+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | The Structural Basis of T4 Phage Lysis Control: DNA as the Signal for Lysis Inhibition. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | J Mol Biol, Vol. 432, Issue 16, Page 4623-4636, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Jul 24, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Inna V Krieger / Vladimir Kuznetsov / Jeng-Yih Chang / Junjie Zhang / Samir H Moussa / Ryland F Young / James C Sacchettini /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Optimal phage propagation depends on the regulation of the lysis of the infected host cell. In T4 phage infection, lysis occurs when the holin protein (T) forms lesions in the host membrane. However, ...Optimal phage propagation depends on the regulation of the lysis of the infected host cell. In T4 phage infection, lysis occurs when the holin protein (T) forms lesions in the host membrane. However, the lethal function of T can be blocked by an antiholin (RI) during lysis inhibition (LIN). LIN sets if the infected cell undergoes superinfection, then the lysis is delayed until host/phage ratio becomes more favorable for the release of progeny. It has been thought that a signal derived from the superinfection is required to activate RI. Here we report structures that suggest a radically different model in which RI binds to T irrespective of superinfection, causing it to accumulate in a membrane as heterotetrameric 2RI-2T complex. Moreover, we show the complex binds non-specifically to DNA, suggesting that the gDNA from the superinfecting phage serves as the LIN signal and that stabilization of the complex by DNA binding is what defines LIN. Finally, we show that soluble domain of free RI crystallizes in a domain-swapped homotetramer, which likely works as a sink for RI molecules released from the RI-T complex to ensure efficient lysis. These results constitute the first structural basis and a new model not only for the historic LIN phenomenon but also for the temporal regulation of phage lysis in general. |
 External links External links |  J Mol Biol / J Mol Biol /  PubMed:32562709 / PubMed:32562709 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 1.65 - 9.4 Å |
| Structure data | 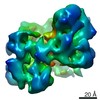 EMDB-22250: 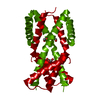 PDB-6psh:  PDB-6psk:  PDB-6px4:  PDB-6pxe: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-EDO:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-SO4:  ChemComp-BTB:  ChemComp-CL: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / phage / lysis inhibition |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



 Escherichia phage T4 (virus)
Escherichia phage T4 (virus)