[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-27959: D-cycloserine and glutamate bound Human GluN1a-GluN2C NMDA recept... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
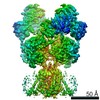
| Title | D-cycloserine and glutamate bound Human GluN1a-GluN2C NMDA receptor in nanodisc - intact conformation | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | B-factor sharpened map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ligand-gated ion channel / ionotropic glutamate receptor / synaptic protein / voltage-gate ion channel / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglycine-gated cation channel activity / excitatory chemical synaptic transmission / directional locomotion / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / protein localization to postsynaptic membrane / propylene metabolic process / response to glycine / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / regulation of monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / Neurexins and neuroligins ...glycine-gated cation channel activity / excitatory chemical synaptic transmission / directional locomotion / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / protein localization to postsynaptic membrane / propylene metabolic process / response to glycine / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / regulation of monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / Neurexins and neuroligins / NMDA glutamate receptor activity / NMDA selective glutamate receptor complex / glutamate binding / neurotransmitter receptor complex / neuromuscular process controlling balance / ligand-gated sodium channel activity / glutamate receptor signaling pathway / calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol / protein heterotetramerization / glycine binding / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol / Long-term potentiation / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / monoatomic cation transport / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / monoatomic cation channel activity / synaptic cleft / calcium ion homeostasis / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / excitatory synapse / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / synaptic membrane / sodium ion transmembrane transport / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of membrane potential / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / regulation of synaptic plasticity / brain development / visual learning / postsynaptic density membrane / response to wounding / calcium ion transmembrane transport / terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle / long-term synaptic potentiation / signaling receptor activity / amyloid-beta binding / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / dendritic spine / response to ethanol / chemical synaptic transmission / postsynaptic membrane / calmodulin binding / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / calcium ion binding / synapse / dendrite / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / glutamatergic synapse / cell surface / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.75 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chou T-H / Furukawa H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022Title: Structural insights into assembly and function of GluN1-2C, GluN1-2A-2C, and GluN1-2D NMDARs. Authors: Tsung-Han Chou / Hyunook Kang / Noriko Simorowski / Stephen F Traynelis / Hiro Furukawa /  Abstract: Neurotransmission mediated by diverse subtypes of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) is fundamental for basic brain functions and development as well as neuropsychiatric diseases and disorders. ...Neurotransmission mediated by diverse subtypes of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) is fundamental for basic brain functions and development as well as neuropsychiatric diseases and disorders. NMDARs are glycine- and glutamate-gated ion channels that exist as heterotetramers composed of obligatory GluN1 and GluN2(A-D) and/or GluN3(A-B). The GluN2C and GluN2D subunits form ion channels with distinct properties and spatio-temporal expression patterns. Here, we provide the structures of the agonist-bound human GluN1-2C NMDAR in the presence and absence of the GluN2C-selective positive allosteric potentiator (PAM), PYD-106, the agonist-bound GluN1-2A-2C tri-heteromeric NMDAR, and agonist-bound GluN1-2D NMDARs by single-particle electron cryomicroscopy. Our analysis shows unique inter-subunit and domain arrangements of the GluN2C NMDARs, which contribute to functional regulation and formation of the PAM binding pocket and is distinct from GluN2D NMDARs. Our findings here provide the fundamental blueprint to study GluN2C- and GluN2D-containing NMDARs, which are uniquely involved in neuropsychiatric disorders. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27959.map.gz emd_27959.map.gz | 229.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27959-v30.xml emd-27959-v30.xml emd-27959.xml emd-27959.xml | 21.8 KB 21.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_27959.png emd_27959.png | 35.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27959.cif.gz emd-27959.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27959_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27959_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27959_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27959_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.5 MB 226.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27959 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27959 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27959 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27959 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8e98MC  8e92C  8e93C  8e94C  8e96C  8e97C  8e99C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27959.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27959.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | B-factor sharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.856 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half map 1
| File | emd_27959_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 2
| File | emd_27959_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Hetero-tetrameric GluN1a-GluN2C NMDA receptors
| Entire | Name: Hetero-tetrameric GluN1a-GluN2C NMDA receptors |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Hetero-tetrameric GluN1a-GluN2C NMDA receptors
| Supramolecule | Name: Hetero-tetrameric GluN1a-GluN2C NMDA receptors / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 95.081688 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSTMHLLTFA LLFSCSFARA ASDPKIVNIG AVLSTRKHEQ MFREAVNQAN KRHGSWKIQL NATSVTHKPN AIQMALSVCE DLISSQVYA ILVSHPPTPN DHFTPTPVSY TAGFYRIPVL GLTTRMSIYS DKSIHLSFLR TVPPYSHQSS VWFEMMRVYS W NHIILLVS ...String: MSTMHLLTFA LLFSCSFARA ASDPKIVNIG AVLSTRKHEQ MFREAVNQAN KRHGSWKIQL NATSVTHKPN AIQMALSVCE DLISSQVYA ILVSHPPTPN DHFTPTPVSY TAGFYRIPVL GLTTRMSIYS DKSIHLSFLR TVPPYSHQSS VWFEMMRVYS W NHIILLVS DDHEGRAAQK RLETLLEERE SKAEKVLQFD PGTKNVTALL MEAKELEARV IILSASEDDA ATVYRAAAML NM TGSGYVW LVGEREISGN ALRYAPDGIL GLQLINGKNE SAHISDAVGV VAQAVHELLE KENITDPPRG CVGNTNIWKT GPL FKRVLM SSKYADGVTG RVEFNEDGDR KFANYSIMNL QNRKLVQVGI YNGTHVIPND RKIIWPGGET EKPRGYQMST RLKI VTIHQ EPFVYVKPTL SDGTCKEEFT VNGDPVKKVI CTGPNDTSPG SPRHTVPQCC YGFCIDLLIK LARTMNFTYE VHLVA DGKF GTQERVNNSN KKEWNGMMGE LLSGQADMIV APLTINNERA QYIEFSKPFK YQGLTILVKK EIPRSTLDSF MQPFQS TLW LLVGLSVHVV AVMLYLLDRF SPFGRFKVNS EEEEEDALTL SSAMWFSWGV LLNSGIGEGA PRSFSARILG MVWAGFA MI IVASYTANLA AFLVLDRPEE RITGINDPRL RNPSDKFIYA TVKQSSVDIY FRRQVELSTM YRHMEKHNYE SAAEAIQA V RDNKLHAFIW DSAVLEFEAS QKCDLVTTGE LFFRSGFGIG MRKDSPWKQN VSLSILKSHE NGFMEDLDKT WVRYQECDS RSNAPATLTF ENMAGVFMLV AGGIVAGIFL IFIEIAYKRH KDANGAQ UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2C
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2C / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 96.958406 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGTMRLFLLA VLFLFSFARA TGWSHPQFEK GGGSGGGSGG SAWSHPQFEK GALVPRGEQG MTVAVVFSSS GPPQAQFRAR LTPQSFLDL PLEIQPLTVG VNTTNPSSLL TQICGLLGAA HVHGIVFEDN VDTEAVAQIL DFISSQTHVP ILSISGGSAV V LTPKEPGS ...String: MGTMRLFLLA VLFLFSFARA TGWSHPQFEK GGGSGGGSGG SAWSHPQFEK GALVPRGEQG MTVAVVFSSS GPPQAQFRAR LTPQSFLDL PLEIQPLTVG VNTTNPSSLL TQICGLLGAA HVHGIVFEDN VDTEAVAQIL DFISSQTHVP ILSISGGSAV V LTPKEPGS AFLQLGVSLE QQLQVLFKVL EEYDWSAFAV ITSLHPGHAL FLEGVRAVAD ASHVSWRLLD VVTLELGPGG PR ARTQRLL RQLDAPVFVA YCSREEAEVL FAEAAQAGLV GPGHVWLVPN LALGSTDAPP ATFPVGLISV VTESWRLSLR QKV RDGVAI LALGAHSYWR QHGTLPAPAG DCRVHPGPVS PAREAFYRHL LNVTWEGRDF SFSPGGYLVQ PTMVVIALNR HRLW EMVGR WEHGVLYMKY PVWPRYSASL QPVVDSRHLT VATLEERPFV IVESPDPGTG GCVPNTVPCR RQSNHTFSSG DVAPY TKLC CKGFCIDILK KLARVVKFSY DLYLVTNGKH GKRVRGVWNG MIGEVYYKRA DMAIGSLTIN EERSEIVDFS VPFVET GIS VMVARSNGTV SPSAFLEPYS PAVWVMMFVM CLTVVAITVF MFEYFSPVSY NQNLTRGKKS GGPAFTIGKS VWLLWAL VF NNSVPIENPR GTTSKIMVLV WAFFAVIFLA SYTANLAAFM IQEQYIDTVS GLSDKKFQRP QDQYPPFRFG TVPNGSTE R NIRSNYRDMH THMVKFNQRS VEDALTSLKM GKLDAFIYDA AVLNYMAGKD EGCKLVTIGS GKVFATTGYG IAMQKDSHW KRAIDLALLQ FLGDGETQKL ETVWLSGICQ NEKNEVMSSK LDIDNMAGVF YMLLVAMGLA LLVFAWEHLV YWKLRHSVPN UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2C |
-Macromolecule #4: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 9 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 85 % / Chamber temperature: 285 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 57.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.8000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.4000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)