[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-14385: Cryo-EM structure of an a-carboxysome RuBisCO enzyme at 2.9 A res... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
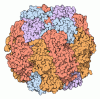
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of an a-carboxysome RuBisCO enzyme at 2.9 A resolution | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM map of an a-carboxysome RuBisCO enzyme at 2.9 A resolution (D4 symmetry) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Carboxysome / carbon fixation / cyanobacteria / PHOTOSYNTHESIS | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphotorespiration / carboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria) | |||||||||
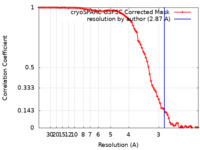
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.87 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mann D / Evans SL / Bergeron JRC | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1 items United Kingdom, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2023 Journal: Structure / Year: 2023Title: Single-particle cryo-EM analysis of the shell architecture and internal organization of an intact α-carboxysome. Authors: Sasha L Evans / Monsour M J Al-Hazeem / Daniel Mann / Nicolas Smetacek / Andrew J Beavil / Yaqi Sun / Taiyu Chen / Gregory F Dykes / Lu-Ning Liu / Julien R C Bergeron /    Abstract: Carboxysomes are proteinaceous bacterial microcompartments that sequester the key enzymes for carbon fixation in cyanobacteria and some proteobacteria. They consist of a virus-like icosahedral shell, ...Carboxysomes are proteinaceous bacterial microcompartments that sequester the key enzymes for carbon fixation in cyanobacteria and some proteobacteria. They consist of a virus-like icosahedral shell, encapsulating several enzymes, including ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO), responsible for the first step of the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle. Despite their significance in carbon fixation and great bioengineering potentials, the structural understanding of native carboxysomes is currently limited to low-resolution studies. Here, we report the characterization of a native α-carboxysome from a marine cyanobacterium by single-particle cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM). We have determined the structure of its RuBisCO enzyme, and obtained low-resolution maps of its icosahedral shell, and of its concentric interior organization. Using integrative modeling approaches, we have proposed a complete atomic model of an intact carboxysome, providing insight into its organization and assembly. This is critical for a better understanding of the carbon fixation mechanism and toward repurposing carboxysomes in synthetic biology for biotechnological applications. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_14385.map.gz emd_14385.map.gz | 4.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-14385-v30.xml emd-14385-v30.xml emd-14385.xml emd-14385.xml | 14.8 KB 14.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_14385_fsc.xml emd_14385_fsc.xml | 8.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_14385.png emd_14385.png | 35.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-14385.cif.gz emd-14385.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14385 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14385 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14385 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14385 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7yyoMC 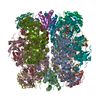 8cmyC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_14385.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_14385.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM map of an a-carboxysome RuBisCO enzyme at 2.9 A resolution (D4 symmetry) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
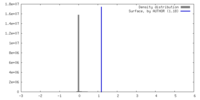
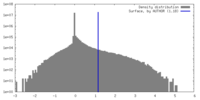
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RuBisCO
| Entire | Name: RuBisCO |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RuBisCO
| Supramolecule | Name: RuBisCO / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 52.526531 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MSKKYDAGVK EYRDTYWTPD YVPLDTDLLA CFKCTGQEGV PKEEVAAAVA AESSTGTWST VWSELLVDLD FYKGRCYRIE DVPGDKEAF YAFIAYPLDL FEEGSVTNVL TSLVGNVFGF KALRHLRLED IRFPMAFIKT CPGPPNGICV ERDRMNKYGR P LLGCTIKP ...String: MSKKYDAGVK EYRDTYWTPD YVPLDTDLLA CFKCTGQEGV PKEEVAAAVA AESSTGTWST VWSELLVDLD FYKGRCYRIE DVPGDKEAF YAFIAYPLDL FEEGSVTNVL TSLVGNVFGF KALRHLRLED IRFPMAFIKT CPGPPNGICV ERDRMNKYGR P LLGCTIKP KLGLSGKNYG RVVYECLRGG LDFTKDDENI NSQPFQRWQN RFEFVAEAVA LAQQETGEKK GHYLNCTAAT PE EMYERAE FAKELGQPII MHDYITGGFT ANTGLSKWCR KNGMLLHIHR AMHAVIDRHP KHGIHFRVLA KCLRLSGGDQ LHT GTVVGK LEGDRQTTLG FIDQLRESFI PEDRSRGNFF DQDWGSMPGV FAVASGGIHV WHMPALVAIF GDDSVLQFGG GTHG HPWGS AAGAAANRVA LEACVKARNA GREIEKESRD ILMEAAKHSP ELAIALETWK EIKFEFDTVD KLDVQ UniProtKB: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain |
-Macromolecule #2: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 12.967611 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Cyanobium (bacteria) Cyanobium (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MPFKSTVGDY QTVATLETFG FLPPMTQDEI YDQIAYIIAQ GWSPLIEHVH PSRSMATYWS YWKLPFFGEK DLGVIVSELE ACHRAYPDH HVRLVGYDAY TQSQGACFVV FEGR UniProtKB: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: 2-CARBOXYARABINITOL-1,5-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-CARBOXYARABINITOL-1,5-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: CAP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 356.115 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CAP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)