+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Membraneless channels sieve cations in ammonia-oxidizing marine archaea. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 630, Issue 8015, Page 230-236, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | May 29, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Andriko von Kügelgen / C Keith Cassidy / Sofie van Dorst / Lennart L Pagani / Christopher Batters / Zephyr Ford / Jan Löwe / Vikram Alva / Phillip J Stansfeld / Tanmay A M Bharat /    |
| PubMed Abstract | Nitrosopumilus maritimus is an ammonia-oxidizing archaeon that is crucial to the global nitrogen cycle. A critical step for nitrogen oxidation is the entrapment of ammonium ions from a dilute marine ...Nitrosopumilus maritimus is an ammonia-oxidizing archaeon that is crucial to the global nitrogen cycle. A critical step for nitrogen oxidation is the entrapment of ammonium ions from a dilute marine environment at the cell surface and their subsequent channelling to the cell membrane of N. maritimus. Here we elucidate the structure of the molecular machinery responsible for this process, comprising the surface layer (S-layer), using electron cryotomography and subtomogram averaging from cells. We supplemented our in situ structure of the ammonium-binding S-layer array with a single-particle electron cryomicroscopy structure, revealing detailed features of this immunoglobulin-rich and glycan-decorated S-layer. Biochemical analyses showed strong ammonium binding by the cell surface, which was lost after S-layer disassembly. Sensitive bioinformatic analyses identified similar S-layers in many ammonia-oxidizing archaea, with conserved sequence and structural characteristics. Moreover, molecular simulations and structure determination of ammonium-enriched specimens enabled us to examine the cation-binding properties of the S-layer, revealing how it concentrates ammonium ions on its cell-facing side, effectively acting as a multichannel sieve on the cell membrane. This in situ structural study illuminates the biogeochemically essential process of ammonium binding and channelling, common to many marine microorganisms that are fundamental to the nitrogen cycle. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:38811725 / PubMed:38811725 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / EM (subtomogram averaging) |
| Resolution | 2.71 - 3.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-16482, PDB-8c8k: EMDB-16483, PDB-8c8l: EMDB-16484, PDB-8c8m:  EMDB-16486: In vitro Nitrosopumilus maritimus S-layer with NH4Cl EMDB-16487, PDB-8c8n: EMDB-16489, PDB-8c8o: EMDB-16492, PDB-8c8r: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Nmar_1547 S-layer |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers








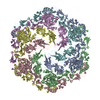





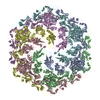
 nitrosopumilus maritimus scm1 (archaea)
nitrosopumilus maritimus scm1 (archaea)