+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3j9t | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
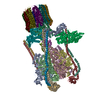
| Title | Yeast V-ATPase state 1 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / V-ATPase / V-type ATPase / vacuolar-type ATPase / proton pump | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / polyphosphate metabolic process / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification / proteasome storage granule assembly ...vacuole-mitochondrion membrane contact site / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / polyphosphate metabolic process / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification / proteasome storage granule assembly / vacuolar transport / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosomal lumen acidification / vacuole organization / protein targeting to vacuole / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / intron homing / intein-mediated protein splicing / pexophagy / fungal-type vacuole / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / cellular hyperosmotic response / vacuolar acidification / fungal-type vacuole membrane / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / ATP metabolic process / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / Neutrophil degranulation / proton transmembrane transport / transmembrane transport / endocytosis / cytoplasmic stress granule / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / ATPase binding / protein-containing complex assembly / endonuclease activity / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / membrane raft / Golgi membrane / mRNA binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao, J. / Benlekbir, S. / Rubinstein, J.L. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2015 Journal: Nature / Year: 2015Title: Electron cryomicroscopy observation of rotational states in a eukaryotic V-ATPase. Authors: Jianhua Zhao / Samir Benlekbir / John L Rubinstein /  Abstract: Eukaryotic vacuolar H(+)-ATPases (V-ATPases) are rotary enzymes that use energy from hydrolysis of ATP to ADP to pump protons across membranes and control the pH of many intracellular compartments. ...Eukaryotic vacuolar H(+)-ATPases (V-ATPases) are rotary enzymes that use energy from hydrolysis of ATP to ADP to pump protons across membranes and control the pH of many intracellular compartments. ATP hydrolysis in the soluble catalytic region of the enzyme is coupled to proton translocation through the membrane-bound region by rotation of a central rotor subcomplex, with peripheral stalks preventing the entire membrane-bound region from turning with the rotor. The eukaryotic V-ATPase is the most complex rotary ATPase: it has three peripheral stalks, a hetero-oligomeric proton-conducting proteolipid ring, several subunits not found in other rotary ATPases, and is regulated by reversible dissociation of its catalytic and proton-conducting regions. Studies of ATP synthases, V-ATPases, and bacterial/archaeal V/A-ATPases have suggested that flexibility is necessary for the catalytic mechanism of rotary ATPases, but the structures of different rotational states have never been observed experimentally. Here we use electron cryomicroscopy to obtain structures for three rotational states of the V-ATPase from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The resulting series of structures shows ten proteolipid subunits in the c-ring, setting the ATP:H(+) ratio for proton pumping by the V-ATPase at 3:10, and reveals long and highly tilted transmembrane α-helices in the a-subunit that interact with the c-ring. The three different maps reveal the conformational changes that occur to couple rotation in the symmetry-mismatched soluble catalytic region to the membrane-bound proton-translocating region. Almost all of the subunits of the enzyme undergo conformational changes during the transitions between these three rotational states. The structures of these states provide direct evidence that deformation during rotation enables the smooth transmission of power through rotary ATPases. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3j9t.cif.gz 3j9t.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3j9t.ent.gz pdb3j9t.ent.gz | 976.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3j9t.json.gz 3j9t.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j9/3j9t https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j9/3j9t ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j9/3j9t ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j9/3j9t | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 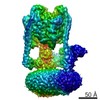 6284MC  6285C 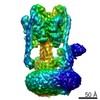 6286C  3j9uC  3j9vC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type proton ATPase subunit ... , 10 types, 25 molecules MNBDFQLHJKGIPbOYRUVTWSXZa
| #1: Protein | Mass: 29235.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 13479.170 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  | ||||||||||||||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 57815.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | | Mass: 39822.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #6: Protein | Mass: 12738.706 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #7: Protein | Mass: 26508.393 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #8: Protein | | Mass: 54482.609 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #9: Protein | | Mass: 95625.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #10: Protein | | Mass: 44241.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | Mass: 16357.501 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein , 1 types, 3 molecules ACE
| #3: Protein | Mass: 67665.305 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Fragment: SEE REMARK 999 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: P17255, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase, Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds |
|---|
-Details
| Sequence details | CHAINS A, C, AND E CONTAIN RESIDUES 2-283 and 738-1071 OF UNP P17255 WITH RESIDUES 284-737 REMOVED. |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Vacuolar-type ATPase / Type: COMPLEX Details: A3B3CDE3FG3HadcXc'Yc''Z where X, Y, and Z indicate unknown stoichiometry and X+Y+Z=10 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.9 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Buffer solution | Name: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 0.02% w/v dodecylmaltoside pH: 7.4 Details: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 0.02% w/v dodecylmaltoside |
| Specimen | Conc.: 10 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: Homemade holey carbon on 400 square mesh Cu/Rh grid, glow-discharged 2 mins |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: OTHER / Temp: 77 K / Humidity: 100 % Details: Blot for 23 seconds before freezing in ethane/propane mixture (FEI VITROBOT MARK III). Method: Blot for 23 seconds before freezing |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 / Date: Oct 19, 2013 / Details: K2 Summit in counting mode, 2 frames/s for 15 s |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 34483 X / Calibrated magnification: 34483 X / Nominal defocus max: 7000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2 mm / Astigmatism: Manually corrected by inspecting FFT |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN / Temperature: 77 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 (4k x 4k) / Details: K2 Summit in counting mode |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 3685 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Each particle | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: Maximum likelihood / Resolution: 6.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 50503 / Nominal pixel size: 1.45 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.45 Å Details: (Single particle details: Particles automatically selected using TMaCS and processed in Relion.) (Single particle--Applied symmetry: C1) Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL Details: REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--flexible DETAILS--Rigid body fitting performed in Chimera first, followed by flexible fitting performed using Molecular Dynamics Flexible Fitting (MDFF). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj















