+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-12400 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
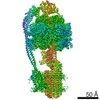
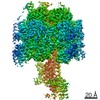
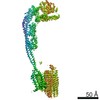
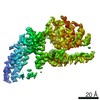
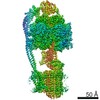
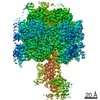
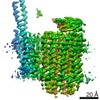
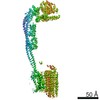
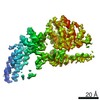
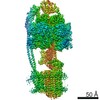
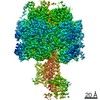
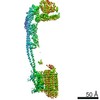
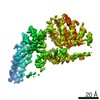
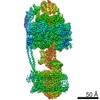
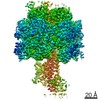
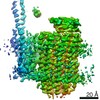
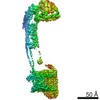
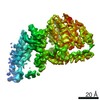
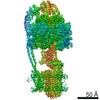
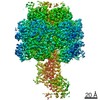
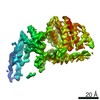
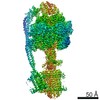
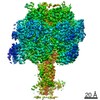
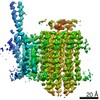
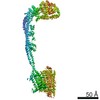
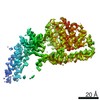
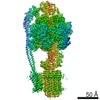
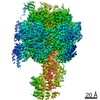
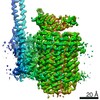
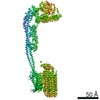
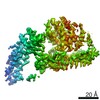
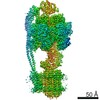
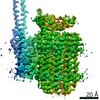
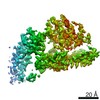
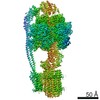
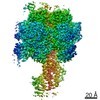
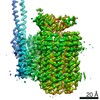
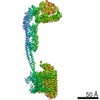
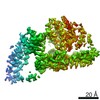
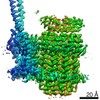
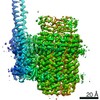
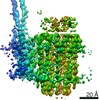
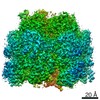
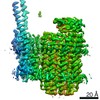
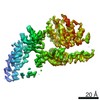
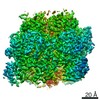
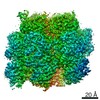
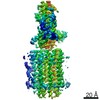
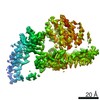
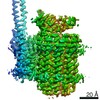
| Title | Mycobacterium smegmatis ATP synthase Peripheral Stalk state 1e | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Msmeg ATP synthase PS state 1e map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, coupling factor F(o) / photosynthetic electron transport in photosystem I / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic core F(1) / photosynthetic electron transport in photosystem II / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / hydrolase activity ...proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, coupling factor F(o) / photosynthetic electron transport in photosystem I / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic core F(1) / photosynthetic electron transport in photosystem II / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / hydrolase activity / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.15 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Petri J / Montgomery MG / Spikes TE / Walker JE | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021Title: Structure of the ATP synthase from provides targets for treating tuberculosis. Authors: Martin G Montgomery / Jessica Petri / Tobias E Spikes / John E Walker /  Abstract: The structure has been determined by electron cryomicroscopy of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase from This analysis confirms features in a prior description of the structure of the enzyme, ...The structure has been determined by electron cryomicroscopy of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase from This analysis confirms features in a prior description of the structure of the enzyme, but it also describes other highly significant attributes not recognized before that are crucial for understanding the mechanism and regulation of the mycobacterial enzyme. First, we resolved not only the three main states in the catalytic cycle described before but also eight substates that portray structural and mechanistic changes occurring during a 360° catalytic cycle. Second, a mechanism of auto-inhibition of ATP hydrolysis involves not only the engagement of the C-terminal region of an α-subunit in a loop in the γ-subunit, as proposed before, but also a "fail-safe" mechanism involving the b'-subunit in the peripheral stalk that enhances engagement. A third unreported characteristic is that the fused bδ-subunit contains a duplicated domain in its N-terminal region where the two copies of the domain participate in similar modes of attachment of the two of three N-terminal regions of the α-subunits. The auto-inhibitory plus the associated "fail-safe" mechanisms and the modes of attachment of the α-subunits provide targets for development of innovative antitubercular drugs. The structure also provides support for an observation made in the bovine ATP synthase that the transmembrane proton-motive force that provides the energy to drive the rotary mechanism is delivered directly and tangentially to the rotor via a Grotthuss water chain in a polar L-shaped tunnel. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_12400.map.gz emd_12400.map.gz | 16.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-12400-v30.xml emd-12400-v30.xml emd-12400.xml emd-12400.xml | 8.7 KB 8.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_12400_fsc.xml emd_12400_fsc.xml | 17.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_12400.png emd_12400.png | 73.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12400 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12400 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12400 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-12400 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_12400_validation.pdf.gz emd_12400_validation.pdf.gz | 319 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_12400_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_12400_full_validation.pdf.gz | 318.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_12400_validation.xml.gz emd_12400_validation.xml.gz | 15.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_12400_validation.cif.gz emd_12400_validation.cif.gz | 21.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12400 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12400 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12400 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-12400 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Sample components
Sample components



 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera