+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Tetracenomycin X inhibits translation by binding within the ribosomal exit tunnel. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Chem Biol, Vol. 16, Issue 10, Page 1071-1077, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Jun 29, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Ilya A Osterman / Maximiliane Wieland / Tinashe P Maviza / Kseniya A Lashkevich / Dmitrii A Lukianov / Ekaterina S Komarova / Yuliya V Zakalyukina / Robert Buschauer / Dmitrii I Shiriaev / Semen A Leyn / Jaime E Zlamal / Mikhail V Biryukov / Dmitry A Skvortsov / Vadim N Tashlitsky / Vladimir I Polshakov / Jingdong Cheng / Yury S Polikanov / Alexey A Bogdanov / Andrei L Osterman / Sergey E Dmitriev / Roland Beckmann / Olga A Dontsova / Daniel N Wilson / Petr V Sergiev /    |
| PubMed Abstract | The increase in multi-drug resistant pathogenic bacteria is making our current arsenal of clinically used antibiotics obsolete, highlighting the urgent need for new lead compounds with distinct ...The increase in multi-drug resistant pathogenic bacteria is making our current arsenal of clinically used antibiotics obsolete, highlighting the urgent need for new lead compounds with distinct target binding sites to avoid cross-resistance. Here we report that the aromatic polyketide antibiotic tetracenomycin (TcmX) is a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis, and does not induce DNA damage as previously thought. Despite the structural similarity to the well-known translation inhibitor tetracycline, we show that TcmX does not interact with the small ribosomal subunit, but rather binds to the large subunit, within the polypeptide exit tunnel. This previously unappreciated binding site is located adjacent to the macrolide-binding site, where TcmX stacks on the noncanonical basepair formed by U1782 and U2586 of the 23S ribosomal RNA. Although the binding site is distinct from the macrolide antibiotics, our results indicate that like macrolides, TcmX allows translation of short oligopeptides before further translation is blocked. |
 External links External links |  Nat Chem Biol / Nat Chem Biol /  PubMed:32601485 PubMed:32601485 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.8 - 2.86 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-10705, PDB-6y69: EMDB-10709, PDB-6y6x: |
| Chemicals | 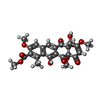 ChemComp-OCW:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / tetracenomycin / ANTIBIOTIC / Translation inhibitor |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers






 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)