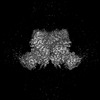
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | the apo structure of human mTORC2 complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | complex / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / regulation of locomotor rhythm / T-helper 1 cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / TORC2 signaling / TORC2 complex ...RNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / regulation of locomotor rhythm / T-helper 1 cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / TORC2 signaling / TORC2 complex / regulation of membrane permeability / cellular response to leucine starvation / heart valve morphogenesis / TFIIIC-class transcription factor complex binding / negative regulation of lysosome organization / TORC1 complex / voluntary musculoskeletal movement / positive regulation of transcription of nucleolar large rRNA by RNA polymerase I / regulation of cellular response to oxidative stress / calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / RNA polymerase III type 3 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of keratinocyte migration / regulation of osteoclast differentiation / regulation of lysosome organization / MTOR signalling / cellular response to L-leucine / energy reserve metabolic process / regulation of autophagosome assembly / Energy dependent regulation of mTOR by LKB1-AMPK / cellular response to nutrient / phosphatidic acid binding / TORC1 signaling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / serine/threonine protein kinase complex / cellular response to methionine / embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching / ruffle organization / phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding / negative regulation of cell size / positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cellular response to osmotic stress / anoikis / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / inositol hexakisphosphate binding / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleus / cardiac muscle cell development / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / regulation of myelination / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / regulation of establishment of cell polarity / negative regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of myotube differentiation / Macroautophagy / lipid biosynthetic process / regulation of cell size / Constitutive Signaling by AKT1 E17K in Cancer / positive regulation of actin filament polymerization / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / germ cell development / behavioral response to pain / oligodendrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / TOR signaling / positive regulation of translational initiation / mTORC1-mediated signalling / CD28 dependent PI3K/Akt signaling / HSF1-dependent transactivation / regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of TOR signaling / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / 'de novo' pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process / response to amino acid / positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / vascular endothelial cell response to laminar fluid shear stress / cellular response to nutrient levels / heart morphogenesis / neuronal action potential / regulation of cellular response to heat / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / cardiac muscle contraction / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / T cell costimulation / phagocytic vesicle / positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / endomembrane system / cytoskeleton organization / substantia nigra development / negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of autophagy / cellular response to amino acid starvation / cellular response to starvation / positive regulation of glycolytic process / regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Regulation of PTEN gene transcription / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / positive regulation of translation / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.28 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yu Z / Chen J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2022 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2022Title: Interactions between mTORC2 core subunits Rictor and mSin1 dictate selective and context-dependent phosphorylation of substrate kinases SGK1 and Akt. Authors: Zanlin Yu / Junliang Chen / Enzo Takagi / Feng Wang / Bidisha Saha / Xi Liu / Lydia-Marie Joubert / Catherine E Gleason / Mingliang Jin / Chengmin Li / Carlos Nowotny / David Agard / Yifan ...Authors: Zanlin Yu / Junliang Chen / Enzo Takagi / Feng Wang / Bidisha Saha / Xi Liu / Lydia-Marie Joubert / Catherine E Gleason / Mingliang Jin / Chengmin Li / Carlos Nowotny / David Agard / Yifan Cheng / David Pearce /  Abstract: Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) is a multi-subunit kinase complex, central to multiple essential signaling pathways. Two core subunits, Rictor and mSin1, distinguish it from the ...Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) is a multi-subunit kinase complex, central to multiple essential signaling pathways. Two core subunits, Rictor and mSin1, distinguish it from the related mTORC1 and support context-dependent phosphorylation of its substrates. mTORC2 structures have been determined previously; however, important questions remain, particularly regarding the structural determinants mediating substrate specificity and context-dependent activity. Here, we used cryo-EM to obtain high-resolution structures of the human mTORC2 apo-complex in the presence of substrates Akt and SGK1. Using functional assays, we then tested predictions suggested by substrate-induced structural changes in mTORC2. For the first time, we visualized in the apo-state the side chain interactions between Rictor and mTOR that sterically occlude recruitment of mTORC1 substrates and confer resistance to the mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin. Also in the apo-state, we observed that mSin1 formed extensive contacts with Rictor via a pair of short α-helices nestled between two Rictor helical repeat clusters, as well as by an extended strand that makes multiple weak contacts with Rictor helical cluster 1. In co-complex structures, we found that SGK1, but not Akt, markedly altered the conformation of the mSin1 N-terminal extended strand, disrupting multiple weak interactions while inducing a large rotation of mSin1 residue Arg-83, which then interacts with a patch of negatively charged residues within Rictor. Finally, we demonstrate mutation of Arg-83 to Ala selectively disrupts mTORC2-dependent phosphorylation of SGK1, but not of Akt, supporting context-dependent substrate selection. These findings provide new structural and functional insights into mTORC2 specificity and context-dependent activity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_26213.map.gz emd_26213.map.gz | 109.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-26213-v30.xml emd-26213-v30.xml emd-26213.xml emd-26213.xml | 18.4 KB 18.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_26213.png emd_26213.png | 27 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-26213.cif.gz emd-26213.cif.gz | 8.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26213 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26213 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26213 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26213 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7tzoMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_26213.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 129.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_26213.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 129.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : apostate of mTORC2 complex, composed of mTOR, Rictor, mLST8 and mSin1
| Entire | Name: apostate of mTORC2 complex, composed of mTOR, Rictor, mLST8 and mSin1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: apostate of mTORC2 complex, composed of mTOR, Rictor, mLST8 and mSin1
| Supramolecule | Name: apostate of mTORC2 complex, composed of mTOR, Rictor, mLST8 and mSin1 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR
| Macromolecule | Name: Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 302.330406 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MVTTLSGLSG EQGPSGDMTT EEDSATHIKF SKRDEDGREL AGATMELRDS SGKTISTWIS DGHVKDFYLY PGKYTFVETA APDGYEVAT PIEFTVNEDG QVTVDGEATE GDAHTGSSGS GSGTGSMLGT GPAAATTAAT TSSNVSVLQQ FASGLKSRNE E TRAKAAKE ...String: MVTTLSGLSG EQGPSGDMTT EEDSATHIKF SKRDEDGREL AGATMELRDS SGKTISTWIS DGHVKDFYLY PGKYTFVETA APDGYEVAT PIEFTVNEDG QVTVDGEATE GDAHTGSSGS GSGTGSMLGT GPAAATTAAT TSSNVSVLQQ FASGLKSRNE E TRAKAAKE LQHYVTMELR EMSQEESTRF YDQLNHHIFE LVSSSDANER KGGILAIASL IGVEGGNATR IGRFANYLRN LL PSNDPVV MEMASKAIGR LAMAGDTFTA EYVEFEVKRA LEWLGADRNE GRRHAAVLVL RELAISVPTF FFQQVQPFFD NIF VAVWDP KQAIREGAVA ALRACLILTT QREPKEMQKP QWYRHTFEEA EKGFDETLAK EKGMNRDDRI HGALLILNEL VRIS SMEGE RLREEMEEIT QQQLVHDKYC KDLMGFGTKP RHITPFTSFQ AVQPQQSNAL VGLLGYSSHQ GLMGFGTSPS PAKST LVES RCCRDLMEEK FDQVCQWVLK CRNSKNSLIQ MTILNLLPRL AAFRPSAFTD TQYLQDTMNH VLSCVKKEKE RTAAFQ ALG LLSVAVRSEF KVYLPRVLDI IRAALPPKDF AHKRQKAMQV DATVFTCISM LARAMGPGIQ QDIKELLEPM LAVGLSP AL TAVLYDLSRQ IPQLKKDIQD GLLKMLSLVL MHKPLRHPGM PKGLAHQLAS PGLTTLPEAS DVGSITLALR TLGSFEFE G HSLTQFVRHC ADHFLNSEHK EIRMEAARTC SRLLTPSIHL ISGHAHVVSQ TAVQVVADVL SKLLVVGITD PDPDIRYCV LASLDERFDA HLAQAENLQA LFVALNDQVF EIRELAICTV GRLSSMNPAF VMPFLRKMLI QILTELEHSG IGRIKEQSAR MLGHLVSNA PRLIRPYMEP ILKALILKLK DPDPDPNPGV INNVLATIGE LAQVSGLEMR KWVDELFIII MDMLQDSSLL A KRQVALWT LGQLVASTGY VVEPYRKYPT LLEVLLNFLK TEQNQGTRRE AIRVLGLLGA LDPYKHKVNI GMIDQSRDAS AV SLSESKS SQDSSDYSTS EMLVNMGNLP LDEFYPAVSM VALMRIFRDQ SLSHHHTMVV QAITFIFKSL GLKCVQFLPQ VMP TFLNVI RVCDGAIREF LFQQLGMLVS FVKSHIRPYM DEIVTLMREF WVMNTSIQST IILLIEQIVV ALGGEFKLYL PQLI PHMLR VFMHDNSPGR IVSIKLLAAI QLFGANLDDY LHLLLPPIVK LFDAPEAPLP SRKAALETVD RLTESLDFTD YASRI IHPI VRTLDQSPEL RSTAMDTLSS LVFQLGKKYQ IFIPMVNKVL VRHRINHQRY DVLICRIVKG YTLADEEEDP LIYQHR MLR SGQGDALASG PVETGPMKKL HVSTINLQKA WGAARRVSKD DWLEWLRRLS LELLKDSSSP SLRSCWALAQ AYNPMAR DL FNAAFVSCWS ELNEDQQDEL IRSIELALTS QDIAEVTQTL LNLAEFMEHS DKGPLPLRDD NGIVLLGERA AKCRAYAK A LHYKELEFQK GPTPAILESL ISINNKLQQP EAAAGVLEYA MKHFGELEIQ ATWYEKLHEW EDALVAYDKK MDTNKDDPE LMLGRMRCLE ALGEWGQLHQ QCCEKWTLVN DETQAKMARM AAAAAWGLGQ WDSMEEYTCM IPRDTHDGAF YRAVLALHQD LFSLAQQCI DKARDLLDAE LTAMAGESYS RAYGAMVSCH MLSELEEVIQ YKLVPERREI IRQIWWERLQ GCQRIVEDWQ K ILMVRSLV VSPHEDMRTW LKYASLCGKS GRLALAHKTL VLLLGVDPSR QLDHPLPTVH PQVTYAYMKN MWKSARKIDA FQ HMQHFVQ TMQQQAQHAI ATEDQQHKQE LHKLMARCFL KLGEWQLNLQ GINESTIPKV LQYYSAATEH DRSWYKAWHA WAV MNFEAV LHYKHQNQAR DEKKKLRHAS GANITNATTA ATTAATATTT ASTEGSNSES EAESTENSPT PSPLQKKVTE DLSK TLLMY TVPAVQGFFR SISLSRGNNL QDTLRVLTLW FDYGHWPDVN EALVEGVKAI QIDTWLQVIP QLIARIDTPR PLVGR LIHQ LLTDIGRYHP QALIYPLTVA SKSTTTARHN AANKILKNMC EHSNTLVQQA MMVSEELIRV AILWHEMWHE GLEEAS RLY FGERNVKGMF EVLEPLHAMM ERGPQTLKET SFNQAYGRDL MEAQEWCRKY MKSGNVKDLT QAWDLYYHVF RRISKQL PQ LTSLELQYVS PKLLMCRDLE LAVPGTYDPN QPIIRIQSIA PSLQVITSKQ RPRKLTLMGS NGHEFVFLLK GHEDLRQD E RVMQLFGLVN TLLANDPTSL RKNLSIQRYA VIPLSTNSGL IGWVPHCDTL HALIRDYREK KKILLNIEHR IMLRMAPDY DHLTLMQKVE VFEHAVNNTA GDDLAKLLWL KSPSSEVWFD RRTNYTRSLA VMSMVGYILG LGDRHPSNLM LDRLSGKILH IDFGDCFEV AMTREKFPEK IPFRLTRMLT NAMEVTGLDG NYRITCHTVM EVLREHKDSV MAVLEAFVYD PLLNWRLMDT N TKGNKRSR TRTDSYSAGQ SVEILDGVEL GEPAHKKTGT TVPESIHSFI GDGLVKPEAL NKKAIQIINR VRDKLTGRDF SH DDTLDVP TQVELLIKQA TSHENLCQCY IGWCPFW UniProtKB: Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
-Macromolecule #2: Target of rapamycin complex subunit LST8
| Macromolecule | Name: Target of rapamycin complex subunit LST8 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 37.998254 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGYPYDVPDY ADLNGGGGGS TMNTSPGTVG SDPVILATAG YDHTVRFWQA HSGICTRTVQ HQDSQVNALE VTPDRSMIAA AGYQHIRMY DLNSNNPNPI ISYDGVNKNI ASVGFHEDGR WMYTGGEDCT ARIWDLRSRN LQCQRIFQVN APINCVCLHP N QAELIVGD ...String: MGYPYDVPDY ADLNGGGGGS TMNTSPGTVG SDPVILATAG YDHTVRFWQA HSGICTRTVQ HQDSQVNALE VTPDRSMIAA AGYQHIRMY DLNSNNPNPI ISYDGVNKNI ASVGFHEDGR WMYTGGEDCT ARIWDLRSRN LQCQRIFQVN APINCVCLHP N QAELIVGD QSGAIHIWDL KTDHNEQLIP EPEVSITSAH IDPDASYMAA VNSTGNCYVW NLTGGIGDEV TQLIPKTKIP AH TRYALQC RFSPDSTLLA TCSADQTCKI WRTSNFSLMT ELSIKSGNPG ESSRGWMWGC AFSGDSQYIV TASSDNLARL WCV ETGEIK REYGGHQKAV VCLAFNDSVL G UniProtKB: Target of rapamycin complex subunit LST8 |
-Macromolecule #3: Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR
| Macromolecule | Name: Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 193.846328 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MDYKDDDDKG STMAAIGRGR SLKNLRVRGR NDSGEENVPL DLTREPSDNL REILQNVARL QGVSNMRKLG HLNNFTKLLC DIGHSEEKL GFHYEDIIIC LRLALLNEAK EVRAAGLRAL RYLIQDSSIL QKVLKLKVDY LIARCIDIQQ SNEVERTQAL R LVRKMITV ...String: MDYKDDDDKG STMAAIGRGR SLKNLRVRGR NDSGEENVPL DLTREPSDNL REILQNVARL QGVSNMRKLG HLNNFTKLLC DIGHSEEKL GFHYEDIIIC LRLALLNEAK EVRAAGLRAL RYLIQDSSIL QKVLKLKVDY LIARCIDIQQ SNEVERTQAL R LVRKMITV NASLFPSSVT NSLIAVGNDG LQERDRMVRA CIAIICELAL QNPEVVALRG GLNTILKNVI DCQLSRINEA LI TTILHLL NHPKTRQYVR ADVELERILA PYTDFHYRHS PDTAEGQLKE DREARFLASK MGIIATFRSW AGIINLCKPG NSG IQSLIG VLCIPNMEIR RGLLEVLYDI FRLPLPVVTE EFIEALLSVD PGRFQDSWRL SDGFVAAEAK TILPHRARSR PDLM DNYLA LILSAFIRNG LLEGLVEVIT NSDDHISVRA TILLGELLHM ANTILPHSHS HHLHCLPTLM NMAASFDIPK EKRLR ASAA LNCLKRFHEM KKRGPKPYSL HLDHIIQKAI ATHQKRDQYL RVQKDIFILK DTEEALLINL RDSQVLQHKE NLEWNW NLI GTILKWPNVN LRNYKDEQLH RFVRRLLYFY KPSSKLYANL DLDFAKAKQL TVVGCQFTEF LLESEEDGQG YLEDLVK DI VQWLNASSGM KPERSLQNNG LLTTLSQHYF LFIGTLSCHP HGVKMLEKCS VFQCLLNLCS LKNQDHLLKL TVSSLDYS R DGLARVILSK ILTAATDACR LYATKHLRVL LRANVEFFNN WGIELLVTQL HDKNKTISSE ALDILDEACE DKANLHALI QMKPALSHLG DKGLLLLLRF LSIPKGFSYL NERGYVAKQL EKWHREYNSK YVDLIEEQLN EALTTYRKPV DGDNYVRRSN QRLQRPHVY LPIHLYGQLV HHKTGCHLLE VQNIITELCR NVRTPDLDKW EEIKKLKASL WALGNIGSSN WGLNLLQEEN V IPDILKLA KQCEVLSIRG TCVYVLGLIA KTKQGCDILK CHNWDAVRHS RKHLWPVVPD DVEQLCNELS SIPSTLSLNS ES TSSRHNS ESESVPSSMF ILEDDRFGSS STSTFFLDIN EDTEPTFYDR SGPIKDKNSF PFFASSKLVK NRILNSLTLP NKK HRSSSD PKGGKLSSES KTSNRRIRTL TEPSVDFNHS DDFTPISTVQ KTLQLETSFM GNKHIEDTGS TPSIGENDLK FTKN FGTEN HRENTSRERL VVESSTSSHM KIRSQSFNTD TTTSGISSMS SSPSRETVGV DATTMDTDCG SMSTVVSTKT IKTSH YLTP QSNHLSLSKS NSVSLVPPGS SHTLPRRAQS LKAPSIATIK SLADCNFSYT SSRDAFGYAT LKRLQQQRMH PSLSHS EAL ASPAKDVLFT DTITMKANSF ESRLTPSRFM KALSYASLDK EDLLSPINQN TLQRSSSVRS MVSSATYGGS DDYIGLA LP VDINDIFQVK DIPYFQTKNI PPHDDRGARA FAHDAGGLPS GTGGLVKNSF HLLRQQMSLT EIMNSIHSDA SLFLESTE D TGLQEHTDDN CLYCVCIEIL GFQPSNQLSA ICSHSDFQDI PYSDWCEQTI HNPLEVVPSK FSGISGCSDG VSQEGSASS TKSTELLLGV KTIPDDTPMC RILLRKEVLR LVINLSSSVS TKCHETGLLT IKEKYPQTFD DICLYSEVSH LLSHCTFRLP CRRFIQELF QDVQFLQMHE EAEAVLATPP KQPIVDTSAE S UniProtKB: Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR |
-Macromolecule #4: Target of rapamycin complex 2 subunit MAPKAP1
| Macromolecule | Name: Target of rapamycin complex 2 subunit MAPKAP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 60.732328 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAFLDNPTII LAHIRQSHVT SDDTGMCEMV LIDHDVDLEK IHPPSMPGDS GSEIQGSNGE TQGYVYAQSV DITSSWDFGI RRRSNTAQR LERLRKERQN QIKCKNIQWK ERNSKQSAQE LKSLFEKKSL KEKPPISGKQ SILSVRLEQC PLQLNNPFNE Y SKFDGKGH ...String: MAFLDNPTII LAHIRQSHVT SDDTGMCEMV LIDHDVDLEK IHPPSMPGDS GSEIQGSNGE TQGYVYAQSV DITSSWDFGI RRRSNTAQR LERLRKERQN QIKCKNIQWK ERNSKQSAQE LKSLFEKKSL KEKPPISGKQ SILSVRLEQC PLQLNNPFNE Y SKFDGKGH VGTTATKKID VYLPLHSSQD RLLPMTVVTM ASARVQDLIG LICWQYTSEG REPKLNDNVS AYCLHIAEDD GE VDTDFPP LDSNEPIHKF GFSTLALVEK YSSPGLTSKE SLFVRINAAH GFSLIQVDNT KVTMKEILLK AVKRRKGSQK VSG PQYRLE KQSEPNVAVD LDSTLESQSA WEFCLVRENS SRADGVFEED SQIDIATVQD MLSSHHYKSF KVSMIHRLRF TTDV QLGIS GDKVEIDPVT NQKASTKFWI KQKPISIDSD LLCACDLAEE KSPSHAIFKL TYLSNHDYKH LYFESDAATV NEIVL KVNY ILESRASTAR ADYFAQKQRK LNRRTSFSFQ KEKKSGQQAA AGGGGYPYDV PDYA UniProtKB: Target of rapamycin complex 2 subunit MAPKAP1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | 3D array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Homemade / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: GRAPHENE OXIDE / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Support film - Film thickness: 0.2 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 22 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.28 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 288538 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)