+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Use of Cryo-EM To Uncover Structural Bases of pH Effect and Cofactor Bispecificity of Ketol-Acid Reductoisomerase. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | J Am Chem Soc, Vol. 141, Issue 15, Page 6136-6140, Year 2019 |
| Publish date | Apr 17, 2019 |
 Authors Authors | Chin-Yu Chen / Yuan-Chih Chang / Bo-Lin Lin / Kuan-Fu Lin / Chun-Hsiang Huang / Dong-Lin Hsieh / Tzu-Ping Ko / Ming-Daw Tsai /  |
| PubMed Abstract | While cryo-EM is revolutionizing structural biology, its impact on enzymology is yet to be fully demonstrated. The ketol-acid reductoisomerase (KARI) catalyzes conversion of (2 S)-acetolactate or (2 ...While cryo-EM is revolutionizing structural biology, its impact on enzymology is yet to be fully demonstrated. The ketol-acid reductoisomerase (KARI) catalyzes conversion of (2 S)-acetolactate or (2 S)-aceto-2-hydroxybutyrate to 2,3-dihydroxy-3-alkylbutyrate. We found that KARI from archaea Sulfolobus solfataricus (Sso-KARI) is unusual in being a dodecamer, bispecific to NADH and NADPH, and losing activity above pH 7.8. While crystals were obtainable only at pH 8.5, cryo-EM structures were solved at pH 7.5 and 8.5 for Sso-KARI:2Mg. The results showed that the distances of the two catalytic Mg ions are lengthened in both structures at pH 8.5. We next solved cryo-EM structures of two Sso-KARI complexes, with NADH+inhibitor and NADPH+inhibitor at pH 7.5, which indicate that the bispecificity can be attributed to a unique asparagine at the cofactor binding loop. Unexpectedly, Sso-KARI also differs from other KARI enzymes in lacking "induced-fit", reflecting structural rigidity. Thus, cryo-EM is powerful for structural and mechanistic enzymology. |
 External links External links |  J Am Chem Soc / J Am Chem Soc /  PubMed:30921515 PubMed:30921515 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.53 - 3.38 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-9798, PDB-6jcv: EMDB-9799, PDB-6jcw: EMDB-9800, PDB-6jcz: EMDB-9801, PDB-6jd1: 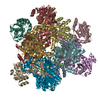 PDB-6jd2: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-NDP:  ChemComp-9TY: 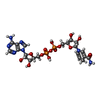 ChemComp-NAI: 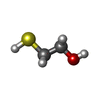 ChemComp-BME: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | ISOMERASE / Bi-specific / Thermostable / Reductoisomerase / Magnesium-dependent / Dodecamer / Knot-structure / Knotted protein |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



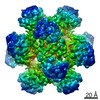
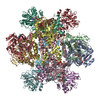

 Sulfolobus solfataricus P2 (archaea)
Sulfolobus solfataricus P2 (archaea)