[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20294: Single particle cryo-EM structure of the voltage-gated K+ channel... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20294 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Single particle cryo-EM structure of the voltage-gated K+ channel Eag1 3-13 deletion mutant bound to calmodulin (conformation 2) | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened map for Eag1 3-13/CaM conformation 2 | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Voltage-gated potassium channel / ion channel / calmodulin / TRANSPORT PROTEIN-CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationVoltage gated Potassium channels / potassium channel complex / regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / nuclear inner membrane / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events ...Voltage gated Potassium channels / potassium channel complex / regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / nuclear inner membrane / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / presynaptic endocytosis / startle response / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / axolemma / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / cellular response to interferon-beta / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Protein methylation / 14-3-3 protein binding / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / titin binding / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / cellular response to calcium ion / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / adenylate cyclase activator activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / sarcomere / regulation of cytokinesis / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / regulation of membrane potential / potassium ion transport / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / postsynaptic density membrane / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Stimuli-sensing channels / spindle pole / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / RAS processing / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Whicher JR / MacKinnon R | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2019 Journal: Elife / Year: 2019Title: Regulation of Eag1 gating by its intracellular domains. Authors: Jonathan R Whicher / Roderick MacKinnon /  Abstract: Voltage-gated potassium channels (Ks) are gated by transmembrane voltage sensors (VS) that move in response to changes in membrane voltage. K10.1 or Eag1 also has three intracellular domains: PAS, C- ...Voltage-gated potassium channels (Ks) are gated by transmembrane voltage sensors (VS) that move in response to changes in membrane voltage. K10.1 or Eag1 also has three intracellular domains: PAS, C-linker, and CNBHD. We demonstrate that the Eag1 intracellular domains are not required for voltage-dependent gating but likely interact with the VS to modulate gating. We identified specific interactions between the PAS, CNBHD, and VS that modulate voltage-dependent gating and provide evidence that VS movement destabilizes these interactions to promote channel opening. Additionally, mutation of these interactions renders Eag1 insensitive to calmodulin inhibition. The structure of the calmodulin insensitive mutant in a pre-open conformation suggests that channel opening may occur through a rotation of the intracellular domains and calmodulin may prevent this rotation by stabilizing interactions between the VS and intracellular domains. Intracellular domains likely play a similar modulatory role in voltage-dependent gating of the related K11-12 channels. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20294.map.gz emd_20294.map.gz | 116.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20294-v30.xml emd-20294-v30.xml emd-20294.xml emd-20294.xml | 16 KB 16 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_20294_fsc.xml emd_20294_fsc.xml | 11.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_20294.png emd_20294.png | 196.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20294.cif.gz emd-20294.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_20294_additional.map.gz emd_20294_additional.map.gz | 92.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20294 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20294 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20294 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20294 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6pbxMC  6pbyC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20294.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20294.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened map for Eag1 3-13/CaM conformation 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
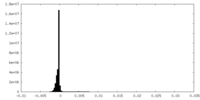
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Unsharpened map for Eag1 3-13/CaM conformation 2
| File | emd_20294_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened map for Eag1 3-13/CaM conformation 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
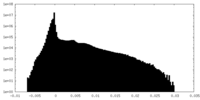
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Voltage-gated potassium channel Eag1 3-13 deletion mutant bound t...
| Entire | Name: Voltage-gated potassium channel Eag1 3-13 deletion mutant bound to calmodulin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Voltage-gated potassium channel Eag1 3-13 deletion mutant bound t...
| Supramolecule | Name: Voltage-gated potassium channel Eag1 3-13 deletion mutant bound to calmodulin type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Voltage-gated potassium channel Eag1 3-13 deletion mutant
| Supramolecule | Name: Voltage-gated potassium channel Eag1 3-13 deletion mutant type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: calmodulin
| Supramolecule | Name: calmodulin / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 96.26143 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAQNTFLENI VRRSNDTNFV LGNAQIVDWP IVYSNDGFCK LSGYHRAEVM QKSSACSFMY GELTDKDTVE KVRQTFENYE MNSFEILMY KKNRTPVWFF VKIAPIRNEQ DKVVLFLCTF SDITAFKQPI EDDSCKGWGK FARLTRALTS SRGVLQQLAP S VQKGENVH ...String: MAQNTFLENI VRRSNDTNFV LGNAQIVDWP IVYSNDGFCK LSGYHRAEVM QKSSACSFMY GELTDKDTVE KVRQTFENYE MNSFEILMY KKNRTPVWFF VKIAPIRNEQ DKVVLFLCTF SDITAFKQPI EDDSCKGWGK FARLTRALTS SRGVLQQLAP S VQKGENVH KHSRLAEVLQ LGSDILPQYK QEAPKTPPHI ILHYCVFKTT WDWIILILTF YTAILVPYNV SFKTRQNNVA WL VVDSIVD VIFLVDIVLN FHTTFVGPAG EVISDPKLIR MNYLKTWFVI DLLSCLPYDV INAFENVDEG ISSLFSSLKV VRL LRLGRV ARKLDHYIEY GAAVLVLLVC VFGLAAHWMA CIWYSIGDYE IFDEDTKTIR NNSWLYQLAL DIGTPYQFNG SGSG KWEGG PSKNSVYISS LYFTMTSLTS VGFGNIAPST DIEKIFAVAI MMIGSLLYAT IFGNVTTIFQ QMYANTNRYH EMLNS VRDF LKLYQVPKGL SERVMDYIVS TWSMSRGIDT EKVLQICPKD MRADICVHLN RKVFKEHPAF RLASDGCLRA LAMEFQ TVH CAPGDLIYHA GESVDSLCFV VSGSLEVIQD DEVVAILGKG DVFGDVFWKE ATLAQSCANV RALTYCDLHV IKRDALQ KV LEFYTAFSHS FSRNLILTYN LRKRIVFRKI SDVKREEEER MKRKNEAPLI LPPDHPVRRL FQRFRQQKEA RLAAERGG R DLDDLDVEKG NALTDHTSAN HSLVKASVVT VRESPATPVS FYPIPEQTLQ ATVLEVKHEL KEDIKALNAK MTSIEKQLS EILRILMSRG SSQSPQDTCE VSRPQSPESD RDIFGASSNS LEVLFQ UniProtKB: Voltage-gated delayed rectifier potassium channel KCNH1, Voltage-gated delayed rectifier potassium channel KCNH1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.852545 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)