+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Atomic structure of a rhinovirus C, a virus species linked to severe childhood asthma. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 113, Issue 32, Page 8997-9002, Year 2016 |
| Publish date | Aug 9, 2016 |
 Authors Authors | Yue Liu / Marchel G Hill / Thomas Klose / Zhenguo Chen / Kelly Watters / Yury A Bochkov / Wen Jiang / Ann C Palmenberg / Michael G Rossmann /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Isolates of rhinovirus C (RV-C), a recently identified Enterovirus (EV) species, are the causative agents of severe respiratory infections among children and are linked to childhood asthma ...Isolates of rhinovirus C (RV-C), a recently identified Enterovirus (EV) species, are the causative agents of severe respiratory infections among children and are linked to childhood asthma exacerbations. The RV-C have been refractory to structure determination because they are difficult to propagate in vitro. Here, we report the cryo-EM atomic structures of the full virion and native empty particle (NEP) of RV-C15a. The virus has 60 "fingers" on the virus outer surface that probably function as dominant immunogens. Because the NEPs also display these fingers, they may have utility as vaccine candidates. A sequence-conserved surface depression adjacent to each finger forms a likely binding site for the sialic acid on its receptor. The RV-C, unlike other EVs, are resistant to capsid-binding antiviral compounds because the hydrophobic pocket in VP1 is filled with multiple bulky residues. These results define potential molecular determinants for designing antiviral therapeutics and vaccines. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:27511920 / PubMed:27511920 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.79 - 3.16 Å |
| Structure data | |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / jelly roll |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



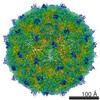

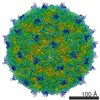

 rhinovirus c
rhinovirus c