+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Structural basis for the regulation of inositol trisphosphate receptors by Ca and IP. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 25, Issue 8, Page 660-668, Year 2018 |
| 掲載日 | 2018年7月16日 |
 著者 著者 | Navid Paknejad / Richard K Hite /  |
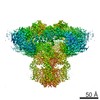
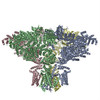
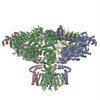
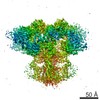
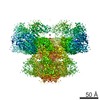
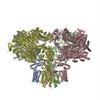
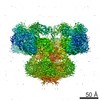
| PubMed 要旨 | Inositol trisphosphate receptors (IPRs) are ubiquitous Ca-permeable channels that mediate release of Ca from the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby regulating numerous processes including cell division, ...Inositol trisphosphate receptors (IPRs) are ubiquitous Ca-permeable channels that mediate release of Ca from the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby regulating numerous processes including cell division, cell death, differentiation and fertilization. IPRs are jointly activated by inositol trisphosphate (IP) and their permeant ion, Ca. At high concentrations, however, Ca inhibits activity, ensuring precise spatiotemporal control over intracellular Ca. Despite extensive characterization of IPR, the mechanisms through which these molecules control channel gating have remained elusive. Here, we present structures of full-length human type 3 IPRs in ligand-bound and ligand-free states. Multiple IP-bound structures demonstrate that the large cytoplasmic domain provides a platform for propagation of long-range conformational changes to the ion-conduction gate. Structures in the presence of Ca reveal two Ca-binding sites that induce the disruption of numerous interactions between subunits, thereby inhibiting IPR. These structures thus provide a mechanistic basis for beginning to understand the regulation of IPR. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:30013099 / PubMed:30013099 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.26 - 6.01 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-7978, PDB-6dqj:  EMDB-7979:  EMDB-7980: EMDB-7981, PDB-6dqn:  EMDB-7982: EMDB-7983, PDB-6dqs: EMDB-7984, PDB-6dqv:  EMDB-7985: EMDB-7986, PDB-6dqz: EMDB-7987, PDB-6dr0: EMDB-7988, PDB-6dr2:  EMDB-7989: 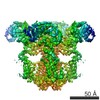 EMDB-7990: EMDB-7991, PDB-6dra: 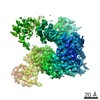 EMDB-7992: 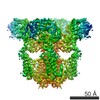 EMDB-7993: EMDB-7994, PDB-6drc:  EMDB-7995:  EMDB-7996: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-ZN: 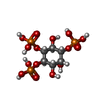 ChemComp-I3P:  ChemComp-CA: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | METAL TRANSPORT / Ion channel / Calcium channel |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




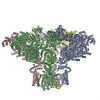
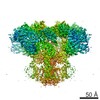

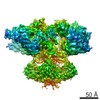
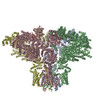
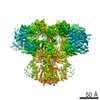
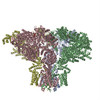
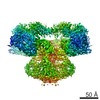
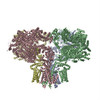

 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)