[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-43304: Structure of mouse RyR1 in complex with S100A1 (high-Ca2+/CFF/ATP... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of mouse RyR1 in complex with S100A1 (high-Ca2+/CFF/ATP dataset) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Mouse RyR1 in complex with S100A1 (high-Ca/CFF/ATP dataset) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Calcium / Ion Channel / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationjunctional membrane complex / TGF-beta receptor signaling activates SMADs / Calcineurin activates NFAT / mTORC1-mediated signalling / cytoplasmic side of membrane / regulation of muscle contraction / Stimuli-sensing channels / Ion homeostasis / heart trabecula formation / S100 protein binding ...junctional membrane complex / TGF-beta receptor signaling activates SMADs / Calcineurin activates NFAT / mTORC1-mediated signalling / cytoplasmic side of membrane / regulation of muscle contraction / Stimuli-sensing channels / Ion homeostasis / heart trabecula formation / S100 protein binding / M band / terminal cisterna / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / ryanodine receptor complex / response to caffeine / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / ossification involved in bone maturation / cellular response to caffeine / skin development / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / FK506 binding / positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis / organelle membrane / regulation of heart contraction / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / outflow tract morphogenesis / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / T cell proliferation / heart morphogenesis / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / skeletal muscle fiber development / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / T-tubule / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / cellular response to calcium ion / muscle contraction / sarcoplasmic reticulum / peptidylprolyl isomerase / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / vasodilation / calcium channel activity / Z disc / cytokine-mediated signaling pathway / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / calcium-dependent protein binding / calcium ion transport / ATPase binding / protease binding / protein homotetramerization / transmembrane transporter binding / calmodulin binding / calcium ion binding / synapse / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / Golgi apparatus / protein homodimerization activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.56 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Weninger G / Marks AR | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024Title: Structural insights into the regulation of RyR1 by S100A1. Authors: Gunnar Weninger / Marco C Miotto / Carl Tchagou / Steven Reiken / Haikel Dridi / Sören Brandenburg / Gabriel C Riedemann / Qi Yuan / Yang Liu / Alexander Chang / Anetta Wronska / Stephan E ...Authors: Gunnar Weninger / Marco C Miotto / Carl Tchagou / Steven Reiken / Haikel Dridi / Sören Brandenburg / Gabriel C Riedemann / Qi Yuan / Yang Liu / Alexander Chang / Anetta Wronska / Stephan E Lehnart / Andrew R Marks /   Abstract: S100A1, a small homodimeric EF-hand Ca-binding protein (~21 kDa), plays an important regulatory role in Ca signaling pathways involved in various biological functions including Ca cycling and ...S100A1, a small homodimeric EF-hand Ca-binding protein (~21 kDa), plays an important regulatory role in Ca signaling pathways involved in various biological functions including Ca cycling and contractile performance in skeletal and cardiac myocytes. One key target of the S100A1 interactome is the ryanodine receptor (RyR), a huge homotetrameric Ca release channel (~2.3 MDa) of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Here, we report cryoelectron microscopy structures of S100A1 bound to RyR1, the skeletal muscle isoform, in absence and presence of Ca. Ca-free apo-S100A1 binds beneath the bridging solenoid (BSol) and forms contacts with the junctional solenoid and the shell-core linker of RyR1. Upon Ca-binding, S100A1 undergoes a conformational change resulting in the exposure of the hydrophobic pocket known to serve as a major interaction site of S100A1. Through interactions of the hydrophobic pocket with RyR1, Ca-bound S100A1 intrudes deeper into the RyR1 structure beneath BSol than the apo-form and induces sideways motions of the C-terminal BSol region toward the adjacent RyR1 protomer resulting in tighter interprotomer contacts. Interestingly, the second hydrophobic pocket of the S100A1-dimer is largely exposed at the hydrophilic surface making it prone to interactions with the local environment, suggesting that S100A1 could be involved in forming larger heterocomplexes of RyRs with other protein partners. Since S100A1 interactions stabilizing BSol are implicated in the regulation of RyR-mediated Ca release, the characterization of the S100A1 binding site conserved between RyR isoforms may provide the structural basis for the development of therapeutic strategies regarding treatments of RyR-related disorders. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_43304.map.gz emd_43304.map.gz | 38.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-43304-v30.xml emd-43304-v30.xml emd-43304.xml emd-43304.xml | 22.8 KB 22.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_43304.png emd_43304.png | 70.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-43304.cif.gz emd-43304.cif.gz | 9.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43304 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43304 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43304 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43304 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8vk4MC  8vjjC  8vjkC  8vk3C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_43304.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_43304.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Mouse RyR1 in complex with S100A1 (high-Ca/CFF/ATP dataset) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.833 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of RyR1 with Calstabin-1 and S100A1 (high-Ca2+/CFF/ATP co...
| Entire | Name: Complex of RyR1 with Calstabin-1 and S100A1 (high-Ca2+/CFF/ATP condition) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of RyR1 with Calstabin-1 and S100A1 (high-Ca2+/CFF/ATP co...
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of RyR1 with Calstabin-1 and S100A1 (high-Ca2+/CFF/ATP condition) type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 / Details: 0.25 mM free Ca2+; 5 mM Caffeine; 10 mM ATP |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1A
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.939629 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MGVQVETISP GDGRTFPKRG QTCVVHYTGM LEDGKKFDSS RDRNKPFKFT LGKQEVIRGW EEGVAQMSVG QRAKLIISSD YAYGATGHP GIIPPHATLV FDVELLKLE UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1A |
-Macromolecule #2: Protein S100A1
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein S100A1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.516784 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSELESAME TLINVFHAHS GKEGDKYKLS KKELKDLLQT ELSGFLDVQK DADAVDKVMK ELDENGDGEV DFKEYVVLVA ALTVACNNF FWETS UniProtKB: Protein S100 |
-Macromolecule #3: Ryanodine receptor 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Ryanodine receptor 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 565.692562 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MGDGGGEGED EVQFLRTDDE VVLQCSATVL KEQLKLCLAA EGFGNRLCFL EPTSNAQNVP PDLAICCFIL EQSLSVRALQ EMLANTVEA GVESSQGGGH RTLLYGHAIL LRHAHSRMYL SCLTTSRSMT DKLAFDVGLQ EDATGEACWW TMHPASKQRS E GEKVRVGD ...String: MGDGGGEGED EVQFLRTDDE VVLQCSATVL KEQLKLCLAA EGFGNRLCFL EPTSNAQNVP PDLAICCFIL EQSLSVRALQ EMLANTVEA GVESSQGGGH RTLLYGHAIL LRHAHSRMYL SCLTTSRSMT DKLAFDVGLQ EDATGEACWW TMHPASKQRS E GEKVRVGD DLILVSVSSE RYLHLSTASG ELQVDASFMQ TLWNMNPICS GCEEGFVTGG HVLRLFHGHM DECLTISPSD SD DQRRLVY YEGGPVCTHA RSLWRLEPLR ISWSGSHLRW GQPLRIRHVT TGRYLGLTED QGLVVVDASK AHTKATSFCF RIS KEKLDV APKRDVEGMG PPEIKYGESL CFVQHVASGL WLTYAAPDPK ALRLGVLKKK AMLHQEGHMD DALSLTRCQQ EESQ AARMI YSTAGLYNQF IKGLDSFSGK PRGSGPPAGS ALPIEGVILS LQDLIGYFEP PSEELQHEEK QTKLRSLRNR QSLFQ EEGM LSLVLNCIDR LNVYTTAAHF AEFAGEEAAE SWKEIVNLLY ELLASLIRGN RTNCALFSTN LDWLVSKLDR LEASSG ILE VLYCVLIESP EVLNIIQENH IKSIISLLDK HGRNHKVLDV LCSLCVCNGV AVRSNQDLIT ENLLPGRELL LQTNLIN YV TSIRPNIFVG RAEGSTQYGK WYFEVMVDEV APFLTAQATH LRVGWALSEG YSPYPGGGEG WGGNGVGDDL YSYGFDGL H LWTGHVARPV TSPGQHLLAP EDVVSCCLDL SVPSISFRIN GCPVQGVFES FNLDGLFFPV VSFSAGIKVR FLLGGRHGE FKFLPPPGYA PCHEAVLPRE RLHLQPIKEY RREGPRGPHL VGPSRCLSHL DFVPCPVDTI QIVLPPHLER IREKLAENIH ELWALTRIE QGWTYGPVRD DNKRLHPCLV NFHSLPEPER NYNLQMSGET LKTLLALGCH VGMADEKAED NLKKTKLPKT Y MMSNGYKP APLDLSHVRL TPAQTTLVDR LAENGHNVWA RDRVAQGWSY SAVQDIPARR NPRLVPYRLL DEATKRSNRD SL CQAVRTL LGYGYNIEPP DQEPSQVDSQ SRGDRARIFR AEKSYAVQSG RWYFEFEAVT TGEMRVGWAR PELRPDVELG ADD LAYVFN GHRGQRWHLG SEPFGRPWQS GDVVGCMIDL TENTIIFTLN GEVLMSDSGS ETAFRDIEIG DGFLPVCSLG PGQV GHLNL GQDVSSLRFF AICGLQEGFE PFAINMQRPV TTWFSKSLPQ FEPVPLEHPH YEVARMDGTV DTPPCLRLTH RTWGS QNSL VEMLFLRLSL PVQFHQHFRC TAGATPLASP GLQPPAEDEA RAAEPDTDYE NLRRSAGGWG EAEGGKDGTA KEGTPG GTA QAGVEAQPAR AENEKDATTE KNKKRGFLFK AKKVAMMTQP PSTPALPRLP RDVVPADNRD DPEIILNTTT YYYSVRV FA GQEPSCVWVG WVTPDYHQHD MSFDLSKVRA VTVTMGDEQG NVHSSLKCSN CYMVWGGDFV SPGQQGRISH TDLVIGCL V DLATGLMTFT ANGKESNTFF QVEPNTKLFP AVFVLPTHQN VVQFELGKQK NIMPLSAAMF LSERKNPAPQ CPPRLEVQM LMPVSWSRMP NHFLQVDTRR AGERLGWAVQ CQEPLMMMAL HIPEENRCMD ILELSERLDL QRFHSHTLSL YRSVCALGNN RVAHALCSH VDQAQLLHAL EDARLPGPLR AGYYDLLISI HLESACRSRR SMLSEYIVPL TPETRAITLF PPGRSAEDGP R RHGLPGVG VTTSLRPPHH FSPPCFVVAL PAAGATEAPA RLSPAIPLEA LRDKALRMLG EAVRDGGQHA RDPVGGSVEF QF VPVLKLV STLLVMGVFS DEDVKQILKM IEPEVFREEE EVEEEGEEEE EDEEEKEEDE EEEAHEKEDE EKEEAEDAAE EEK EELEEG LLQMKLPESV KLQMCHLLEY FCDQELQHRV ESLAAFAECY VDKMQGNQRG RYGLLMKAFT MSAAETARRT REFR SPPQE QINMLLHFKN GADEEECPLP EEIRQELVNF HQDLLAHCGI QLEGEEEEPE EESTLGSRLM SLLEKVKLVK KTEEK PEEE PAPEEHKPQS LQELVSHTVV RWAQEDFVQS PELVRAMFSL LHRQYDGLGE LLRALPRAYT ISVSSVEDTM SLLECL GQI RSLLIVQMGP QEENLMIQSI GNIMNNKVFY QHPNLMRALG MHETVMEVMV NVLGGGESKE IRFPKMVTSC CRFLCYF CR ISRQNQRSMF DHLSYLLENS GIGLGMQGST PLDVAAASVI DNNELALALQ EQDLEKVVSY LAGCGLQSCP MLLAKGYP D IGWNPCGGER YLDFLRFAVF VNGESVEENA NVVVRLLIRK PECFGPALRG EGGSGLLAAI EEAIRISEDP ARDGPGVRR DRRREHFGEE PPEENRVHLG HAIMSFYAAL IDLLGRCAPE THLIQAGKGE ALRIRAILRS LVPLDDLVGI ISLPLQIPTL GKDGALVQP KMSASFVPDH KASMVLFLDR VYGIENQDFL LHVLDVGFLP DMRAAASLDT ATFSTTEMAL ALNRYLCLAV L PLITKCAP LFAGTEHRAI MVDSMLHTVY RLSRGRSLTK AQRDVIEDCL MALCRYIRPS MLQHLLRRLV FDVPILNEFA KM PLKLLTN HYERCWKYYC LPTGWANFGV TSEEELHLTR KLFWGIFDSL AHKKYDQELY RIAMPCLCAI AGALPPDYVD ASY SSKTEK KATVDAEGNF DPRPVETLNV IIPEKLDSFI NKFAEYTHEK WAFDKIQNNW SYGENIDEEL KTHPMLRPYK TFSE KDKEI YRWPIKESLK AMIAWEWTVE KAREGEEEKT EKKKTRKISQ TAQTYDPREG YNPQPPDLSV VTLSRELQAM AEQLA ENYH NTWGRKKKQE LEAKGGGSHP LLVPYDTLTA KEKARDREKA QELLKFLQMN GYAVTRGLKD MELDTSSIEK RFAFGF LQQ LLRWMDISQE FIAHLEAVVS SGRVEKSPHE QEIKFFAKIL LPLINQYFTN HCLYFLSTPA KVLGSGGHAS NKEKEMI TS LFCKLAALVR HRVSLFGTDA PAVVNCLHIL ARSLDARTVM KSGPEIVKAG LRSFFESASE DIEKMVENLR LGKVSQAR T QVKGVGQNLT YTTVALLPVL TTLFQHIAQH QFGDDVILDD VQVSCYRTLC SIYSLGTTRN PYVEKLRPAL GECLARLAA AMPVAFLEPE LNEYNACSVY TTKSPRERAI LGLPNSVEEM CPDIPVLERL MAEIGGLAES GARYTEMPHV IEITLPMLCS YLPRWWERG PEAPPPALPA GAPPPCTAVT SDHLNSLLGN ILRIIVNNLG IDEASWMKRL AVFAQPIVSR ARPELLRSHF I PTIGRLRK RAGKVVAEEE QLRLEAKAEA EEGELLVRDE FSVLCRDLYA LYPLLIRYVD NNRAHWLTEP NPNAEELFRM VG EIFIYWS KSHNFKREEQ NFVVQNEINN MSFLTADNKS KMAKAGDVQS GGSDQERTKK KRRGDRYSVQ TSLIVATLKK MLP IGLNMC APTDQDLIVL AKARYALKDT DEEVREFLQN NLNLQGKVEG SPSLRWQMAL YRGVPGREED ADDPEKIVRR VQEV SAVLY HLDQTEHPYK SKKAVWHKLL SKQRRRAVVA CFRMTPLYNL PTHRACNMFL ESYKASWILT EDHSFEDRMI DDLSK AGEQ EEEEEEVEEK KPDPLHQLVL HFSRTALTEK SKLDEDYLYM AYADIMAKSC HLEEGGENGE EGGEEEEVEV SFEEKE MEK QRLLYQQSRL HNRGAAEMVL QMISACKGET GAMVSSTLKL GISILNGGNA EVQQKMLDYL KDKKEVGFFQ SIQALMQ TC SVLDLNAFER QNKAEGLGMV NEDGTVINRQ NGEKVMADDE FTQDLFRFLQ LLCEGHNNDF QNYLRTQTGN TTTINIII C TVDYLLRLQE SISDFYWYYS GKDVIEEQGK RNFSKAMSVA KQVFNSLTEY IQGPCTGNQQ SLAHSRLWDA VVGFLHVFA HMMMKLAQDS SQIELLKELL DLQKDMVVML LSLLEGNVVN GMIARQMVDM LVESSSNVEM ILKFFDMFLK LKDIVGSEAF QDYVTDPRG LISKKDFQKA MDSQKQFTGP EIQFLLSCSE ADENEMINCE EFANRFQEPA RDIGFNVAVL LTNLSEHVPH D PRLRNFLE LAESILEYFR PYLGRIEIMG ASRRIERIYF EISETNRAQW EMPQVKESKR QFIFDVVNEG GESEKMEMFV SF CEDTIFE MQIAAQISEP EGEPEEDEDE GAEEAEEGAA GSDGSGSAAA AGVWVWLAAT AGRTLRGLSY RSLRRRVRRL RRL TAREAA TAVAALLWAL VTRAGGAGAG AAAGALRLLW GSLFGGGLVD SAKKVTVTEL LAGMPDPTGD EVHGQQPSGA GSDA EGEGE GEGEGDAADG AGDEEAAADQ AGTGGADGAV AVADGSPFRP EGAGGLGDMG DTTPVEPPTP EGSPILKRKL GVDGE EEEP PPEPEPEPEP EPEKADTENG EKEVPEPPPE PPKKTPPPPP PKKEEAGGAG LEEFWGELEV QRVKFLNYLS RNFYTL RFL ALFLAFAINF ILLFYKVSDS PPGEDDIEGS GAGDMSGAGS GDGSGWGSRA GEEVEGDEDE NMVYYFLEES TGYMEPA LR CLSLLHTLVA FLCIIGYNCL KVPLVIFKRE KELARKLEFD GLYITEQPED DDVKGQWDRL VLNTPSFPSN YWDKFVKR K VLDKHGDIFG RERIAELLGM DLASLEITAH NERKPDPPPG LLTWIMSIDV KYQIWKFGVI FTDNSFLYLG WYMVMSLLG HYNNFFFAAH LLDIAMGVKT LRTILSSVTH NGKQLVMTVG LLAVVVYLYT VVAFNFFRKF YNKSEDEDEP DMKCDDMMTC YLFHMYVGV RAGGGIGDEI EDPAGDEYEL YRVVFDITFF FFVIVILLAI IQGLIIDAFG ELRDQQEQVK EDMETKCFIC G IGSDYFDT TPHGFETHTL EEHNLANYMF FLMYLINKDE TEHTGQESYV WKMYQERCWD FFPAGDCFRK QYEDQLS UniProtKB: Ryanodine receptor 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 20 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: CAFFEINE
| Macromolecule | Name: CAFFEINE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CFF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 194.191 Da |
| Chemical component information | 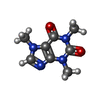 ChemComp-CFF: |
-Macromolecule #7: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #8: 1,2-DIOLEOYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-DIOLEOYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: PCW |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 787.121 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PCW: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 8.5 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R0.6/1 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | 0.15 mmol/L S100A1-dimer |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 12555 / Average electron dose: 58.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL / In silico model: CryoSPARC ab initio |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.56 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Number images used: 31572 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Details: CryoSPARC branch-and-bound |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Details: CryoSPARC branch-and-bound |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




















