+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of TmaT-TMA complexes | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TMA / ELECTRON TRANSPORT | |||||||||
| Function / homology | BCCT transporter family / BCCT, betaine/carnitine/choline family transporter / transmembrane transporter activity / plasma membrane / Trimethylamine transporter Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Myroides profundi (bacteria) Myroides profundi (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.09 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chao G | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2025 Journal: mBio / Year: 2025Title: Structural basis of a microbial trimethylamine transporter. Authors: Chao Gao / Hai-Tao Ding / Kang Li / Hai-Yan Cao / Ning Wang / Zeng-Tian Gu / Qing Wang / Mei-Ling Sun / Xiu-Lan Chen / Yin Chen / Yu-Zhong Zhang / Hui-Hui Fu / Chun-Yang Li /   Abstract: Trimethylamine (TMA), a simple trace biogenic amine resulting from the decomposition of proteins and other macromolecules, is ubiquitous in nature. It is found in the human gut as well as in various ...Trimethylamine (TMA), a simple trace biogenic amine resulting from the decomposition of proteins and other macromolecules, is ubiquitous in nature. It is found in the human gut as well as in various terrestrial and marine ecosystems. While the role of TMA in promoting cardiovascular diseases and depolarizing olfactory sensory neurons in humans has only recently been explored, many microbes are well known for their ability to utilize TMA as a carbon, nitrogen, and energy source. Here, we report the first structure of a TMA transporter, TmaT, originally identified from a marine bacterium. TmaT is a member of the betaine-choline-carnitine transporter family, and we show that TmaT is an Na/TMA symporter, which possessed high specificity and binding affinity toward TMA. Furthermore, the structures of TmaT and two TmaT-TMA complexes were solved by cryo-EM. TmaT forms a homotrimer structure in solution. Each TmaT monomer has 12 transmembrane helices, and the TMA transport channel is formed by a four-helix bundle. TMA can move between different aromatic boxes, which provides the structural basis of TmaT importing TMA. When TMA is bound in location I, residues Trp146, Trp151, Tyr154, and Trp326 form an aromatic box to accommodate TMA. Moreover, Met105 also plays an important role in the binding of TMA. When TMA is transferred to location II, it is bound in the aromatic box formed by Trp325, Trp326, and Trp329. Based on our results, we proposed the TMA transport mechanism by TmaT. This study provides novel insights into TMA transport across biological membranes. IMPORTANCE: The volatile trimethylamine (TMA) plays an important role in promoting cardiovascular diseases and depolarizing olfactory sensory neurons in humans and serves as a key nutrient source for ...IMPORTANCE: The volatile trimethylamine (TMA) plays an important role in promoting cardiovascular diseases and depolarizing olfactory sensory neurons in humans and serves as a key nutrient source for a variety of ubiquitous marine microbes. While the TMA transporter TmaT has been identified from a marine bacterium, the structure of TmaT and the molecular mechanism involved in TMA transport remain unclear. In this study, we elucidated the high-resolution cryo-EM structures of TmaT and TmaT-TMA complexes and revealed the TMA binding and transport mechanisms by structural and biochemical analyses. The results advance our understanding of the TMA transport processes across biological membranes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_60548.map.gz emd_60548.map.gz | 59.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-60548-v30.xml emd-60548-v30.xml emd-60548.xml emd-60548.xml | 16.6 KB 16.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_60548_fsc.xml emd_60548_fsc.xml | 8.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_60548.png emd_60548.png | 71 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-60548.cif.gz emd-60548.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_60548_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60548_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60548_half_map_2.map.gz emd_60548_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.3 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60548 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60548 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60548 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60548 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_60548_validation.pdf.gz emd_60548_validation.pdf.gz | 861.2 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_60548_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_60548_full_validation.pdf.gz | 860.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_60548_validation.xml.gz emd_60548_validation.xml.gz | 16.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_60548_validation.cif.gz emd_60548_validation.cif.gz | 21.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60548 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60548 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60548 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60548 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8zxpMC  8zw8C  8zxkC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_60548.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_60548.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : sodium-trimethylamine symporter TmaT binding with TMA
| Entire | Name: sodium-trimethylamine symporter TmaT binding with TMA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: sodium-trimethylamine symporter TmaT binding with TMA
| Supramolecule | Name: sodium-trimethylamine symporter TmaT binding with TMA / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Myroides profundi (bacteria) Myroides profundi (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Trimethylamine transporter
| Macromolecule | Name: Trimethylamine transporter / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Myroides profundi (bacteria) Myroides profundi (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 59.955051 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MFKKLLDNKN LVINPPVFIT SILLIVALIL TCVLFPEKVG VWFPAAQLAV TSNFGWFFVV TVNVILIFAI YLAFSKFGRI RLGGDDAEP EFTKASWFAM LFSTGMGIGI MFFSIAEPVS HFFNTPRPVD TDIEAAVQAM QFTSLHWGLH AWGIYAMVGL A LAFFGFNR ...String: MFKKLLDNKN LVINPPVFIT SILLIVALIL TCVLFPEKVG VWFPAAQLAV TSNFGWFFVV TVNVILIFAI YLAFSKFGRI RLGGDDAEP EFTKASWFAM LFSTGMGIGI MFFSIAEPVS HFFNTPRPVD TDIEAAVQAM QFTSLHWGLH AWGIYAMVGL A LAFFGFNR KLPMTFRSLF YPFWGERIHG WWGHIIDILS ALATVFGLST SLGLGVIQIT AGLEYLYGWE ISPMMQAGII LF VIGIATI SVFSGLDKGV KILSNANMYI AASFMLLIFI LGPTLFIMKG YVENTGAYLA NFIDISTWND TYLGSGWQNV WTI FYWAWW IAWSPFVGSF IARISKGRTV KEFVLGVLIV PGLITLLWMN VFGGSALHTI LSGDVTMIAA VKADVSTALF VFLE NFPFT KFLSIVAIIL IFSFFITSSD SGSLVVDNIT SGSNGESPVW QRVFWSFAQG IIAIVLLWGG GLDALQTAVI ITGLP FAVI LLVMCYSLQK GLKEELAKSS KKAKSKEEKS YKEIIAELLD EPQSKHHHHH HHHHH UniProtKB: Trimethylamine transporter |
-Macromolecule #2: N,N-dimethylmethanamine
| Macromolecule | Name: N,N-dimethylmethanamine / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: KEN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 59.11 Da |
| Chemical component information | 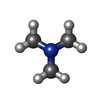 ChemComp-KEN: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.23 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: 4D-STEM / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





