[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6b43: CryoEM structure and atomic model of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associa... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6b43 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure and atomic model of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus capsid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / human herpesvirus 8 / human tumor virus / dsDNA virus capsid assembly / HK97-like fold | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationT=16 icosahedral viral capsid / viral capsid assembly / viral process / viral capsid / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity / DNA binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Human herpesvirus 8 Human herpesvirus 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dai, X.H. / Gong, D.Y. / Sun, R. / Zhou, Z.H. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 8items United States, 8items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Structure and mutagenesis reveal essential capsid protein interactions for KSHV replication. Authors: Xinghong Dai / Danyang Gong / Hanyoung Lim / Jonathan Jih / Ting-Ting Wu / Ren Sun / Z Hong Zhou /  Abstract: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) causes Kaposi's sarcoma, a cancer that commonly affects patients with AIDS and which is endemic in sub-Saharan Africa. The KSHV capsid is highly ...Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) causes Kaposi's sarcoma, a cancer that commonly affects patients with AIDS and which is endemic in sub-Saharan Africa. The KSHV capsid is highly pressurized by its double-stranded DNA genome, as are the capsids of the eight other human herpesviruses. Capsid assembly and genome packaging of herpesviruses are prone to interruption and can therefore be targeted for the structure-guided development of antiviral agents. However, herpesvirus capsids-comprising nearly 3,000 proteins and over 1,300 Å in diameter-present a formidable challenge to atomic structure determination and functional mapping of molecular interactions. Here we report a 4.2 Å resolution structure of the KSHV capsid, determined by electron-counting cryo-electron microscopy, and its atomic model, which contains 46 unique conformers of the major capsid protein (MCP), the smallest capsid protein (SCP) and the triplex proteins Tri1 and Tri2. Our structure and mutagenesis results reveal a groove in the upper domain of the MCP that contains hydrophobic residues that interact with the SCP, which in turn crosslinks with neighbouring MCPs in the same hexon to stabilize the capsid. Multiple levels of MCP-MCP interaction-including six sets of stacked hairpins lining the hexon channel, disulfide bonds across channel and buttress domains in neighbouring MCPs, and an interaction network forged by the N-lasso domain and secured by the dimerization domain-define a robust capsid that is resistant to the pressure exerted by the enclosed genome. The triplexes, each composed of two Tri2 molecules and a Tri1 molecule, anchor to the capsid floor via a Tri1 N-anchor to plug holes in the MCP network and rivet the capsid floor. These essential roles of the MCP N-lasso and Tri1 N-anchor are verified by serial-truncation mutageneses. Our proof-of-concept demonstration of the use of polypeptides that mimic the smallest capsid protein to inhibit KSHV lytic replication highlights the potential for exploiting the interaction hotspots revealed in our atomic structure to develop antiviral agents. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6b43.cif.gz 6b43.cif.gz | 4.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6b43.ent.gz pdb6b43.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6b43.json.gz 6b43.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/6b43 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/6b43 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/6b43 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b4/6b43 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6038M  7047MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 60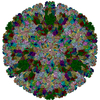
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | x 5
|
| 4 | x 6
|
| 5 | 
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 153574.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 16 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Details: Coded by gene ORF25. / Source: (natural)   Human herpesvirus 8 / Variant: clone BAC16 / References: UniProt: D0UZN7 Human herpesvirus 8 / Variant: clone BAC16 / References: UniProt: D0UZN7#2: Protein | Mass: 18597.824 Da / Num. of mol.: 15 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Details: Coded by gene ORF65. / Source: (natural)   Human herpesvirus 8 / Variant: clone BAC16 / References: UniProt: Q76RF4 Human herpesvirus 8 / Variant: clone BAC16 / References: UniProt: Q76RF4#3: Protein | Mass: 36374.840 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Coded by gene ORF62. It is the monomer in the heterotrimeric triplex structure. Source: (natural)   Human herpesvirus 8 / Variant: clone BAC16 / References: UniProt: Q76RF6 Human herpesvirus 8 / Variant: clone BAC16 / References: UniProt: Q76RF6#4: Protein | Mass: 34278.473 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Coded by gene ORF26. Forms the dimer in the heterotrimeric triplex structure. Source: (natural)   Human herpesvirus 8 / Variant: clone BAC16 / References: UniProt: C7E5A9 Human herpesvirus 8 / Variant: clone BAC16 / References: UniProt: C7E5A9Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human herpesvirus 8 / Type: VIRUS Details: KSHV lytic replication was induced in an iSLK-puro cell line harboring the KSHV-BAC16 plasmid. Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 200 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human herpesvirus 8 / Strain: JSC-1 Human herpesvirus 8 / Strain: JSC-1 |
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: YES / Isolate: STRAIN / Type: VIRION |
| Natural host | Organism: Homo sapiens |
| Virus shell | Name: capsid / Diameter: 1300 nm / Triangulation number (T number): 16 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Buffer component | Name: phosphate buffered saline / Formula: PBS |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber temperature: 298 K Details: The sample was manually blotted and frozen with a homemade plunger. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 14000 X / Calibrated magnification: 24271 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (min): 79 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 13 sec. / Electron dose: 25 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 3 / Num. of real images: 8007 |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 2.5 µm / Width: 7676 / Height: 7420 / Movie frames/image: 26 / Used frames/image: 1-26 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: dev_2875: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 44343 Details: Particles were boxed with ETHAN, and then manually examined. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: I (icosahedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 25315 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj
