[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-48042: RNA polymerase II-DSIF-SPT6-PAF1c-TFIIS-IWS1-SETD2-nucleosome, 30... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | RNA polymerase II-DSIF-SPT6-PAF1c-TFIIS-IWS1-SETD2-nucleosome, 30 bp upstream | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SETD2 / Transcription / H3K36me3 / TRANSFERASE-RNA-DNA complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationB-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / peptidyl-lysine trimethylation / blastocyst growth / microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in mitosis ...B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / peptidyl-lysine trimethylation / blastocyst growth / microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in mitosis / Ski complex / mRNA decay by 3' to 5' exoribonuclease / RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphoserine binding / [histone H3]-lysine36 N-trimethyltransferase / inner cell mass cell differentiation / positive regulation of mRNA 3'-end processing / regulation of mRNA export from nucleus / regulation of isotype switching / Cdc73/Paf1 complex / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, 3'-5' exonucleolytic nonsense-mediated decay / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / regulation of muscle cell differentiation / histone H3K36 trimethyltransferase activity / endodermal cell fate commitment / negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation / positive regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition / regulation of mRNA processing / DSIF complex / trophectodermal cell differentiation / histone H3K36 methyltransferase activity / regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / blastocyst hatching / response to alkaloid / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / FGFR2 alternative splicing / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / mRNA Capping / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / response to type I interferon / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / nucleosome organization / blastocyst formation / protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity / positive regulation of ossification / mRNA 3'-end processing / regulation of protein localization to chromatin / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / response to metal ion / Abortive elongation of HIV-1 transcript in the absence of Tat / histone H3 methyltransferase activity / poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus / regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / transcription factor TFIID complex / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / interleukin-6-mediated signaling pathway / stem cell population maintenance / negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE during HIV infection / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Formation of the HIV-1 Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / endodermal cell differentiation / RNA polymerase II complex binding / maintenance of transcriptional fidelity during transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of interferon-alpha production / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / positive regulation of macroautophagy / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / cell surface receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / mRNA transport / protein localization to nucleus / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / alpha-tubulin binding / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / RNA polymerase I complex / RNA polymerase III complex / mismatch repair Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Markert J / Farnung L | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2025 Journal: Science / Year: 2025Title: Structural basis of H3K36 trimethylation by SETD2 during chromatin transcription. Authors: Jonathan W Markert / Jelly H Soffers / Lucas Farnung Abstract: During transcription, RNA polymerase II traverses through chromatin, and posttranslational modifications including histone methylations mark regions of active transcription. Histone protein H3 lysine ...During transcription, RNA polymerase II traverses through chromatin, and posttranslational modifications including histone methylations mark regions of active transcription. Histone protein H3 lysine 36 trimethylation (H3K36me3), which is established by the histone methyltransferase SET domain containing 2 (SETD2), suppresses cryptic transcription, regulates splicing, and serves as a binding site for transcription elongation factors. The mechanism by which the transcription machinery coordinates the deposition of H3K36me3 is not well understood. Here we provide cryo-electron microscopy structures of mammalian RNA polymerase II-DSIF-SPT6-PAF1c-TFIIS-IWS1-SETD2-nucleosome elongation complexes, revealing that the transcription machinery regulates H3K36me3 deposition by SETD2 on downstream and upstream nucleosomes. SPT6 binds the exposed H2A-H2B dimer during transcription, and the SPT6 death-like domain mediates an interaction with SETD2 bound to a nucleosome upstream of RNA polymerase II. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_48042.map.gz emd_48042.map.gz | 440.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-48042-v30.xml emd-48042-v30.xml emd-48042.xml emd-48042.xml | 55.2 KB 55.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_48042.png emd_48042.png | 102.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-48042.cif.gz emd-48042.cif.gz | 17.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48042 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48042 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48042 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48042 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 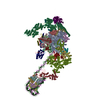 9eh0MC  9egxC  9egyC  9egzC  9eh1C  9eh2C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_48042.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_48042.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 476.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : SETD2 downstream complex
+Supramolecule #1: SETD2 downstream complex
+Macromolecule #1: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit
+Macromolecule #2: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta
+Macromolecule #3: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB3
+Macromolecule #4: RNA polymerase Rpb4/RPC9 core domain-containing protein
+Macromolecule #5: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit E
+Macromolecule #6: DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit RPABC2
+Macromolecule #7: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB7
+Macromolecule #8: DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit RPABC3
+Macromolecule #9: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB9
+Macromolecule #10: DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit RPABC5
+Macromolecule #11: RNA polymerase II subunit J
+Macromolecule #12: RNA polymerase II subunit K
+Macromolecule #13: Transcription elongation factor SPT6
+Macromolecule #15: Protein IWS1 homolog
+Macromolecule #17: RNA polymerase-associated protein CTR9 homolog
+Macromolecule #18: RNA polymerase-associated protein RTF1 homolog
+Macromolecule #19: Transcription elongation factor A protein 1
+Macromolecule #21: RNA polymerase-associated protein LEO1
+Macromolecule #22: RNA polymerase II-associated factor 1 homolog
+Macromolecule #23: WDR61
+Macromolecule #24: Parafibromin
+Macromolecule #25: Transcription elongation factor SPT4
+Macromolecule #26: Transcription elongation factor SPT5
+Macromolecule #27: Histone H3
+Macromolecule #28: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #29: Histone H2A type 1
+Macromolecule #30: Histone H2B 1.1
+Macromolecule #31: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD2
+Macromolecule #14: Non-template
+Macromolecule #20: Template DNA
+Macromolecule #16: RNA
+Macromolecule #32: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #33: MAGNESIUM ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 301837 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


































































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




















 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)
Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)
