[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-44438: Cryo-EM structure of Thermococcus kodakarensis FttA-dependent tra... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Thermococcus kodakarensis FttA-dependent transcription pre-termination complex containing 44 nt RNA | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | composite map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RNA polymerase / pre-termination complex / FttA / archaea / TRANSCRIPTION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationexonuclease activity / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / translation elongation factor activity / RNA endonuclease activity / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / : / : / : / : ...exonuclease activity / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / translation elongation factor activity / RNA endonuclease activity / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / : / : / : / : / : / : / DNA-templated transcription initiation / DNA-templated transcription termination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / chromosome / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / protein dimerization activity / DNA-templated transcription / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / metal ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) / synthetic construct (others) Thermococcus kodakarensis (archaea) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
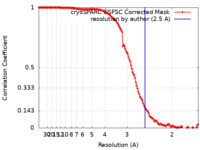
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | You L / Ebright RH | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis of archaeal FttA-dependent transcription termination. Authors: Linlin You / Chengyuan Wang / Vadim Molodtsov / Konstantin Kuznedelov / Xinyi Miao / Breanna R Wenck / Paul Ulisse / Travis J Sanders / Craig J Marshall / Emre Firlar / Jason T Kaelber / ...Authors: Linlin You / Chengyuan Wang / Vadim Molodtsov / Konstantin Kuznedelov / Xinyi Miao / Breanna R Wenck / Paul Ulisse / Travis J Sanders / Craig J Marshall / Emre Firlar / Jason T Kaelber / Thomas J Santangelo / Richard H Ebright /    Abstract: The ribonuclease FttA (also known as aCPSF and aCPSF1) mediates factor-dependent transcription termination in archaea. Here we report the structure of a Thermococcus kodakarensis transcription pre- ...The ribonuclease FttA (also known as aCPSF and aCPSF1) mediates factor-dependent transcription termination in archaea. Here we report the structure of a Thermococcus kodakarensis transcription pre-termination complex comprising FttA, Spt4, Spt5 and a transcription elongation complex (TEC). The structure shows that FttA interacts with the TEC in a manner that enables RNA to proceed directly from the TEC RNA-exit channel to the FttA catalytic centre and that enables endonucleolytic cleavage of RNA by FttA, followed by 5'→3' exonucleolytic cleavage of RNA by FttA and concomitant 5'→3' translocation of FttA on RNA, to apply mechanical force to the TEC and trigger termination. The structure further reveals that Spt5 bridges FttA and the TEC, explaining how Spt5 stimulates FttA-dependent termination. The results reveal functional analogy between bacterial and archaeal factor-dependent termination, functional homology between archaeal and eukaryotic factor-dependent termination, and fundamental mechanistic similarities in factor-dependent termination in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44438.map.gz emd_44438.map.gz | 116.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44438-v30.xml emd-44438-v30.xml emd-44438.xml emd-44438.xml | 31.3 KB 31.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44438_fsc.xml emd_44438_fsc.xml | 13.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44438.png emd_44438.png | 152 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44438.cif.gz emd-44438.cif.gz | 9.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44438 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44438 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44438 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44438 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_44438_validation.pdf.gz emd_44438_validation.pdf.gz | 555.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_44438_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_44438_full_validation.pdf.gz | 555.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_44438_validation.xml.gz emd_44438_validation.xml.gz | 13.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_44438_validation.cif.gz emd_44438_validation.cif.gz | 18 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44438 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44438 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44438 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44438 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 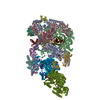 9bctMC 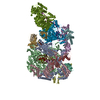 9bcuC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44438.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44438.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | composite map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.825 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
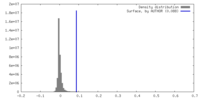
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : FttA-dependent transcription termination complex
+Supramolecule #1: FttA-dependent transcription termination complex
+Macromolecule #1: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit A'
+Macromolecule #2: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit B
+Macromolecule #3: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit A"
+Macromolecule #4: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit D
+Macromolecule #5: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit E
+Macromolecule #6: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit F
+Macromolecule #7: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit H
+Macromolecule #8: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit K
+Macromolecule #9: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit L
+Macromolecule #10: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit N
+Macromolecule #11: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit P
+Macromolecule #12: Transcription elongation factor Spt5
+Macromolecule #13: Transcription elongation factor Spt4
+Macromolecule #14: Transcription termination factor FttA
+Macromolecule #15: non-template strand DNA
+Macromolecule #16: template strand DNA
+Macromolecule #17: RNA
+Macromolecule #18: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #19: ZINC ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: GOLD / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 300 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-9bct: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)