[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-1336: The structures of bacteriophages K1E and K1-5 explain processive ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1336 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
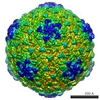
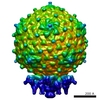
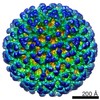
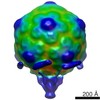
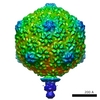
| Title | The structures of bacteriophages K1E and K1-5 explain processive degradation of polysaccharide capsules and evolution of new host specificities. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Model of the complete phage K1E particle | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Enterobacteria phage K1E (virus) Enterobacteria phage K1E (virus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / negative staining / Resolution: 17.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Leiman PG / Battisti AJ / Bowman VD / Stummeyer K / Muhlenhoff M / Gerardy-Schahn R / Scholl D / Molineux IJ | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2007 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2007Title: The structures of bacteriophages K1E and K1-5 explain processive degradation of polysaccharide capsules and evolution of new host specificities. Authors: Petr G Leiman / Anthony J Battisti / Valorie D Bowman / Katharina Stummeyer / Martina Mühlenhoff / Rita Gerardy-Schahn / Dean Scholl / Ian J Molineux /  Abstract: External polysaccharides of many pathogenic bacteria form capsules protecting the bacteria from the animal immune system and phage infection. However, some bacteriophages can digest these capsules ...External polysaccharides of many pathogenic bacteria form capsules protecting the bacteria from the animal immune system and phage infection. However, some bacteriophages can digest these capsules using glycosidases displayed on the phage particle. We have utilized cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structures of phages K1E and K1-5 and thereby establish the mechanism by which these phages attain and switch their host specificity. Using a specific glycosidase, both phages penetrate the capsule and infect the neuroinvasive human pathogen Escherichia coli K1. In addition to the K1-specific glycosidase, each K1-5 particle carries a second enzyme that allows it to infect E. coli K5, whose capsule is chemically different from that of K1. The enzymes are organized into a multiprotein complex attached via an adapter protein to the virus portal vertex, through which the DNA is ejected during infection. The structure of the complex suggests a mechanism for the apparent processivity of degradation that occurs as the phage drills through the polysaccharide capsule. The enzymes recognize the adapter protein by a conserved N-terminal sequence, providing a mechanism for phages to acquire different enzymes and thus to evolve new host specificities. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1336.map.gz emd_1336.map.gz | 45.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1336-v30.xml emd-1336-v30.xml emd-1336.xml emd-1336.xml | 9.9 KB 9.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  1336.gif 1336.gif | 53.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1336 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1336 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1336 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1336 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_1336_validation.pdf.gz emd_1336_validation.pdf.gz | 232.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_1336_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_1336_full_validation.pdf.gz | 232.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_1336_validation.xml.gz emd_1336_validation.xml.gz | 6.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1336 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1336 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1336 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1336 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1336.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 68.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1336.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 68.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Model of the complete phage K1E particle | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.47 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complete model of bacteriophage K1E
| Entire | Name: Complete model of bacteriophage K1E |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Complete model of bacteriophage K1E
| Supramolecule | Name: Complete model of bacteriophage K1E / type: sample / ID: 1000 Details: This is a model of the phage obtained by merging two maps obtained from the same set of particles: 1) Reconstruction of the capsid with 5-fold symmetry imposed; 2) Reconstruction of the tail ...Details: This is a model of the phage obtained by merging two maps obtained from the same set of particles: 1) Reconstruction of the capsid with 5-fold symmetry imposed; 2) Reconstruction of the tail with 6-fold symmetry imposed. The relative orientation of the two maps was found using a lower resolution reconstrution with no symmetry imposed. Number unique components: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 58 MDa / Theoretical: 58 MDa / Method: Primary sequence |
-Supramolecule #1: Enterobacteria phage K1E
| Supramolecule | Name: Enterobacteria phage K1E / type: virus / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: phage K1E Details: The model obtained by combining maps with 5- and 6-fold symmetries imposed NCBI-ID: 344022 / Sci species name: Enterobacteria phage K1E / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: SPECIES / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No / Syn species name: phage K1E |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 58 MDa / Theoretical: 58 MDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining, cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Details: 50 mM Tris HCl pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 8 mM MgSO4 |
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Details: no staining |
| Grid | Details: quantifoil grid |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 300 K / Instrument: OTHER / Details: Vitrification instrument: Vitrobot |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI/PHILIPS CM300FEG/T |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Average: 100 K |
| Date | May 10, 2005 |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: ZEISS SCAI / Digitization - Sampling interval: 7 µm / Number real images: 122 / Average electron dose: 25 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 12 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 47000 / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.3 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7 µm / Nominal magnification: 45000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Side entry liquid nitrogen-cooled cryo specimen holder Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: Each particle |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C5 (5 fold cyclic) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 17.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: Spider, EMAN / Number images used: 6105 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















