+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human apoferritin | |||||||||
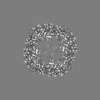
 Map data Map data | Map of human apoferritin. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Iron binding protein / METAL BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationiron ion sequestering activity / ferritin complex / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / negative regulation of ferroptosis / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / ferroxidase / autolysosome / ferroxidase activity / intracellular sequestering of iron ion / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation ...iron ion sequestering activity / ferritin complex / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / negative regulation of ferroptosis / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / ferroxidase / autolysosome / ferroxidase activity / intracellular sequestering of iron ion / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / autophagosome / ferric iron binding / Iron uptake and transport / ferrous iron binding / tertiary granule lumen / iron ion transport / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / immune response / iron ion binding / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / Neutrophil degranulation / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / identical protein binding / membrane / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
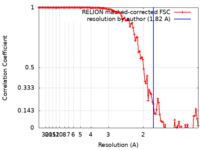
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 1.82 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Last MGF / Noteborn WEM / Sharp TH | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Netherlands, 1 items Netherlands, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2023Title: Super-resolution fluorescence imaging of cryosamples does not limit achievable resolution in cryoEM. Authors: Mart G F Last / Willem E M Noteborn / Lenard M Voortman / Thomas H Sharp /  Abstract: Correlated super-resolution cryo-fluorescence and cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) has been gaining popularity as a method to investigate biological samples with high resolution and specificity. A ...Correlated super-resolution cryo-fluorescence and cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) has been gaining popularity as a method to investigate biological samples with high resolution and specificity. A concern in this combined method (called SR-cryoCLEM), however, is whether and how fluorescence imaging prior to cryoEM acquisition is detrimental to sample integrity. In this report, we investigated the effect of high-dose laser light (405, 488, and 561 nm) irradiation on apoferritin samples prepared for cryoEM with excitation wavelengths commonly used in fluorescence microscopy, and compared these samples to controls that were kept in the dark. We found that laser illumination, of equal duration and intensity as used in cryo-single molecule localization microscopy (cryoSMLM) and in the presence of high concentrations of fluorescent protein, did not affect the achievable resolution in cryoEM, with final reconstructions reaching resolutions of ∼ 1.8 Å regardless of the laser illumination. The finding that super-resolution fluorescence imaging of cryosamples prior to cryoEM data acquisition does not limit the achievable resolution suggests that super-resolution cryo-fluorescence microscopy and in situ structural biology using cryoEM are entirely compatible. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16784.map.gz emd_16784.map.gz | 15.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16784-v30.xml emd-16784-v30.xml emd-16784.xml emd-16784.xml | 16.7 KB 16.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_16784_fsc.xml emd_16784_fsc.xml | 10.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_16784.png emd_16784.png | 202.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16784.cif.gz emd-16784.cif.gz | 5.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16784_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16784_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16784_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16784_half_map_2.map.gz | 76.4 MB 76.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16784 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16784 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16784 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16784 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_16784_validation.pdf.gz emd_16784_validation.pdf.gz | 851.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_16784_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_16784_full_validation.pdf.gz | 851.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_16784_validation.xml.gz emd_16784_validation.xml.gz | 18 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_16784_validation.cif.gz emd_16784_validation.cif.gz | 23.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16784 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16784 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16784 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-16784 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8cpsMC  8cpmC  8cptC  8cpuC  8cpvC  8cpwC  8cpxC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16784.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16784.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map of human apoferritin. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.656 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
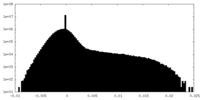
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half map 1
| File | emd_16784_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
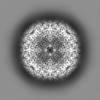
| Annotation | Half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 2
| File | emd_16784_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
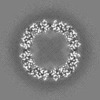
| Annotation | Half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Apoferritin
| Entire | Name: Apoferritin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Apoferritin
| Supramolecule | Name: Apoferritin / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 484 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Ferritin heavy chain, N-terminally processed
| Macromolecule | Name: Ferritin heavy chain, N-terminally processed / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 24 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 20.21857 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: STSQVRQNYH QDSEAAINRQ INLELYASYV YLSMSYYFDR DDVALKNFAK YFLHQSHEER EHAEKLMKLQ NQRGGRIFLQ DIQKPD(CSX)DD WESGLNAMEC ALHLEKNVNQ SLLELHKLAT DKNDPHLCDF IETHYLNEQV KAIKELGDHV TNLRKMG AP ESGLAEYLFD KHTLG UniProtKB: Ferritin heavy chain |
-Macromolecule #2: SODIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: SODIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 24 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.99 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 14 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1916 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: GOLD / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 50 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)