+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure and function of H/K pump mutants reveal Na/K pump mechanisms. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 13, Issue 1, Page 5270, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Sep 9, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Victoria C Young / Hanayo Nakanishi / Dylan J Meyer / Tomohiro Nishizawa / Atsunori Oshima / Pablo Artigas / Kazuhiro Abe /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Ion-transport mechanisms evolve by changing ion-selectivity, such as switching from Na to H selectivity in secondary-active transporters or P-type-ATPases. Here we study primary-active transport via ...Ion-transport mechanisms evolve by changing ion-selectivity, such as switching from Na to H selectivity in secondary-active transporters or P-type-ATPases. Here we study primary-active transport via P-type ATPases using functional and structural analyses to demonstrate that four simultaneous residue substitutions transform the non-gastric H/K pump, a strict H-dependent electroneutral P-type ATPase, into a bona fide Na-dependent electrogenic Na/K pump. Conversion of a H-dependent primary-active transporter into a Na-dependent one provides a prototype for similar studies of ion-transport proteins. Moreover, we solve the structures of the wild-type non-gastric H/K pump, a suitable drug target to treat cystic fibrosis, and of its Na/K pump-mimicking mutant in two major conformations, providing insight on how Na binding drives a concerted mechanism leading to Na/K pump phosphorylation. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:36085139 / PubMed:36085139 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.8 - 3.4 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-32954, PDB-7x21: EMDB-32955, PDB-7x22: EMDB-32956, PDB-7x23: EMDB-32957, PDB-7x24:  PDB-7x20: |
| Chemicals | 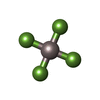 ChemComp-ALF:  ChemComp-K:  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-CLR:  ChemComp-PCW: 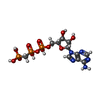 ChemComp-ACP:  ChemComp-NA: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / P-type ATPase / transporter / proton pump / colon / kidney / airway |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers












