+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7per | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
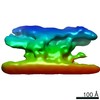
| Title | Model of the inner ring of the human nuclear pore complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Nuclear Pore Complex / NPC | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcentriole assembly / positive regulation of centriole replication / regulation of protein import into nucleus / regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / positive regulation of mitotic cytokinetic process / protein localization to nuclear inner membrane / nuclear envelope organization / nuclear pore inner ring / nuclear pore central transport channel / transcription-dependent tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery ...centriole assembly / positive regulation of centriole replication / regulation of protein import into nucleus / regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / positive regulation of mitotic cytokinetic process / protein localization to nuclear inner membrane / nuclear envelope organization / nuclear pore inner ring / nuclear pore central transport channel / transcription-dependent tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore complex assembly / nuclear pore organization / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / positive regulation of protein localization to centrosome / Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC) Disassembly / Regulation of Glucokinase by Glucokinase Regulatory Protein / Defective TPR may confer susceptibility towards thyroid papillary carcinoma (TPC) / Transport of Ribonucleoproteins into the Host Nucleus / miRNA processing / Transport of the SLBP independent Mature mRNA / Transport of the SLBP Dependant Mature mRNA / NS1 Mediated Effects on Host Pathways / negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus / SUMOylation of SUMOylation proteins / nuclear localization sequence binding / structural constituent of nuclear pore / Transport of Mature mRNA Derived from an Intronless Transcript / Rev-mediated nuclear export of HIV RNA / Nuclear import of Rev protein / Flemming body / SUMOylation of RNA binding proteins / mitotic centrosome separation / NEP/NS2 Interacts with the Cellular Export Machinery / RNA export from nucleus / Transport of Mature mRNA derived from an Intron-Containing Transcript / tRNA processing in the nucleus / Postmitotic nuclear pore complex (NPC) reformation / centrosome cycle / negative regulation of programmed cell death / nucleocytoplasmic transport / positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway / Viral Messenger RNA Synthesis / PTB domain binding / poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / SUMOylation of ubiquitinylation proteins / Vpr-mediated nuclear import of PICs / negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / regulation of signal transduction / mRNA transport / nuclear pore / mRNA export from nucleus / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / Hsp70 protein binding / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / SH2 domain binding / nuclear periphery / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / ubiquitin binding / HCMV Late Events / Hsp90 protein binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / phospholipid binding / ISG15 antiviral mechanism / protein import into nucleus / HCMV Early Events / spindle pole / mitotic spindle / cellular senescence / nuclear envelope / protein transport / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / snRNP Assembly / nuclear membrane / cell surface receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / ribonucleoprotein complex / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / centrosome / chromatin binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / protein-containing complex binding / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
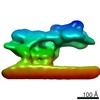
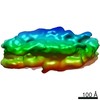
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 35 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Schuller, A.P. / Wojtynek, M. / Mankus, D. / Tatli, M. / Kronenberg-Tenga, R. / Regmi, S.G. / Dasso, M. / Weis, K. / Medalia, O. / Schwartz, T.U. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 3items Switzerland, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: The cellular environment shapes the nuclear pore complex architecture. Authors: Anthony P Schuller / Matthias Wojtynek / David Mankus / Meltem Tatli / Rafael Kronenberg-Tenga / Saroj G Regmi / Phat V Dip / Abigail K R Lytton-Jean / Edward J Brignole / Mary Dasso / ...Authors: Anthony P Schuller / Matthias Wojtynek / David Mankus / Meltem Tatli / Rafael Kronenberg-Tenga / Saroj G Regmi / Phat V Dip / Abigail K R Lytton-Jean / Edward J Brignole / Mary Dasso / Karsten Weis / Ohad Medalia / Thomas U Schwartz /   Abstract: Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) create large conduits for cargo transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm across the nuclear envelope (NE). These multi-megadalton structures are composed of about ...Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) create large conduits for cargo transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm across the nuclear envelope (NE). These multi-megadalton structures are composed of about thirty different nucleoporins that are distributed in three main substructures (the inner, cytoplasmic and nucleoplasmic rings) around the central transport channel. Here we use cryo-electron tomography on DLD-1 cells that were prepared using cryo-focused-ion-beam milling to generate a structural model for the human NPC in its native environment. We show that-compared with previous human NPC models obtained from purified NEs-the inner ring in our model is substantially wider; the volume of the central channel is increased by 75% and the nucleoplasmic and cytoplasmic rings are reorganized. Moreover, the NPC membrane exhibits asymmetry around the inner-ring complex. Using targeted degradation of Nup96, a scaffold nucleoporin of the cytoplasmic and nucleoplasmic rings, we observe the interdependence of each ring in modulating the central channel and maintaining membrane asymmetry. Our findings highlight the inherent flexibility of the NPC and suggest that the cellular environment has a considerable influence on NPC dimensions and architecture. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7per.cif.gz 7per.cif.gz | 2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7per.ent.gz pdb7per.ent.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7per.json.gz 7per.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7per_validation.pdf.gz 7per_validation.pdf.gz | 1022.3 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7per_full_validation.pdf.gz 7per_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7per_validation.xml.gz 7per_validation.xml.gz | 310.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7per_validation.cif.gz 7per_validation.cif.gz | 502 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pe/7per https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pe/7per ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pe/7per ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pe/7per | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  12814MC  7peqC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10700 (Title: Cryo electron tomography of FIB-milled lamella of human DLD-1 cells EMPIAR-10700 (Title: Cryo electron tomography of FIB-milled lamella of human DLD-1 cellsData size: 8.0 Data #1: Un-aligned tilt series of FIB-lamella of human DLD-1 cells [tilt series])  EMPIAR-10701 (Title: Cryo electron tomography of FIB-milled lamella of human DLD-1 cells EMPIAR-10701 (Title: Cryo electron tomography of FIB-milled lamella of human DLD-1 cellsData size: 8.0 Data #1: Un-aligned tilt series of FIB-milled lamella of Nup96-depleted human DLD-1 cells [tilt series]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 8
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 12 molecules FXLRGYMSHZNT
| #1: Protein | Mass: 55491.156 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q7Z3B4 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q7Z3B4#2: Protein | Mass: 60941.480 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BVL2 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BVL2#3: Protein | Mass: 53289.574 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P37198 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P37198 |
|---|
-Nuclear pore complex protein ... , 3 types, 12 molecules PVDJWKEQCIOU
| #4: Protein | Mass: 228172.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q92621 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q92621#5: Protein | Mass: 155357.281 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75694 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O75694#6: Protein | Mass: 93599.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8N1F7 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8N1F7 |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: CELL / 3D reconstruction method: subtomogram averaging |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Nup96::Neon-AID DLD-1 / Type: CELL / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: cryo-FIB milled sections of DLD1 cells |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE Details: Cells were grown on holey carbon, Au-mesh supports. Grids were rinsed briefly with PBS and manually blotted before plunging into liquid ethane. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2500 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 2.4 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name:  UCSF Chimera / Version: 1.14 / Category: model fitting UCSF Chimera / Version: 1.14 / Category: model fitting |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C8 (8 fold cyclic) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 35 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1252 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT |
| EM volume selection | Num. of tomograms: 54 / Num. of volumes extracted: 1552 |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5IJN Accession code: 5IJN / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj