Kim / Orlando D Schärer / Youngjin Kim / Jung-Eun Yeo / Ho Min Kim / Yunje Cho /  Abstract: Monoubiquitination of the Fanconi anemia complementation group D2 (FANCD2) protein by the FA core ubiquitin ligase complex is the central event in the FA pathway. FANCA and FANCG play major roles in ...Monoubiquitination of the Fanconi anemia complementation group D2 (FANCD2) protein by the FA core ubiquitin ligase complex is the central event in the FA pathway. FANCA and FANCG play major roles in the nuclear localization of the FA core complex. Mutations of these two genes are the most frequently observed genetic alterations in FA patients, and most point mutations in FANCA are clustered in the C-terminal domain (CTD). To understand the basis of the FA-associated FANCA mutations, we determined the cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of Xenopus laevis FANCA alone at 3.35 Å and 3.46 Å resolution and two distinct FANCA-FANCG complexes at 4.59 and 4.84 Å resolution, respectively. The FANCA CTD adopts an arc-shaped solenoid structure that forms a pseudo-symmetric dimer through its outer surface. FA- and cancer-associated point mutations are widely distributed over the CTD. The two different complex structures capture independent interactions of FANCG with either FANCA C-terminal HEAT repeats, or the N-terminal region. We show that mutations that disturb either of these two interactions prevent the nuclear localization of FANCA, thereby leading to an FA pathway defect. The structure provides insights into the function of FANCA CTD, and provides a framework for understanding FA- and cancer-associated mutations. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6lhv.cif.gz 6lhv.cif.gz | 304 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6lhv.ent.gz pdb6lhv.ent.gz | 243.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6lhv.json.gz 6lhv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6lhv_validation.pdf.gz 6lhv_validation.pdf.gz | 615.2 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6lhv_full_validation.pdf.gz 6lhv_full_validation.pdf.gz | 622.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6lhv_validation.xml.gz 6lhv_validation.xml.gz | 25.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6lhv_validation.cif.gz 6lhv_validation.cif.gz | 46.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lh/6lhv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lh/6lhv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lh/6lhv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lh/6lhv | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 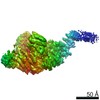 0900MC 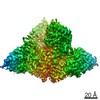 0896C 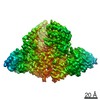 0899C  0901C 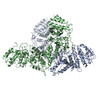 6lhsC  6lhuC  6lhwC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 34059.902 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 68101.625 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)Sequence details | The authors know the complete sequence as follows. But they are not sure which part of sequential ...The authors know the complete sequence as follows. But they are not sure which part of sequential amino acids corresponds with sample sequence. So the number of residues is meaningless. chain C sequence MDYKDDDDKD | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: FANCA / Type: COMPLEX / Details: homo dimer / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 500 kDa/nm / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.8 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron lens | Mode: DIFFRACTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image recording |
|
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.59 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 89678 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj