+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Small siphophage binding to an open state of the LptDE outer membrane lipopolysaccharide translocon. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 122, Issue 48, Page e2516650122, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Dec 2, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Emily Dunbar / Robert Clark / Arnaud Baslé / Shenaz Allyjaun / Hector Newman / Julia Hubbard / Syma Khalid / Bert van den Berg /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Bacteriophages are bacterial viruses that provide alternatives to small-molecule drugs to combat infections by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. To infect a bacterial host, a phage needs to bind to the ...Bacteriophages are bacterial viruses that provide alternatives to small-molecule drugs to combat infections by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. To infect a bacterial host, a phage needs to bind to the bacterial surface via receptor binding proteins (RBPs), which are critical for determining host specificity. For functionally important receptors, the RBP-receptor interaction could be exploited via phage steering, where emerging bacterial resistance due to receptor modification could make bacteria less fit or virulent. Despite this, relatively little is known about RBP-receptor interactions. Here, we build on the recent discovery of coliphages that have the outer membrane (OM) lipopolysaccharide translocon LptDE as their terminal receptor and show via cryogenic electron microscopy that, surprisingly, the RBP of the small siphophage Oekolampad binds to a hitherto unobserved, open state of LptDE. The open lateral gate of LptD is occupied by a β-strand peptide originating from the degraded N-terminal jellyroll domain of LptD, suggesting the possibility of LptD inhibition via peptidomimetics. A structure of LptDE in complex with the superinfection exclusion (SE) protein Rtp45 of the Oekolampad-related phage Rtp shows a mechanism of SE where Rtp45-induced conformational changes in LptD resulting from steric clashes preclude RBP binding. Finally, analysis of spontaneous Oekolampad-resistant mutants identifies mutations in LptD that abolish the LptDE-RBP interaction in vitro. SDS-EDTA sensitivity assays of the mutants show no major OM defects, consistent with largely preserved LptDE function, and suggesting that phage steering via LptDE might be challenging. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:41296721 / PubMed:41296721 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.76 - 3.2 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-54169, PDB-9rpr: EMDB-54170, PDB-9rps: EMDB-54171, PDB-9rpt: EMDB-54173, PDB-9rpw: EMDB-54175, PDB-9rqi: |
| Chemicals | 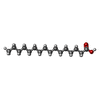 ChemComp-PLM: 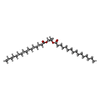 ChemComp-PXS: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / lipopolysaccharide transport / outer membrane protein complex / beta-barrel / lipoprotein / outer membrane complex / superinfection exclusion / bacteriophage / receptor-binding protein |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers













 shigella flexneri (bacteria)
shigella flexneri (bacteria) escherichia phage rtp (virus)
escherichia phage rtp (virus)