+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7mqd | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
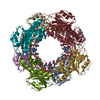
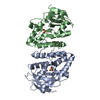
| Title | Bartonella henselae NrnC complexed with pAGG. D4 symmetry. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RNA BINDING PROTEIN/RNA / RNase / bacteria / enzyme / RNA BINDING PROTEIN / RNA BINDING PROTEIN-RNA complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / 3'-5' exonuclease activity / nucleic acid binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Bartonella henselae (bacteria) Bartonella henselae (bacteria)synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.25 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lormand, J.D. / Brownfield, B. / Fromme, J.C. / Sondermann, H. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2021 Journal: Elife / Year: 2021Title: Structural characterization of NrnC identifies unifying features of dinucleotidases. Authors: Justin D Lormand / Soo-Kyoung Kim / George A Walters-Marrah / Bryce A Brownfield / J Christopher Fromme / Wade C Winkler / Jonathan R Goodson / Vincent T Lee / Holger Sondermann /   Abstract: RNA degradation is fundamental for cellular homeostasis. The process is carried out by various classes of endolytic and exolytic enzymes that together degrade an RNA polymer to mono-ribonucleotides. ...RNA degradation is fundamental for cellular homeostasis. The process is carried out by various classes of endolytic and exolytic enzymes that together degrade an RNA polymer to mono-ribonucleotides. Within the exoribonucleases, nano-RNases play a unique role as they act on the smallest breakdown products and hence catalyze the final steps in the process. We recently showed that oligoribonuclease (Orn) acts as a dedicated diribonucleotidase, defining the ultimate step in RNA degradation that is crucial for cellular fitness (Kim et al., 2019). Whether such a specific activity exists in organisms that lack Orn-type exoribonucleases remained unclear. Through quantitative structure-function analyses, we show here that NrnC-type RNases share this narrow substrate length preference with Orn. Although NrnC and Orn employ similar structural features that distinguish these two classes of dinucleotidases from other exonucleases, the key determinants for dinucleotidase activity are realized through distinct structural scaffolds. The structures, together with comparative genomic analyses of the phylogeny of DEDD-type exoribonucleases, indicate convergent evolution as the mechanism of how dinucleotidase activity emerged repeatedly in various organisms. The evolutionary pressure to maintain dinucleotidase activity further underlines the important role these analogous proteins play for cell growth. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7mqd.cif.gz 7mqd.cif.gz | 362.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7mqd.ent.gz pdb7mqd.ent.gz | 279.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7mqd.json.gz 7mqd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7mqd_validation.pdf.gz 7mqd_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7mqd_full_validation.pdf.gz 7mqd_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7mqd_validation.xml.gz 7mqd_validation.xml.gz | 46.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7mqd_validation.cif.gz 7mqd_validation.cif.gz | 68.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mq/7mqd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mq/7mqd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mq/7mqd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mq/7mqd | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23943MC  7mplC  7mpmC  7mpnC  7mpoC  7mppC  7mpqC  7mprC  7mpsC  7mptC  7mpuC  7mqbC  7mqcC  7mqeC  7mqfC  7mqgC  7mqhC  7mqiC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 23446.725 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Bartonella henselae (bacteria) / Gene: BM1374165_00260 / Production host: Bartonella henselae (bacteria) / Gene: BM1374165_00260 / Production host:  #2: RNA chain | Mass: 974.660 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 186.621 kDa/nm / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.2_3874: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: D4 (2x4 fold dihedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.25 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 94063 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 PDBj
PDBj
