[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-7116: CryoEM structure of MyosinVI-actin complex in the rigor (nucleoti... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7116 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
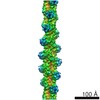
| Title | CryoEM structure of MyosinVI-actin complex in the rigor (nucleotide-free) state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM structure of myosin VI-actin complex, B factor sharpened to -150 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cytoskeleton / Filament / complex / CONTRACTILE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCH domain binding / regulation of secretion / inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation / actin filament-based movement / myosin complex / clathrin-coated vesicle / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / inner ear morphogenesis / myosin heavy chain binding / microfilament motor activity ...CH domain binding / regulation of secretion / inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation / actin filament-based movement / myosin complex / clathrin-coated vesicle / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / inner ear morphogenesis / myosin heavy chain binding / microfilament motor activity / myosin binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / microvillus / cytoskeletal motor activity / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / ruffle / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / clathrin-coated pit / actin filament organization / actin filament / filopodium / intracellular protein transport / DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / sensory perception of sound / ADP binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / ruffle membrane / endocytosis / disordered domain specific binding / calcium-dependent protein binding / actin filament binding / intracellular protein localization / myelin sheath / actin cytoskeleton / lamellipodium / protein transport / cell body / cytoplasmic vesicle / cell cortex / nuclear membrane / calmodulin binding / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / centrosome / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / magnesium ion binding / Golgi apparatus / protein-containing complex / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
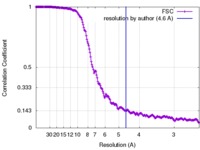
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gurel PS / Alushin GA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation | Journal: Nat Nanotechnol / Year: 2018 Title: Controllable molecular motors engineered from myosin and RNA. Authors: Tosan Omabegho / Pinar S Gurel / Clarence Y Cheng / Laura Y Kim / Paul V Ruijgrok / Rhiju Das / Gregory M Alushin / Zev Bryant /  Abstract: Engineering biomolecular motors can provide direct tests of structure-function relationships and customized components for controlling molecular transport in artificial systems or in living cells . ...Engineering biomolecular motors can provide direct tests of structure-function relationships and customized components for controlling molecular transport in artificial systems or in living cells . Previously, synthetic nucleic acid motors and modified natural protein motors have been developed in separate complementary strategies to achieve tunable and controllable motor function. Integrating protein and nucleic-acid components to form engineered nucleoprotein motors may enable additional sophisticated functionalities. However, this potential has only begun to be explored in pioneering work harnessing DNA scaffolds to dictate the spacing, number and composition of tethered protein motors . Here, we describe myosin motors that incorporate RNA lever arms, forming hybrid assemblies in which conformational changes in the protein motor domain are amplified and redirected by nucleic acid structures. The RNA lever arm geometry determines the speed and direction of motor transport and can be dynamically controlled using programmed transitions in the lever arm structure . We have characterized the hybrid motors using in vitro motility assays, single-molecule tracking, cryo-electron microscopy and structural probing . Our designs include nucleoprotein motors that reversibly change direction in response to oligonucleotides that drive strand-displacement reactions. In multimeric assemblies, the controllable motors walk processively along actin filaments at speeds of 10-20 nm s. Finally, to illustrate the potential for multiplexed addressable control, we demonstrate sequence-specific responses of RNA variants to oligonucleotide signals. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7116.map.gz emd_7116.map.gz | 420 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7116-v30.xml emd-7116-v30.xml emd-7116.xml emd-7116.xml | 26.7 KB 26.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_7116_fsc.xml emd_7116_fsc.xml | 21 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_7116_1.png emd_7116_1.png emd_7116_2.png emd_7116_2.png | 179.5 KB 268.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_7116_msk_1.map emd_7116_msk_1.map emd_7116_msk_2.map emd_7116_msk_2.map | 512 MB 512 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7116.cif.gz emd-7116.cif.gz | 7.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_7116_additional.map.gz emd_7116_additional.map.gz emd_7116_half_map_1.map.gz emd_7116_half_map_1.map.gz emd_7116_half_map_2.map.gz emd_7116_half_map_2.map.gz | 84.3 MB 85.3 MB 85.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7116 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7116 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7116 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7116 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 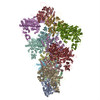 6bnpMC 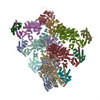 6bnvMC  7115C  7117C  6bnoC  6bnqC  6bnuC  6bnwC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7116.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7116.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of myosin VI-actin complex, B factor sharpened to -150 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.27 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_7116_msk_1.map emd_7116_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
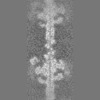
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
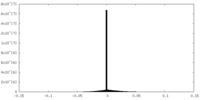
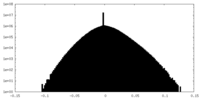
| Density Histograms |
-Mask #2
| File |  emd_7116_msk_2.map emd_7116_msk_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
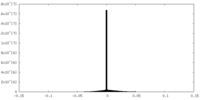
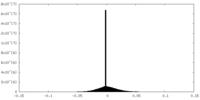
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: unsharpened density map of myosin VI-actin complex
| File | emd_7116_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | unsharpened density map of myosin VI-actin complex | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
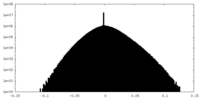
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map of the full myosin VI-actin reconstruction
| File | emd_7116_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map of the full myosin VI-actin reconstruction | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map of the full myosin VI-actin reconstruction
| File | emd_7116_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map of the full myosin VI-actin reconstruction | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : myosin VI-actin in the rigor (nucleotide-free) state
| Entire | Name: myosin VI-actin in the rigor (nucleotide-free) state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: myosin VI-actin in the rigor (nucleotide-free) state
| Supramolecule | Name: myosin VI-actin in the rigor (nucleotide-free) state / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 42 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: myosin VI
| Supramolecule | Name: myosin VI / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: actin
| Supramolecule | Name: actin / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Unconventional myosin-VI
| Macromolecule | Name: Unconventional myosin-VI / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 79.837367 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EDGKPVWAPH PTDGFQVGNI VDIGPDSLTI EPLNQKGKTF LALINQVFPA EEDSKKDVED NCSLMYLNEA TLLHNIKVRY SKDRIYTYV ANILIAVNPY FDIPKIYSSE TIKSYQGKSL GTMPPHVFAI ADKAFRDMKV LKLSQSIIVS GESGAGKTEN T KFVLRYLT ...String: EDGKPVWAPH PTDGFQVGNI VDIGPDSLTI EPLNQKGKTF LALINQVFPA EEDSKKDVED NCSLMYLNEA TLLHNIKVRY SKDRIYTYV ANILIAVNPY FDIPKIYSSE TIKSYQGKSL GTMPPHVFAI ADKAFRDMKV LKLSQSIIVS GESGAGKTEN T KFVLRYLT ESYGTGQDID DRIVEANPLL EAFGNAKTVR NNNSSRFGKF VEIHFNEKSS VVGGFVSHYL LEKSRICVQG KE ERNYHIF YRLCAGASED IRERLHLSSP DNFRYLNRGC TRYFANKETD KQILQNRKSP EYLKAGSLKD PLLDDHGDFI RMC TAMKKI GLDDEEKLDL FRVVAGVLHL GNIDFEEAGS TSGGCNLKNK STQALEYCAE LLGLDQDDLR VSLTTRVMLT TAGG AKGTV IKVPLKVEQA NNARDALAKT VYSHLFDHVV NRVNQCFPFE TSSYFIGVLD IAGFEYFEHN SFEQFCINYC NEKLQ QFFN ERILKEEQEL YQKEGLGVNE VHYVDNQDCI DLIEARLVGI LDILDEENRL PQPSDQHFTS AVHQKHKDHF RLSIPR KSK LAIHRNIRDD EGFIIRHFAG AVCYETTQFV EKNNDALHMS LESLICESRD KFIRELFESS TNNNKDTKQK AGKLSFI SV GNKFKTQLNL LLDKLRSTGA SFIRCIKPNL KMTSHHFEGA QILSQLQCSG MVSVLDLMQG GF UniProtKB: Unconventional myosin-VI |
-Macromolecule #2: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.560266 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MCDEDETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIEHGIITN WDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLDSGD G VTHNVPIY ...String: MCDEDETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIEHGIITN WDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLDSGD G VTHNVPIY EGYALPHAIM RLDLAGRDLT DYLMKILTER GYSFVTTAER EIVRDIKEKL CYVALDFENE MATAASSSSL EK SYELPDG QVITIGNERF RCPETLFQPS FIGMESAGIH ETTYNSIMKC DIDIRKDLYA NNVMSGGTTM YPGIADRMQK EIT ALAPST MKIKIIAPPE RKYSVWIGGS ILASLSTFQQ MWITKQEYDE AGPSIVH UniProtKB: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.45 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: Buffer was filtered through 0.44 um filter and degassed. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: C-flat-1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 6 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP Details: Sample was applied to a glow-discharged holey carbon grid. 3 uL actin was incubated for 60 seconds. 3 uL of myosin VI was added and incubated for 60 seconds. 3 uL solution was removed. An ...Details: Sample was applied to a glow-discharged holey carbon grid. 3 uL actin was incubated for 60 seconds. 3 uL of myosin VI was added and incubated for 60 seconds. 3 uL solution was removed. An additional 3 uL of myosin VI was applied. After 60 seconds, 3 uL solution was removed, and the grid was blotted for 3 seconds from the backside with filter paper.. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | 0.45 mg/mL myosin VI was added to 0.025 mg/mL actin |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI 20 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3838 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3710 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-24 / Number grids imaged: 3 / Number real images: 778 / Average exposure time: 0.25 sec. / Average electron dose: 1.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 29000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN 626 SINGLE TILT LIQUID NITROGEN CRYO TRANSFER HOLDER Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | Initial models were assembled from 8 actins (3J8A) and 6 myosins (2BKI) through rigid body docking in Chimera, followed by flexible fitting with DireX. Resulting models were subjected to MDFF. |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 150 |
| Output model |  PDB-6bnp:  PDB-6bnv: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)