+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Liganded-state E.coli PatZ | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Acetyltransferase / TRANSFERASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationacyltransferase activity, transferring groups other than amino-acyl groups / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 1.99 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Park JB / Roh SH | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Korea, Republic Of, 1 items Korea, Republic Of, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation | Journal: mBio / Year: 2018 Title: Identification of Novel Protein Lysine Acetyltransferases in Escherichia coli. Authors: David G Christensen / Jesse G Meyer / Jackson T Baumgartner / Alexandria K D'Souza / William C Nelson / Samuel H Payne / Misty L Kuhn / Birgit Schilling / Alan J Wolfe /  Abstract: Posttranslational modifications, such as ε-lysine acetylation, regulate protein function. ε-lysine acetylation can occur either nonenzymatically or enzymatically. The nonenzymatic mechanism uses ...Posttranslational modifications, such as ε-lysine acetylation, regulate protein function. ε-lysine acetylation can occur either nonenzymatically or enzymatically. The nonenzymatic mechanism uses acetyl phosphate (AcP) or acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA) as acetyl donor to modify an ε-lysine residue of a protein. The enzymatic mechanism uses ε-lysine acetyltransferases (KATs) to specifically transfer an acetyl group from AcCoA to ε-lysine residues on proteins. To date, only one KAT (YfiQ, also known as Pka and PatZ) has been identified in Here, we demonstrate the existence of 4 additional KATs: RimI, YiaC, YjaB, and PhnO. In a genetic background devoid of all known acetylation mechanisms (most notably AcP and YfiQ) and one deacetylase (CobB), overexpression of these putative KATs elicited unique patterns of protein acetylation. We mutated key active site residues and found that most of them eliminated enzymatic acetylation activity. We used mass spectrometry to identify and quantify the specificity of YfiQ and the four novel KATs. Surprisingly, our analysis revealed a high degree of substrate specificity. The overlap between KAT-dependent and AcP-dependent acetylation was extremely limited, supporting the hypothesis that these two acetylation mechanisms play distinct roles in the posttranslational modification of bacterial proteins. We further showed that these novel KATs are conserved across broad swaths of bacterial phylogeny. Finally, we determined that one of the novel KATs (YiaC) and the known KAT (YfiQ) can negatively regulate bacterial migration. Together, these results emphasize distinct and specific nonenzymatic and enzymatic protein acetylation mechanisms present in bacteria.ε-Lysine acetylation is one of the most abundant and important posttranslational modifications across all domains of life. One of the best-studied effects of acetylation occurs in eukaryotes, where acetylation of histone tails activates gene transcription. Although bacteria do not have true histones, ε-lysine acetylation is prevalent; however, the role of these modifications is mostly unknown. We constructed an strain that lacked both known acetylation mechanisms to identify four new ε-lysine acetyltransferases (RimI, YiaC, YjaB, and PhnO). We used mass spectrometry to determine the substrate specificity of these acetyltransferases. Structural analysis of selected substrate proteins revealed site-specific preferences for enzymatic acetylation that had little overlap with the preferences of the previously reported acetyl-phosphate nonenzymatic acetylation mechanism. Finally, YiaC and YfiQ appear to regulate flagellum-based motility, a phenotype critical for pathogenesis of many organisms. These acetyltransferases are highly conserved and reveal deeper and more complex roles for bacterial posttranslational modification. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_60853.map.gz emd_60853.map.gz | 310.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-60853-v30.xml emd-60853-v30.xml emd-60853.xml emd-60853.xml | 15.1 KB 15.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_60853.png emd_60853.png | 49.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-60853.cif.gz emd-60853.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60853 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60853 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60853 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60853 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9it0MC  9isbC  9isqC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_60853.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_60853.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.76 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Acetyltransferase
| Entire | Name: Acetyltransferase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Acetyltransferase
| Supramolecule | Name: Acetyltransferase / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Protein acetyltransferase
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein acetyltransferase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 98.099375 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSQRGLEALL RPKSIAVIGA SMKPNRAGYL MMRNLLAGGF NGPVLPVTPA WKAVLGVLAW PDIASLPFTP DLAVLCTNAS RNLALLEEL GEKGCKTCII LSAPASQHED LRACALRHNM RLLGPNSLGL LAPWQGLNAS FSPVPIKRGK LAFISQSAAV S NTILDWAQ ...String: MSQRGLEALL RPKSIAVIGA SMKPNRAGYL MMRNLLAGGF NGPVLPVTPA WKAVLGVLAW PDIASLPFTP DLAVLCTNAS RNLALLEEL GEKGCKTCII LSAPASQHED LRACALRHNM RLLGPNSLGL LAPWQGLNAS FSPVPIKRGK LAFISQSAAV S NTILDWAQ QRKMGFSYFI ALGDSLDIDV DELLDYLARD SKTSAILLYL EQLSDARRFV SAARSASRNK PILVIKSGRS PA AQRLLNT TAGMDPAWDA AIQRAGLLRV QDTHELFSAV ETLSHMRPLR GDRLMIISNG AAPAALALDA LWSRNGKLAT LSE ETCQKL RDALPEHVAI SNPLDLRDDA SSEHYIKTLD ILLHSQDFDA LMVIHSPSAA APATESAQVL IEAVKHHPRS KYVS LLTNW CGEHSSQEAR RLFSEAGLPT YRTPEGTITA FMHMVEYRRN QKQLRETPAL PSNLTSNTAE AHLLLQQAIA EGATS LDTH EVQPILQAYG MNTLPTWIAS DSTEAVHIAE QIGYPVALKL RSPDIPHKSE VQGVMLYLRT ANEVQQAANA IFDRVK MAW PQARVHGLLV QSMANRAGAQ ELRVVVEHDP VFGPLIMLGE GGVEWRPEDQ AVVALPPLNM NLARYLVIQG IKSKKIR AR SALRPLDVAG LSQLLVQVSN LIVDCPEIQR LDIHPLLASG SEFTALDVTL DISPFEGDNE SRLAVRPYPH QLEEWVEL K NGERCLFRPI LPEDEPQLQQ FISRVTKEDL YYRYFSEINE FTHEDLANMT QIDYDREMAF VAVRRIDQTE EILGVTRAI SDPDNIDAEF AVLVRSDLKG LGLGRRLMEK LITYTRDHGL QRLNGITMPN NRGMVALARK LGFNVDIQLE EGIVGLTLNL AQREES UniProtKB: Protein lysine acetyltransferase |
-Macromolecule #2: ACETYL COENZYME *A
| Macromolecule | Name: ACETYL COENZYME *A / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: ACO |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 809.571 Da |
| Chemical component information | 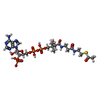 ChemComp-ACO: |
-Macromolecule #3: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 507 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 8.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




















