[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-29770: Coagulation factor VIII bound to a patient-derived anti-C1 domain... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Coagulation factor VIII bound to a patient-derived anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Blood coagulation factor VIII bound to patient-derived anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Immune system / BLOOD CLOTTING | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDefective F8 accelerates dissociation of the A2 domain / Defective F8 binding to the cell membrane / Defective F8 secretion / Defective F8 sulfation at Y1699 / Gamma carboxylation, hypusinylation, hydroxylation, and arylsulfatase activation / Defective F8 binding to von Willebrand factor / blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway / Cargo concentration in the ER / COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle / Defective factor IX causes thrombophilia ...Defective F8 accelerates dissociation of the A2 domain / Defective F8 binding to the cell membrane / Defective F8 secretion / Defective F8 sulfation at Y1699 / Gamma carboxylation, hypusinylation, hydroxylation, and arylsulfatase activation / Defective F8 binding to von Willebrand factor / blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway / Cargo concentration in the ER / COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle / Defective factor IX causes thrombophilia / Defective cofactor function of FVIIIa variant / Defective F9 variant does not activate FX / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / Defective F8 cleavage by thrombin / Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / platelet alpha granule lumen / acute-phase response / Golgi lumen / blood coagulation / Platelet degranulation / oxidoreductase activity / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / copper ion binding / extracellular space / extracellular region / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
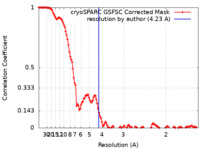
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.23 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Childers KC / Davulcu O / Haynes RM / Lollar P / Doering CB / Coxon CH / Spiegel PC | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5 items United States, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Blood / Year: 2023 Journal: Blood / Year: 2023Title: Structure of coagulation factor VIII bound to a patient-derived anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor. Authors: Kenneth C Childers / Nathan G Avery / Kevin A Estrada Alamo / Omar Davulcu / Rose Marie Haynes / Pete Lollar / Christopher B Doering / Carmen H Coxon / P Clint Spiegel /   Abstract: The development of pathogenic antibody inhibitors against coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) occurs in ∼30% of patients with congenital hemophilia A receiving FVIII replacement therapy, as well as in ...The development of pathogenic antibody inhibitors against coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) occurs in ∼30% of patients with congenital hemophilia A receiving FVIII replacement therapy, as well as in all cases of acquired hemophilia A. KM33 is an anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor previously isolated from a patient with severe hemophilia A. In addition to potently blocking FVIII binding to von Willebrand factor and phospholipid surfaces, KM33 disrupts FVIII binding to lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), which drives FVIII hepatic clearance and antigen presentation in dendritic cells. Here, we report on the structure of FVIII bound to NB33, a recombinant derivative of KM33, via single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. Structural analysis revealed that the NB33 epitope localizes to the FVIII residues R2090-S2094 and I2158-R2159, which constitute membrane-binding loops in the C1 domain. Further analysis revealed that multiple FVIII lysine and arginine residues, previously shown to mediate binding to LRP1, dock onto an acidic cleft at the NB33 variable domain interface, thus blocking a putative LRP1 binding site. Together, these results demonstrate a novel mechanism of FVIII inhibition by a patient-derived antibody inhibitor and provide structural evidence for engineering FVIII with reduced LRP1-mediated clearance. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_29770.map.gz emd_29770.map.gz | 167.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-29770-v30.xml emd-29770-v30.xml emd-29770.xml emd-29770.xml | 22.1 KB 22.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_29770_fsc.xml emd_29770_fsc.xml | 12 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_29770.png emd_29770.png | 102.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-29770.cif.gz emd-29770.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_29770_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29770_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29770_half_map_2.map.gz emd_29770_half_map_2.map.gz | 165.1 MB 165.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29770 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29770 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29770 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29770 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8g6iMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_29770.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_29770.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Blood coagulation factor VIII bound to patient-derived anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
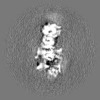
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.788 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
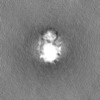
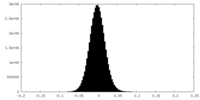
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Blood coagulation factor VIII bound to patient-derived anti-C1...
| File | emd_29770_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Blood coagulation factor VIII bound to patient-derived anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor; half-map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Blood coagulation factor VIII bound to patient-derived anti-C1...
| File | emd_29770_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Blood coagulation factor VIII bound to patient-derived anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor; half-map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Structure of coagulation factor VIII bound to a patient-derived a...
| Entire | Name: Structure of coagulation factor VIII bound to a patient-derived anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Structure of coagulation factor VIII bound to a patient-derived a...
| Supramolecule | Name: Structure of coagulation factor VIII bound to a patient-derived anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Coagulation factor VIII (molecule 1) is a chimera of human+pig proteins which was expressed in CHO cells. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 220 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Coagulation factor VIII chimera from human and pig
| Macromolecule | Name: Coagulation factor VIII chimera from human and pig / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: This protein is a chimera of human+pig coagulation factor VIII (PDB: 6MF0). Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 168.287047 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MQLELSTCVF LCLLPLGFSA IRRYYLGAVE LSWDYRQSEL LRELHVDTRF PATAPGALPL GPSVLYKKTV FVEFTDQLFS VARPRPPWM GLLGPTIQAE VYDTVVVTLK NMASHPVSLH AVGVSFWKSS EGAEYEDHTS QREKEDDKVL PGKSQTYVWQ V LKENGPTA ...String: MQLELSTCVF LCLLPLGFSA IRRYYLGAVE LSWDYRQSEL LRELHVDTRF PATAPGALPL GPSVLYKKTV FVEFTDQLFS VARPRPPWM GLLGPTIQAE VYDTVVVTLK NMASHPVSLH AVGVSFWKSS EGAEYEDHTS QREKEDDKVL PGKSQTYVWQ V LKENGPTA SDPPCLTYSY LSHVDLVKDL NSGLIGALLV CREGSLTRER TQNLHEFVLL FAVFDEGKSW HSARNDSWTR AM DPAPARA QPAMHTVNGY VNRSLPGLIG CHKKSVYWHV IGMGTSPEVH SIFLEGHTFL VRHHRQASLE ISPLTFLTAQ TFL MDLGQF LLFCHISSHH HGGMEAHVRV ESCAEEPQLR RKADEEEDYD DNLYDSDMDV VRLDGDDVSP FIQIRSVAKK HPKT WVHYI AAEEEDWDYA PLVLAPDDRS YKSQYLNNGP QRIGRKYKKV RFMAYTDETF KTREAIQHES GILGPLLYGE VGDTL LIIF KNQASRPYNI YPHGITDVRP LYSRRLPKGV KHLKDFPILP GEIFKYKWTV TVEDGPTKSD PRCLTRYYSS FVNMER DLA SGLIGPLLIC YKESVDQRGN QIMSDKRNVI LFSVFDENRS WYLTENIQRF LPNPAGVQLE DPEFQASNIM HSINGYV FD SLQLSVCLHE VAYWYILSIG AQTDFLSVFF SGYTFKHKMV YEDTLTLFPF SGETVFMSME NPGLWILGCH NSDFRNRG M TALLKVSSCD KNTGDYYEDS YEDISAYLLS KNNAIEPRSF AQNSRPPSAS APKPPVLRRH QRDISLPTFQ PEEDKMDYD DIFSTETKGE DFDIYGEDEN QDPRSFQKRT RHYFIAAVEQ LWDYGMSESP RALRNRAQNG EVPRFKKVVF REFADGSFTQ PSYRGELNK HLGLLGPYIR AEVEDNIMVT FKNQASRPYS FYSSLISYPD DQEQGAEPRH NFVQPNETRT YFWKVQHHMA P TEDEFDCK AWAYFSDVDL EKDVHSGLIG PLLICRANTL NAAHGRQVTV QEFALFFTIF DETKSWYFTE NVERNCRAPC HL QMEDPTL KENYRFHAIN GYVMDTLPGL VMAQNQRIRW YLLSMGSNEN IHSIHFSGHV FSVRKKEEYK MAVYNLYPGV FET VEMLPS KVGIWRIECL IGEHLQAGMS TTFLVYSKKC QTPLGMASGH IRDFQITASG QYGQWAPKLA RLHYSGSINA WSTK EPFSW IKVDLLAPMI IHGIKTQGAR QKFSSLYISQ FIIMYSLDGK KWQTYRGNST GTLMVFFGNV DSSGIKHNIF NPPII ARYI RLHPTHYSIR STLRMELMGC DLNSCSMPLG MESKAISDAQ ITASSYFTNM FATWSPSKAR LHLQGRSNAW RPQVNN PKE WLQVDFQKTM KVTGVTTQGV KSLLTSMYVK EFLISSSQDG HQWTLFFQNG KVKVFQGNQD SFTPVVNSLD PPLLTRY LR IHPQSWVHQI ALRMEVLGCE AQDLY UniProtKB: Coagulation factor VIII, Coagulation factor VIII, Coagulation factor VIII, Coagulation factor VIII |
-Macromolecule #2: NB33 light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: NB33 light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.972436 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: DIQMTQSPSS LSASVGDTVT IACRASRDIR NDLAWYQQKP GKAPKLLIYA TSRLQSGVPS RFSGSGSFTD FTLTINSLQP DDSATYYCL QDSDYPLTFG GGTKVDIKGT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS ...String: DIQMTQSPSS LSASVGDTVT IACRASRDIR NDLAWYQQKP GKAPKLLIYA TSRLQSGVPS RFSGSGSFTD FTLTINSLQP DDSATYYCL QDSDYPLTFG GGTKVDIKGT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS KDSTYSLSST LTLSKADYEK HKVYACEVTH QGLSSPVTKS FNR |
-Macromolecule #3: NB33 heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: NB33 heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.94566 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EVQLVESGGG VVQPGRSLRL SCVDSGLTFS SYGMHWVRQA PGAGLEWVAV ISYDGNDKYY ADSVKGRFAI SRDNAKNTLY LQMNSLTIE DTAVYYCAKD LIESNIAEAF WGQGTLVTVS SKGPSVFPLA PCSRSTSEST AALGCLVKDY FPEPVTVSWN S GALTSGVH ...String: EVQLVESGGG VVQPGRSLRL SCVDSGLTFS SYGMHWVRQA PGAGLEWVAV ISYDGNDKYY ADSVKGRFAI SRDNAKNTLY LQMNSLTIE DTAVYYCAKD LIESNIAEAF WGQGTLVTVS SKGPSVFPLA PCSRSTSEST AALGCLVKDY FPEPVTVSWN S GALTSGVH TFPAVLQSSG LYSLSSVVTV PSSSLGTATY TCNVDHKPSN TKVDKRV |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
Details: 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM HEPES pH 7.4 | |||||||||
| Grid | Model: EMS Lacey Carbon / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: LACEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I | |||||||||
| Details | This sample was monodisperse. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 6993 / Average exposure time: 1.565 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)