+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-9997 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Complex of yeast cytoplasmic dynein MTBD-High and MT with DTT | |||||||||
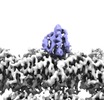
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM map of MTBD-High/MT complex, filtered to the local resolution. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Dynein / Microtubule / MOTOR PROTEIN-STRUCTURAL PROTEIN complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationkaryogamy / nuclear migration along microtubule / astral microtubule / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / spindle pole body / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / motile cilium / nuclear migration ...karyogamy / nuclear migration along microtubule / astral microtubule / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / spindle pole body / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / motile cilium / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / Neutrophil degranulation / mitotic spindle organization / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / neuron migration / mitotic cell cycle / cell cortex / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / hydrolase activity / GTPase activity / GTP binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.62 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Komori Y / Nishida N | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 2 items Japan, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis for two-way communication between dynein and microtubules. Authors: Noritaka Nishida / Yuta Komori / Osamu Takarada / Atsushi Watanabe / Satoko Tamura / Satoshi Kubo / Ichio Shimada / Masahide Kikkawa /  Abstract: The movements of cytoplasmic dynein on microtubule (MT) tracks is achieved by two-way communication between the microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) and the ATPase domain via a coiled-coil stalk, but ...The movements of cytoplasmic dynein on microtubule (MT) tracks is achieved by two-way communication between the microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) and the ATPase domain via a coiled-coil stalk, but the structural basis of this communication remains elusive. Here, we regulate MTBD either in high-affinity or low-affinity states by introducing a disulfide bond to the stalk and analyze the resulting structures by NMR and cryo-EM. In the MT-unbound state, the affinity changes of MTBD are achieved by sliding of the stalk α-helix by a half-turn, which suggests that structural changes propagate from the ATPase-domain to MTBD. In addition, MT binding induces further sliding of the stalk α-helix even without the disulfide bond, suggesting how the MT-induced conformational changes propagate toward the ATPase domain. Based on differences in the MT-binding surface between the high- and low-affinity states, we propose a potential mechanism for the directional bias of dynein movement on MT tracks. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_9997.map.gz emd_9997.map.gz | 14.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-9997-v30.xml emd-9997-v30.xml emd-9997.xml emd-9997.xml | 15.8 KB 15.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_9997.png emd_9997.png | 115.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-9997.cif.gz emd-9997.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9997 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9997 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9997 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9997 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6kiqMC  9996C  6kioC  6kjnC  6kjoC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10661 (Title: Complex of yeast cytoplasmic dynein MTBD-High and MT with DTT EMPIAR-10661 (Title: Complex of yeast cytoplasmic dynein MTBD-High and MT with DTTData size: 124.3 Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs of the complex of yeast cytoplasmic dynein MTBD-High and MT with DTT [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_9997.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_9997.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM map of MTBD-High/MT complex, filtered to the local resolution. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
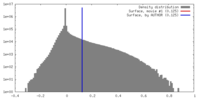
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.32 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
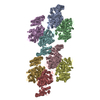
-Entire : MTBD-High/MT complex with DTT
| Entire | Name: MTBD-High/MT complex with DTT |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: MTBD-High/MT complex with DTT
| Supramolecule | Name: MTBD-High/MT complex with DTT / type: cell / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: DTT was added to cleave the disulfide bond between CC1 and CC2 of MTBD-High |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Alpha tubulin
| Macromolecule | Name: Alpha tubulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.95998 KDa |
| Sequence | String: RECISIHVGQ AGVQIGNACW ELYCLEHGIQ PDGHVPRAVF VDLEPTVIDE VRTGTYRQLF HPEQLITGKE DAANNYARGH YTIGKEIID LVLDRIRKLA DQCTGLQGFS VFHSFGGGTG SGFTSLLMER LSVDYGKKSK LEFSIYPAPQ VSTAVVEPYN S ILTTHTTL ...String: RECISIHVGQ AGVQIGNACW ELYCLEHGIQ PDGHVPRAVF VDLEPTVIDE VRTGTYRQLF HPEQLITGKE DAANNYARGH YTIGKEIID LVLDRIRKLA DQCTGLQGFS VFHSFGGGTG SGFTSLLMER LSVDYGKKSK LEFSIYPAPQ VSTAVVEPYN S ILTTHTTL EHSDCAFMVD NEAIYDICRR NLDIERPTYT NLNRLIGQIV SSITASLRFD GALNVDLTEF QTNLVPYPRG HF PLATYAP VISAEKAYHE QLSVAEITNA CFEPANQMVK CDPRHGKYMA CCLLYRGDVV PKDVNAAIAT IKTKRTIQFV DWC PTGFKV GINYEPPTVV PGGDLAKVQR AVCMLSNTTA IAEAWARLDH KFDLMYAKRA FVHWYVGEGM EEGEFSEARE DMAA LEKDY EEVGVDS |
-Macromolecule #2: Tubulin beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.809746 KDa |
| Sequence | String: REIVHIQAGQ CGNQIGAKFW EVISDEHGID PTGSYHGDSD LQLERINVYY NEAAGNKYVP RAILVDLEPG TMDSVRSGPF GQIFRPDNF VFGQSGAGNN WAKGHYTEGA ELVDSVLDVV RKESESCDCL QGFQLTHSLG GGTGSGMGTL LISKIREEYP D RIMNTFSV ...String: REIVHIQAGQ CGNQIGAKFW EVISDEHGID PTGSYHGDSD LQLERINVYY NEAAGNKYVP RAILVDLEPG TMDSVRSGPF GQIFRPDNF VFGQSGAGNN WAKGHYTEGA ELVDSVLDVV RKESESCDCL QGFQLTHSLG GGTGSGMGTL LISKIREEYP D RIMNTFSV VPSPKVSDTV VEPYNATLSV HQLVENTDET YCIDNEALYD ICFRTLKLTT PTYGDLNHLV SATMSGVTTC LR FPGQLNA DLRKLAVNMV PFPRLHFFMP GFAPLTSRGS QQYRALTVPE LTQQMFDAKN MMAACDPRHG RYLTVAAVFR GRM SMKEVD EQMLNVQNKN SSYFVEWIPN NVKTAVCDIP PRGLKMSATF IGNSTAIQEL FKRISEQFTA MFRRKAFLHW YTGE GMDEM EFTEAESNMN DLVSEYQQYQ D UniProtKB: Tubulin beta chain |
-Macromolecule #3: Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic
| Macromolecule | Name: Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.264564 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKSIQDCEPT ILEAQRGVKN IKKQQLTEIR SMVNPPSGVK IVMEAVCAIL GYQFSNWRDI QQFIRKDDFI HNIVHYDTTL HMKPQIRKY MEEEFLSDPN FTYETINRAS KACGPLYQWV NAQINFSKCL E UniProtKB: Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 Component:
Details: DTT was added to the final concentration of 1 mM. | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER/RHODIUM | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 279.0 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-40 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 621 / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 54.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Calibrated defocus max: 2.5 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: OTHER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 9.2219 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: -25.7519 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.62 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Details: FSCtrue was calculated to validate the resolution. / Number images used: 32666 |
|---|---|
| Segment selection | Number selected: 35636 / Details: particles were collected using PyFilamentPicker |
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: Cryo-EM map of microtubule filtered to 8 Angstroms |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE / Software - Name: FREALIGN (ver. 9.11) Details: FREALIGN v9.11 and "super-particle" based approach were used to refine the angular assignment |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6kiq: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)