+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Bent ADP-Pi-F-actin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Main map, bent ADP-Pi F-actin | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cytoskeleton / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationStriated Muscle Contraction / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / actin filament / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / actin cytoskeleton / hydrolase activity / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.71 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Reynolds MJ / Alushin GM | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Bending forces and nucleotide state jointly regulate F-actin structure. Authors: Matthew J Reynolds / Carla Hachicho / Ayala G Carl / Rui Gong / Gregory M Alushin /  Abstract: ATP-hydrolysis-coupled actin polymerization is a fundamental mechanism of cellular force generation. In turn, force and actin filament (F-actin) nucleotide state regulate actin dynamics by tuning F- ...ATP-hydrolysis-coupled actin polymerization is a fundamental mechanism of cellular force generation. In turn, force and actin filament (F-actin) nucleotide state regulate actin dynamics by tuning F-actin's engagement of actin-binding proteins through mechanisms that are unclear. Here we show that the nucleotide state of actin modulates F-actin structural transitions evoked by bending forces. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of ADP-F-actin and ADP-P-F-actin with sufficient resolution to visualize bound solvent reveal intersubunit interfaces bridged by water molecules that could mediate filament lattice flexibility. Despite extensive ordered solvent differences in the nucleotide cleft, these structures feature nearly identical lattices and essentially indistinguishable protein backbone conformations that are unlikely to be discriminable by actin-binding proteins. We next introduce a machine-learning-enabled pipeline for reconstructing bent filaments, enabling us to visualize both continuous structural variability and side-chain-level detail. Bent F-actin structures reveal rearrangements at intersubunit interfaces characterized by substantial alterations of helical twist and deformations in individual protomers, transitions that are distinct in ADP-F-actin and ADP-P-F-actin. This suggests that phosphate rigidifies actin subunits to alter the bending structural landscape of F-actin. As bending forces evoke nucleotide-state dependent conformational transitions of sufficient magnitude to be detected by actin-binding proteins, we propose that actin nucleotide state can serve as a co-regulator of F-actin mechanical regulation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27117.map.gz emd_27117.map.gz | 7.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27117-v30.xml emd-27117-v30.xml emd-27117.xml emd-27117.xml | 22 KB 22 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27117_fsc.xml emd_27117_fsc.xml | 18.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_27117.png emd_27117.png | 86.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_27117_msk_1.map emd_27117_msk_1.map | 512 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27117.cif.gz emd-27117.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27117_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27117_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27117_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27117_half_map_2.map.gz | 411 MB 411.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27117 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27117 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27117 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27117 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8d16MC  8d13C  8d14C  8d15C  8d17C  8d18C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-11129 (Title: Cryo-EM of ADP-Pi-F-actin / Data size: 2.5 TB EMPIAR-11129 (Title: Cryo-EM of ADP-Pi-F-actin / Data size: 2.5 TBData #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs of ADP-F-actin [micrographs - multiframe] Data #2: Polished single-frame particles of bent ADP-Pi-F-actin segments [picked particles - single frame - processed] Data #3: Polished single-frame particles of helical ADP-Pi-F-actin segments, for high-resolution [picked particles - single frame - processed]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27117.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27117.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Main map, bent ADP-Pi F-actin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.03 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
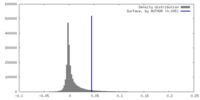
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_27117_msk_1.map emd_27117_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
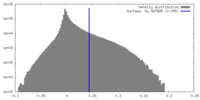
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-map 2, bent ADP-Pi F-actin
| File | emd_27117_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-map 2, bent ADP-Pi F-actin | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-map 1, bent ADP-Pi F-actin
| File | emd_27117_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-map 1, bent ADP-Pi F-actin | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Bent F-actin, ADP-Pi nucleotide state
| Entire | Name: Bent F-actin, ADP-Pi nucleotide state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Bent F-actin, ADP-Pi nucleotide state
| Supramolecule | Name: Bent F-actin, ADP-Pi nucleotide state / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: Mechanically deformed filamentous actin in the ADP-Pi state |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.1 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle, intermediate form
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle, intermediate form / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.387227 KDa |
| Sequence | String: TTALVCDNGS GLVKAGFAGD DAPRAVFPSI VGRPRHQGVM VGMGQKDSYV GDEAQSKRGI LTLKYPIE(HIC)G IITNWD DME KIWHHTFYNE LRVAPEEHPT LLTEAPLNPK ANREKMTQIM FETFNVPAMY VAIQAVLSLY ASGRTTGIVL DSGDGVT HN VPIYEGYALP ...String: TTALVCDNGS GLVKAGFAGD DAPRAVFPSI VGRPRHQGVM VGMGQKDSYV GDEAQSKRGI LTLKYPIE(HIC)G IITNWD DME KIWHHTFYNE LRVAPEEHPT LLTEAPLNPK ANREKMTQIM FETFNVPAMY VAIQAVLSLY ASGRTTGIVL DSGDGVT HN VPIYEGYALP HAIMRLDLAG RDLTDYLMKI LTERGYSFVT TAEREIVRDI KEKLCYVALD FENEMATAAS SSSLEKSY E LPDGQVITIG NERFRCPETL FQPSFIGMES AGIHETTYNS IMKCDIDIRK DLYANNVMSG GTTMYPGIAD RMQKEITAL APSTMKIKII APPERKYSVW IGGSILASLS TFQQMWITKQ EYDEAGPSIV HRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 7 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 7 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 7 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-40 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)