+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | How short peptides disassemble tau fibrils in Alzheimer's disease. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 644, Issue 8078, Page 1020-1027, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Jul 9, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Ke Hou / Peng Ge / Michael R Sawaya / Liisa Lutter / Joshua L Dolinsky / Yuan Yang / Yi Xiao Jiang / David R Boyer / Xinyi Cheng / Justin Pi / Jeffrey Zhang / Jiahui Lu / Romany Abskharon / Shixin Yang / Zhiheng Yu / Juli Feigon / David S Eisenberg /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Reducing fibrous aggregates of the protein tau is a possible strategy for halting the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Previously, we found that in vitro, the D-enantiomeric peptide (D- ...Reducing fibrous aggregates of the protein tau is a possible strategy for halting the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Previously, we found that in vitro, the D-enantiomeric peptide (D-peptide) D-TLKIVWC disassembles ultra-stable tau fibrils extracted from the autopsied brains of individuals with AD (hereafter, these tau fibrils are referred to as AD-tau) into benign segments, with no energy source other than ambient thermal agitation. To consider D-peptide-mediated disassembly as a potential route to therapeutics for AD, it is essential to understand the mechanism and energy source of the disassembly action. Here, we show that the assembly of D-peptides into amyloid-like ('mock-amyloid') fibrils is essential for AD-tau disassembly. These mock-amyloid fibrils have a right-handed twist but are constrained to adopt a left-handed twist when templated in complex with AD-tau. The release of strain that accompanies the conversion of left-twisted to right-twisted, relaxed mock-amyloid produces a torque that is sufficient to break the local hydrogen bonding between tau molecules, and leads to the fragmentation of AD-tau. This strain-relief mechanism seems to operate in other examples of amyloid fibril disassembly, and could inform the development of first-in-class therapeutics for amyloid diseases. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:40634605 / PubMed:40634605 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (helical sym.) |
| Resolution | 3.1 - 3.7 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-44181, PDB-9b4i: EMDB-44182, PDB-9b4j: EMDB-44183, PDB-9b4k: EMDB-44184, PDB-9b4l: EMDB-44185, PDB-9b4m: EMDB-44186, PDB-9b4n: EMDB-44187, PDB-9b4o: |
| Chemicals | 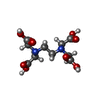 ChemComp-EDT: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | UNKNOWN FUNCTION / Alzheimer's disease / Tau / fibril / cryo-EM / helix / PROTEIN FIBRIL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers














 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)