[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-60147: Structure of DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 core (RhoG/DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 dataset... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
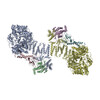
| Title | Structure of DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 core (RhoG/DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 dataset, class 2) | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ELMO / DOCK / GEF / GTPASE / RHO / RAC / SIGNALING PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction / regulation of respiratory burst / regulation of neutrophil migration / localization within membrane / negative regulation of interleukin-23 production / podosome assembly / Activated NTRK2 signals through CDK5 / negative regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis / ruffle assembly / regulation of hydrogen peroxide metabolic process ...negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction / regulation of respiratory burst / regulation of neutrophil migration / localization within membrane / negative regulation of interleukin-23 production / podosome assembly / Activated NTRK2 signals through CDK5 / negative regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis / ruffle assembly / regulation of hydrogen peroxide metabolic process / NTRK2 activates RAC1 / engulfment of apoptotic cell / Inactivation of CDC42 and RAC1 / NADPH oxidase complex / respiratory burst / cortical cytoskeleton organization / WNT5:FZD7-mediated leishmania damping / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor complex / SEMA3A-Plexin repulsion signaling by inhibiting Integrin adhesion / hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway / bone remodeling / myoblast fusion / ruffle organization / regulation of stress fiber assembly / thioesterase binding / cell projection assembly / negative regulation of fibroblast migration / RHO GTPases activate CIT / sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling pathway / Nef and signal transduction / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / RHO GTPases activate KTN1 / regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / PCP/CE pathway / Activation of RAC1 / motor neuron axon guidance / positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis / regulation of lamellipodium assembly / Azathioprine ADME / MET activates RAP1 and RAC1 / DCC mediated attractive signaling / anchoring junction / positive regulation of cell-substrate adhesion / Sema4D mediated inhibition of cell attachment and migration / CD28 dependent Vav1 pathway / Ephrin signaling / podosome / Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway / lamellipodium assembly / small GTPase-mediated signal transduction / regulation of cell size / Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / phagocytosis, engulfment / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / NRAGE signals death through JNK / positive regulation of epithelial cell migration / Rac protein signal transduction / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly / Sema3A PAK dependent Axon repulsion / semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway / ficolin-1-rich granule membrane / RHOG GTPase cycle / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / RHO GTPases Activate NADPH Oxidases / anatomical structure morphogenesis / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / PTK6 Regulates RHO GTPases, RAS GTPase and MAP kinases / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / RHO GTPases activate PKNs / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / GPVI-mediated activation cascade / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / RAC1 GTPase cycle / regulation of cell migration / actin filament polymerization / positive regulation of endothelial cell migration / GTPase activator activity / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / cell-matrix adhesion / cell chemotaxis / secretory granule membrane / small monomeric GTPase / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / Signal transduction by L1 / actin filament organization / cell projection / cell motility / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization / FCERI mediated MAPK activation / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / neuron migration Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
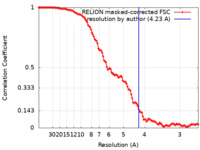
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.23 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kukimoto-Niino M / Katsura K / Ishizuka-Katsura Y / Mishima-Tsumagari C / Yonemochi M / Inoue M / Nakagawa R / Kaushik R / Zhang KYJ / Shirouzu M | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 3 items Japan, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2024 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2024Title: RhoG facilitates a conformational transition in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor complex DOCK5/ELMO1 to an open state. Authors: Mutsuko Kukimoto-Niino / Kazushige Katsura / Yoshiko Ishizuka-Katsura / Chiemi Mishima-Tsumagari / Mayumi Yonemochi / Mio Inoue / Reiko Nakagawa / Rahul Kaushik / Kam Y J Zhang / Mikako Shirouzu /  Abstract: The dedicator of cytokinesis (DOCK)/engulfment and cell motility (ELMO) complex serves as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the GTPase Rac. RhoG, another GTPase, activates the ELMO-DOCK- ...The dedicator of cytokinesis (DOCK)/engulfment and cell motility (ELMO) complex serves as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the GTPase Rac. RhoG, another GTPase, activates the ELMO-DOCK-Rac pathway during engulfment and migration. Recent cryo-EM structures of the DOCK2/ELMO1 and DOCK2/ELMO1/Rac1 complexes have identified closed and open conformations that are key to understanding the autoinhibition mechanism. Nevertheless, the structural details of RhoG-mediated activation of the DOCK/ELMO complex remain elusive. Herein, we present cryo-EM structures of DOCK5/ELMO1 alone and in complex with RhoG and Rac1. The DOCK5/ELMO1 structure exhibits a closed conformation similar to that of DOCK2/ELMO1, suggesting a shared regulatory mechanism of the autoinhibitory state across DOCK-A/B subfamilies (DOCK1-5). Conversely, the RhoG/DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 complex adopts an open conformation that differs from that of the DOCK2/ELMO1/Rac1 complex, with RhoG binding to both ELMO1 and DOCK5. The alignment of the DOCK5 phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate binding site with the RhoG C-terminal lipidation site suggests simultaneous binding of RhoG and DOCK5/ELMO1 to the plasma membrane. Structural comparison of the apo and RhoG-bound states revealed that RhoG facilitates a closed-to-open state conformational change of DOCK5/ELMO1. Biochemical and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) assays confirm that RhoG enhances the Rac GEF activity of DOCK5/ELMO1 and increases its binding affinity for Rac1. Further analysis of structural variability underscored the conformational flexibility of the DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 complex core, potentially facilitating the proximity of the DOCK5 GEF domain to the plasma membrane. These findings elucidate the structural mechanism underlying the RhoG-induced allosteric activation and membrane binding of the DOCK/ELMO complex. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_60147.map.gz emd_60147.map.gz | 140.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-60147-v30.xml emd-60147-v30.xml emd-60147.xml emd-60147.xml | 22.5 KB 22.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_60147_fsc.xml emd_60147_fsc.xml | 12 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_60147.png emd_60147.png | 69.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-60147.cif.gz emd-60147.cif.gz | 7.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_60147_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60147_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60147_half_map_2.map.gz emd_60147_half_map_2.map.gz | 117.1 MB 116.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60147 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60147 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60147 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60147 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_60147_validation.pdf.gz emd_60147_validation.pdf.gz | 963.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_60147_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_60147_full_validation.pdf.gz | 962.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_60147_validation.xml.gz emd_60147_validation.xml.gz | 19.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_60147_validation.cif.gz emd_60147_validation.cif.gz | 25.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60147 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60147 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60147 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60147 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 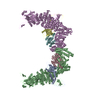 8zjjMC  8jhkC 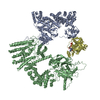 8xm7C  8zj2C  8zjiC  8zjkC  8zjlC  8zjmC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_60147.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_60147.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.33 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
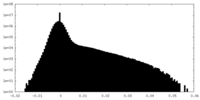
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_60147_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_60147_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 complex
| Entire | Name: DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: DOCK5/ELMO1/Rac1 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Engulfment and cell motility protein 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Engulfment and cell motility protein 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 84.337719 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GGSGGSMPPP ADIVKVAIEW PGAYPKLMEI DQKKPLSAII KEVCDGWSLA NHEYFALQHA DSSNFYITEK NRNEIKNGTI LRLTTSPAQ NAQQLHERIQ SSSMDAKLEA LKDLASLSRD VTFAQEFINL DGISLLTQMV ESGTERYQKL QKIMKPCFGD M LSFTLTAF ...String: GGSGGSMPPP ADIVKVAIEW PGAYPKLMEI DQKKPLSAII KEVCDGWSLA NHEYFALQHA DSSNFYITEK NRNEIKNGTI LRLTTSPAQ NAQQLHERIQ SSSMDAKLEA LKDLASLSRD VTFAQEFINL DGISLLTQMV ESGTERYQKL QKIMKPCFGD M LSFTLTAF VELMDHGIVS WDTFSVAFIK KIASFVNKSA IDISILQRSL AILESMVLNS HDLYQKVAQE ITIGQLIPHL QG SDQEIQT YTIAVINALF LKAPDERRQE MANILAQKQL RSIILTHVIR AQRAINNEMA HQLYVLQVLT FNLLEDRMMT KMD PQDQAQ RDIIFELRRI AFDAESEPNN SSGSMEKRKS MYTRDYKKLG FINHVNPAMD FTQTPPGMLA LDNMLYFAKH HQDA YIRIV LENSSREDKH ECPFGRSSIE LTKMLCEILK VGELPSETCN DFHPMFFTHD RSFEEFFCIC IQLLNKTWKE MRATS EDFN KVMQVVKEQV MRALTTKPSS LDQFKSKLQN LSYTEILKIR QSERMNQEDF QSRPILELKE KIQPEILELI KQQRLN RLV EGTCFRKLNA RRRQDKFWYC RLSPNHKVLH YGDLEESPQG EVPHDSLQDK LPVADIKAVV TGKDCPHMKE KGALKQN KE VLELAFSILY DSNCQLNFIA PDKHEYCIWT DGLNALLGKD MMSDLTRNDL DTLLSMEIKL RLLDLENIQI PDAPPPIP K EPSNYDFVYD CN UniProtKB: Engulfment and cell motility protein 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 5
| Macromolecule | Name: Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 5 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 191.492125 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GGSGGSMARW IPTKRQKYGV AIYNYNASQD VELSLQIGDT VHILEMYEGW YRGYTLQNKS KKGIFPETYI HLKEATVEDL GQHETVIPG ELPLVQELTS TLREWAVIWR KLYVNNKLTL FRQLQQMTYS LIEWRSQILS GTLPKDELAE LKKKVTAKID H GNRMLGLD ...String: GGSGGSMARW IPTKRQKYGV AIYNYNASQD VELSLQIGDT VHILEMYEGW YRGYTLQNKS KKGIFPETYI HLKEATVEDL GQHETVIPG ELPLVQELTS TLREWAVIWR KLYVNNKLTL FRQLQQMTYS LIEWRSQILS GTLPKDELAE LKKKVTAKID H GNRMLGLD LVVRDDNGNI LDPDETSTIA LFKAHEVASK RIEEKIQEEK SILQNLDLRG QSIFSTIHTY GLYVNFKNFV CN IGEDAEL FMALYDPDQS TFISENYLIR WGSNGMPKEI EKLNNLQAVF TDLSSMDLIR PRVSLVCQIV RVGHMELKEG KKH TCGLRR PFGVAVMDIT DIIHGKVDDE EKQHFIPFQQ IAMETYIRQR QLIMSPLITS HVIGENEPLT SVLNKVIAAK EVNH KGQGL WVSLKLLPGD LTQVQKNFSH LVDRSTAIAR KMGFPEIILP GDVRNDIYVT LIHGEFDKGK KKTPKNVEVT MSVHD EEGK LLEKAIHPGA GYEGISEYKS VVYYQVKQPC WYETVKVSIA IEEVTRCHIR FTFRHRSSQE TRDKSERAFG VAFVKL MNP DGTTLQDGRH DLVVYKGDNK KMEDAKFYLT LPGTKMEMEE KELQASKNLV TFTPSKDSTK DSFQIATLIC STKLTQN VD LLGLLNWRSN SQNIKHNLKK LMEVDGGEIV KFLQDTLDAL FNIMMEMSDS ETYDFLVFDA LVFIISLIGD IKFQHFNP V LETYIYKHFS ATLAYVKLSK VLNFYVANAD DSSKTELLFA ALKALKYLFR FIIQSRVLYL RFYGQSKDGD EFNNSIRQL FLAFNMLMDR PLEEAVKIKG AALKYLPSII NDVKLVFDPV ELSVLFCKFI QSIPDNQLVR QKLNCMTKIV ESTLFRQSEC REVLLPLLT DQLSGQLDDN SNKPDHEASS QLLSNILEVL DRKDVGATAV HIQLIMERLL RRINRTVIGM NRQSPHIGSF V ACMIALLQ QMDDSHYSHY ISTFKTRQDI IDFLMETFIM FKDLIGKNVY AKDWMVMNMT QNRVFLRAIN QFAEVLTRFF MD QASFELQ LWNNYFHLAV AFLTHESLQL ETFSQAKRNK IVKKYGDMRK EIGFRIRDMW YNLGPHKIKF IPSMVGPILE VTL TPEVEL RKATIPIFFD MMQCEFNFSG NGNFHMFENE LITKLDQEVE GGRGDEQYKV LLEKLLLEHC RKHKYLSSSG EVFA LLVSS LLENLLDYRT IIMQDESKEN RMSCTVNVLN FYKEKKREDI YIRYLYKLRD LHRDCENYTE AAYTLLLHAE LLQWS DKPC VPHLLQRDSY YVYTQQELKE KLYQEIISYF DKGKMWEKAI KLSKELAETY ESKVFDYEGL GNLLKKRASF YENIIK AMR PQPEYFAVGY YGQGFPSFLR NKIFIYRGKE YERREDFSLR LLTQFPNAEK MTSTTPPGED IKSSPKQYMQ CFTVKPV MS LPPSYKDKPV PEQILNYYRA NEVQQFRYSR PFRKGEKDPD NEFATMWIER TTYTTAYTFP GILKWFEVKQ ISTEEISP L ENAIETMELT NERISNCVQQ HAWDRSLSVH PLSMLLSGIV DPAVMGGFSN YEKAFFTEKY LQEHPEDQEK VELLKRLIA LQMPLLTEGI RIHGEKLTEQ LKPLHERLSS CFRELKEKVE KHYGVITL UniProtKB: Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 5 |
-Macromolecule #3: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: small monomeric GTPase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 20.244258 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSSGSSGMQA IKCVVVGDGA VAKTCLLISY TTNAFPGEYI PTVFDNYSAN VMVDGKPVNL GLWDTAGQED YDRLRPLSYP QTDVFLICF SLVSPASFEN VRAKWYPEVR HHCPNTPIIL VGTKLDLRDD KDTIEKLKEK KLTPITYPQG LAMAKEIGAV K YLECSALT QRGLKTVFDE AIRAVL UniProtKB: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - #0 - Film type ID: 1 / Support film - #0 - Material: CARBON / Support film - #0 - topology: HOLEY / Support film - #1 - Film type ID: 2 / Support film - #1 - Material: GRAPHENE / Support film - #1 - topology: HOLEY |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 11976 / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 64000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)