+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2971 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
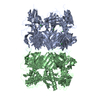
| Title | Structure and assembly of the mouse ASC filament | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of ASC-PYD filament | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ASC Apoptosis associated speck like protein containing a CARD / CARD caspase recruitment and activation domain / PYD PYRIN domain / PYHIN pyrin domain and hematopoietic expression / interferon inducibility / nuclear localization domain containing / NLR NOD like receptor / BIR Baculovirus IAP repeat domain | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCLEC7A/inflammasome pathway / The NLRP3 inflammasome / peptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process / NLRP6 inflammasome complex / myosin I binding / Pyrin domain binding / myeloid dendritic cell activation involved in immune response / positive regulation of antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class II / regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / IkappaB kinase complex ...CLEC7A/inflammasome pathway / The NLRP3 inflammasome / peptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process / NLRP6 inflammasome complex / myosin I binding / Pyrin domain binding / myeloid dendritic cell activation involved in immune response / positive regulation of antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class II / regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / IkappaB kinase complex / interleukin-6 receptor binding / AIM2 inflammasome complex / NLRP1 inflammasome complex / macropinocytosis / canonical inflammasome complex / NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly / BMP receptor binding / NLRP3 inflammasome complex / positive regulation of adaptive immune response / negative regulation of interferon-beta production / osmosensory signaling pathway / regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / regulation of GTPase activity / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production / tropomyosin binding / positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / positive regulation of actin filament polymerization / pyroptotic inflammatory response / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / positive regulation of interleukin-10 production / cellular response to interleukin-1 / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / positive regulation of T cell migration / positive regulation of chemokine production / positive regulation of defense response to virus by host / Neutrophil degranulation / negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response / activation of innate immune response / positive regulation of phagocytosis / negative regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / positive regulation of interleukin-8 production / response to bacterium / regulation of protein stability / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / protein homooligomerization / regulation of autophagy / positive regulation of JNK cascade / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of type II interferon production / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / positive regulation of inflammatory response / regulation of inflammatory response / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide / protease binding / regulation of apoptotic process / defense response to virus / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / microtubule / transmembrane transporter binding / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / protein dimerization activity / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / inflammatory response / Golgi membrane / innate immune response / neuronal cell body / apoptotic process / nucleolus / endoplasmic reticulum / protein homodimerization activity / mitochondrion / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sborgi L / Ravotti F / Dandey VP / Dick MS / Mazur A / Reckel S / Chami M / Scherer S / Bockmann A / Egelman EH ...Sborgi L / Ravotti F / Dandey VP / Dick MS / Mazur A / Reckel S / Chami M / Scherer S / Bockmann A / Egelman EH / Stahlberg H / Broz P / Meier BH / Hiller S | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2015 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2015Title: Structure and assembly of the mouse ASC inflammasome by combined NMR spectroscopy and cryo-electron microscopy. Authors: Lorenzo Sborgi / Francesco Ravotti / Venkata P Dandey / Mathias S Dick / Adam Mazur / Sina Reckel / Mohamed Chami / Sebastian Scherer / Matthias Huber / Anja Böckmann / Edward H Egelman / ...Authors: Lorenzo Sborgi / Francesco Ravotti / Venkata P Dandey / Mathias S Dick / Adam Mazur / Sina Reckel / Mohamed Chami / Sebastian Scherer / Matthias Huber / Anja Böckmann / Edward H Egelman / Henning Stahlberg / Petr Broz / Beat H Meier / Sebastian Hiller /    Abstract: Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes that control the innate immune response by activating caspase-1, thus promoting the secretion of cytokines in response to invading pathogens and endogenous ...Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes that control the innate immune response by activating caspase-1, thus promoting the secretion of cytokines in response to invading pathogens and endogenous triggers. Assembly of inflammasomes is induced by activation of a receptor protein. Many inflammasome receptors require the adapter protein ASC [apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase-recruitment domain (CARD)], which consists of two domains, the N-terminal pyrin domain (PYD) and the C-terminal CARD. Upon activation, ASC forms large oligomeric filaments, which facilitate procaspase-1 recruitment. Here, we characterize the structure and filament formation of mouse ASC in vitro at atomic resolution. Information from cryo-electron microscopy and solid-state NMR spectroscopy is combined in a single structure calculation to obtain the atomic-resolution structure of the ASC filament. Perturbations of NMR resonances upon filament formation monitor the specific binding interfaces of ASC-PYD association. Importantly, NMR experiments show the rigidity of the PYD forming the core of the filament as well as the high mobility of the CARD relative to this core. The findings are validated by structure-based mutagenesis experiments in cultured macrophages. The 3D structure of the mouse ASC-PYD filament is highly similar to the recently determined human ASC-PYD filament, suggesting evolutionary conservation of ASC-dependent inflammasome mechanisms. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2971.map.gz emd_2971.map.gz | 6.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2971-v30.xml emd-2971-v30.xml emd-2971.xml emd-2971.xml | 10.1 KB 10.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_2971.jpg emd_2971.jpg | 1.9 MB | ||
| Filedesc structureFactors |  emd_2971_sf.cif.gz emd_2971_sf.cif.gz | 684.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2971 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2971 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2971 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2971 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2n1fMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2971.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 23.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2971.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 23.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of ASC-PYD filament | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.67 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Mouse ASC-PYD filament
| Entire | Name: Mouse ASC-PYD filament |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Mouse ASC-PYD filament
| Supramolecule | Name: Mouse ASC-PYD filament / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: mouse ASC filament
| Macromolecule | Name: mouse ASC filament / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 / Details: 25mM Tris 300mM NaCl |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: vitrified by plunging into liquid nitrogen-cooled liquid ethane Method: The grids were blotted for 1 s before plunging |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Date | Oct 10, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: DIRECT ELECTRON DE-10 (5k x 4k) / Digitization - Sampling interval: 5 µm / Number real images: 21138 / Average electron dose: 20 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source: TUNGSTEN HAIRPIN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION / Nominal magnification: 22500 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Tilt angle min: -12 / Tilt angle max: 12 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | The particles were aligned using IHRSR |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 14.2 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 53 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C3 (3 fold cyclic) Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: EMAN2, IHRSR, SPIDER |
| CTF correction | Details: CTFFIND3 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















