+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-12890 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
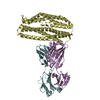
| Title | Tetanus neurotoxin HC domain in complex with TT104-Fab1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Tetanus neurotoxin HC domain in complex with TT104-Fab1 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | tetanus / tetanus neurotoxin / humAbs / monoclonal antibody / tetanus prophylaxis / spastic paralysis / tetanus immunoglobulin / TIG / TOXIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Clostridium tetani (bacteria) / Clostridium tetani (bacteria) /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Pirazzini M / Grinzato A | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Clin Invest / Year: 2021 Journal: J Clin Invest / Year: 2021Title: Exceptionally potent human monoclonal antibodies are effective for prophylaxis and treatment of tetanus in mice. Authors: Marco Pirazzini / Alessandro Grinzato / Davide Corti / Sonia Barbieri / Oneda Leka / Francesca Vallese / Marika Tonellato / Chiara Silacci-Fregni / Luca Piccoli / Eaazhisai Kandiah / ...Authors: Marco Pirazzini / Alessandro Grinzato / Davide Corti / Sonia Barbieri / Oneda Leka / Francesca Vallese / Marika Tonellato / Chiara Silacci-Fregni / Luca Piccoli / Eaazhisai Kandiah / Giampietro Schiavo / Giuseppe Zanotti / Antonio Lanzavecchia / Cesare Montecucco /     Abstract: We used human monoclonal antibodies (humAbs) to study the mechanism of neuron intoxication by tetanus neurotoxin and to evaluate these antibodies as a safe preventive and therapeutic substitute for ...We used human monoclonal antibodies (humAbs) to study the mechanism of neuron intoxication by tetanus neurotoxin and to evaluate these antibodies as a safe preventive and therapeutic substitute for hyperimmune sera to treat tetanus in mice. By screening memory B cells from immune donors, we selected 2 tetanus neurotoxin-specific mAbs with exceptionally high neutralizing activities and extensively characterized them both structurally and functionally. We found that these antibodies interfered with the binding and translocation of the neurotoxin into neurons by interacting with 2 epitopes, whose identification pinpoints crucial events in the cellular pathogenesis of tetanus. Our observations explain the neutralization ability of these antibodies, which we found to be exceptionally potent in preventing experimental tetanus when injected into mice long before the toxin. Moreover, their Fab derivatives neutralized tetanus neurotoxin in post-exposure experiments, suggesting their potential for therapeutic use via intrathecal injection. As such, we believe these humAbs, as well as their Fab derivatives, meet the requirements to be considered for prophylactic and therapeutic use in human tetanus and are ready for clinical trials. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_12890.map.gz emd_12890.map.gz | 96.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-12890-v30.xml emd-12890-v30.xml emd-12890.xml emd-12890.xml | 15.4 KB 15.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_12890.png emd_12890.png | 48.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-12890.cif.gz emd-12890.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12890 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12890 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12890 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12890 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7oh0MC  7oh1C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_12890.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_12890.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Tetanus neurotoxin HC domain in complex with TT104-Fab1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.827 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Tetanus neurotoxin HC domain in complex with TT104-Fab1
| Entire | Name: Tetanus neurotoxin HC domain in complex with TT104-Fab1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Tetanus neurotoxin HC domain in complex with TT104-Fab1
| Supramolecule | Name: Tetanus neurotoxin HC domain in complex with TT104-Fab1 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Tetanus toxin
| Supramolecule | Name: Tetanus toxin / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Clostridium tetani (bacteria) Clostridium tetani (bacteria) |
-Supramolecule #3: FAB TT110
| Supramolecule | Name: FAB TT110 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Tetanus toxin
| Macromolecule | Name: Tetanus toxin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Clostridium tetani (bacteria) Clostridium tetani (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 50.476918 KDa |
| Sequence | String: EDIDVILKKS TILNLDINND IISDISGFNS SVITYPDAQL VPGINGKAIH LVNNESSEVI VHKAMDIEYN DMFNNFTVSF WLRVPKVSA SHLEQYGTNE YSIISSMKKH SLSIGSGWSV SLKGNNLIWT LKDSAGEVRQ ITFRDLPDKF NAYLANKWVF I TITNDRLS ...String: EDIDVILKKS TILNLDINND IISDISGFNS SVITYPDAQL VPGINGKAIH LVNNESSEVI VHKAMDIEYN DMFNNFTVSF WLRVPKVSA SHLEQYGTNE YSIISSMKKH SLSIGSGWSV SLKGNNLIWT LKDSAGEVRQ ITFRDLPDKF NAYLANKWVF I TITNDRLS SANLYINGVL MGSAEITGLG AIREDNNITL KLDRCNNNNQ YVSIDKFRIF CKALNPKEIE KLYTSYLSIT FL RDFWGNP LRYDTEYYLI PVASSSKDVQ LKNITDYMYL TNAPSYTNGK LNIYYRRLYN GLKFIIKRYT PNNEIDSFVK SGD FIKLYV SYNNNEHIVG YPKDGNAFNN LDRILRVGYN APGIPLYKKM EAVKLRDLKT YSVQLKLYDD KNASLGLVGT HNGQ IGNDP NRDILIASNW YFNHLKDKIL GCDWYFVPTD EGWTND UniProtKB: Tetanus toxin |
-Macromolecule #2: Fab TT104
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab TT104 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.647295 KDa |
| Sequence | String: QLQLQESGPG LVRPSETLSL TCSVSDDSMG SSTYYWAWIR QPPGKGLEWI GNVYYNGVTY YNSSLESRLT LSIDPSKNQF SLILSSVTA ADTAVYYCAR QADNWFDPWG QGTLVTVSSA STKGPSVFPL APSSKSTSGG TAALGCLVKD YFPEPVTVSW N SGALTSGV ...String: QLQLQESGPG LVRPSETLSL TCSVSDDSMG SSTYYWAWIR QPPGKGLEWI GNVYYNGVTY YNSSLESRLT LSIDPSKNQF SLILSSVTA ADTAVYYCAR QADNWFDPWG QGTLVTVSSA STKGPSVFPL APSSKSTSGG TAALGCLVKD YFPEPVTVSW N SGALTSGV HTFPAVLQSS GLYSLSSVVT VPSSSLGTQT YICNVNHKPS NTKVDKRVEP KSC |
-Macromolecule #3: Fab TT104
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab TT104 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.462094 KDa |
| Sequence | String: IMMTQSPATL SVSPGERATL SCRASQSVGS DLAWYQQKPG QAPRLLIYGA SYRATGIPAR FSGGGSGTEF TLTISSMQSE DFAVYYCQQ YYNWPPYTFG QGTKVEIKRT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS ...String: IMMTQSPATL SVSPGERATL SCRASQSVGS DLAWYQQKPG QAPRLLIYGA SYRATGIPAR FSGGGSGTEF TLTISSMQSE DFAVYYCQQ YYNWPPYTFG QGTKVEIKRT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS KDSTYSLSST LTLSKADYEK HKVYACEVTH QGLSSPVTKS FNRGEC |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















