+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
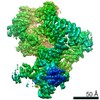
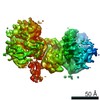
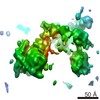
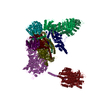
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7lsy | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
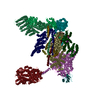
| Title | NHEJ Short-range synaptic complex | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN/DNA / NHEJ / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFHA domain binding / positive regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of ligase activity / DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligase activity / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / DNA ligase (ATP) / Ku70:Ku80 complex / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / negative regulation of t-circle formation ...FHA domain binding / positive regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of ligase activity / DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligase activity / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / DNA ligase (ATP) / Ku70:Ku80 complex / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / negative regulation of t-circle formation / pro-B cell differentiation / DNA end binding / DNA ligase (ATP) activity / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination / nonhomologous end joining complex / nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling / single strand break repair / V(D)J recombination / regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / cellular response to X-ray / isotype switching / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / nuclear telomere cap complex / protein localization to site of double-strand break / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / IRF3-mediated induction of type I IFN / recombinational repair / positive regulation of neurogenesis / regulation of telomere maintenance / DNA biosynthetic process / U3 snoRNA binding / protein localization to chromosome, telomeric region / cellular response to lithium ion / cellular hyperosmotic salinity response / response to ionizing radiation / 2-LTR circle formation / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / ligase activity / telomeric DNA binding / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / Lyases; Carbon-oxygen lyases; Other carbon-oxygen lyases / site of DNA damage / T cell differentiation / somatic stem cell population maintenance / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / response to X-ray / chromosome organization / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / telomere maintenance via telomerase / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / condensed chromosome / DNA polymerase binding / neurogenesis / activation of innate immune response / DNA helicase activity / telomere maintenance / B cell differentiation / cyclin binding / central nervous system development / stem cell proliferation / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / response to gamma radiation / cellular response to ionizing radiation / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / small-subunit processome / enzyme activator activity / cellular response to gamma radiation / protein-DNA complex / base-excision repair / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / establishment of integrated proviral latency / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / fibrillar center / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation / T cell differentiation in thymus / double-strand break repair / site of double-strand break / double-stranded DNA binding / neuron apoptotic process / fibroblast proliferation / scaffold protein binding / secretory granule lumen / DNA recombination / transcription regulator complex / in utero embryonic development / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / damaged DNA binding / chromosome, telomeric region / cell population proliferation / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / ribonucleoprotein complex / innate immune response / cell division / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 8.4 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | He, Y. / Chen, S. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 6items United States, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structural basis of long-range to short-range synaptic transition in NHEJ. Authors: Siyu Chen / Linda Lee / Tasmin Naila / Susan Fishbain / Annie Wang / Alan E Tomkinson / Susan P Lees-Miller / Yuan He /   Abstract: DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are a highly cytotoxic form of DNA damage and the incorrect repair of DSBs is linked to carcinogenesis. The conserved error-prone non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) ...DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are a highly cytotoxic form of DNA damage and the incorrect repair of DSBs is linked to carcinogenesis. The conserved error-prone non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway has a key role in determining the effects of DSB-inducing agents that are used to treat cancer as well as the generation of the diversity in antibodies and T cell receptors. Here we applied single-particle cryo-electron microscopy to visualize two key DNA-protein complexes that are formed by human NHEJ factors. The Ku70/80 heterodimer (Ku), the catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PKcs), DNA ligase IV (LigIV), XRCC4 and XLF form a long-range synaptic complex, in which the DNA ends are held approximately 115 Å apart. Two DNA end-bound subcomplexes comprising Ku and DNA-PKcs are linked by interactions between the DNA-PKcs subunits and a scaffold comprising LigIV, XRCC4, XLF, XRCC4 and LigIV. The relative orientation of the DNA-PKcs molecules suggests a mechanism for autophosphorylation in trans, which leads to the dissociation of DNA-PKcs and the transition into the short-range synaptic complex. Within this complex, the Ku-bound DNA ends are aligned for processing and ligation by the XLF-anchored scaffold, and a single catalytic domain of LigIV is stably associated with a nick between the two Ku molecules, which suggests that the joining of both strands of a DSB involves both LigIV molecules. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7lsy.cif.gz 7lsy.cif.gz | 856.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7lsy.ent.gz pdb7lsy.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7lsy.json.gz 7lsy.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7lsy_validation.pdf.gz 7lsy_validation.pdf.gz | 953.8 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7lsy_full_validation.pdf.gz 7lsy_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7lsy_validation.xml.gz 7lsy_validation.xml.gz | 137 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7lsy_validation.cif.gz 7lsy_validation.cif.gz | 203.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ls/7lsy https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ls/7lsy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ls/7lsy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ls/7lsy | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23509MC  7lt3C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-X-ray repair cross-complementing protein ... , 2 types, 4 molecules AJBK
| #1: Protein | Mass: 68872.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC6, G22P1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC6, G22P1 / Production host:  unidentified baculovirus unidentified baculovirusReferences: UniProt: P12956, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement, Lyases; Carbon-oxygen lyases; Other carbon-oxygen lyases #2: Protein | Mass: 82812.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC5, G22P2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC5, G22P2 / Production host:  unidentified baculovirus unidentified baculovirusReferences: UniProt: P13010, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|
-DNA chain , 5 types, 5 molecules DEMNV
| #3: DNA chain | Mass: 7936.151 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 4284.812 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 4271.830 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 7964.145 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 6185.046 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Protein , 3 types, 8 molecules FGOPHIXY
| #5: Protein | Mass: 38337.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC4 / Production host:  unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: Q13426 unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: Q13426#6: Protein | Mass: 33372.234 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NHEJ1, XLF / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NHEJ1, XLF / Production host:  #10: Protein | Mass: 104124.953 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LIG4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LIG4 / Production host:  unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P49917, DNA ligase (ATP) unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P49917, DNA ligase (ATP) |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Short-range synaptic complex of NHEJ / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.72 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R3.5/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: DARK FIELD / Nominal magnification: 30000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 0.0426 sec. / Electron dose: 46 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 32723 |
| Image scans | Width: 11520 / Height: 8184 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1766936 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 8.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 175866 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj