+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | High-resolution microtubule structures reveal the structural transitions in αβ-tubulin upon GTP hydrolysis. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Cell, Vol. 157, Issue 5, Page 1117-1129, Year 2014 |
| Publish date | May 22, 2014 |
 Authors Authors | Gregory M Alushin / Gabriel C Lander / Elizabeth H Kellogg / Rui Zhang / David Baker / Eva Nogales /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Dynamic instability, the stochastic switching between growth and shrinkage, is essential for microtubule function. This behavior is driven by GTP hydrolysis in the microtubule lattice and is ...Dynamic instability, the stochastic switching between growth and shrinkage, is essential for microtubule function. This behavior is driven by GTP hydrolysis in the microtubule lattice and is inhibited by anticancer agents like Taxol. We provide insight into the mechanism of dynamic instability, based on high-resolution cryo-EM structures (4.7-5.6 Å) of dynamic microtubules and microtubules stabilized by GMPCPP or Taxol. We infer that hydrolysis leads to a compaction around the E-site nucleotide at longitudinal interfaces, as well as movement of the α-tubulin intermediate domain and H7 helix. Displacement of the C-terminal helices in both α- and β-tubulin subunits suggests an effect on interactions with binding partners that contact this region. Taxol inhibits most of these conformational changes, allosterically inducing a GMPCPP-like state. Lateral interactions are similar in all conditions we examined, suggesting that microtubule lattice stability is primarily modulated at longitudinal interfaces. |
 External links External links |  Cell / Cell /  PubMed:24855948 / PubMed:24855948 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 4.7 - 6.6 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-5895: Cryo EM density of microtubules stabilized by GMPCPP EMDB-5896: Cryo EM density of GDP-bound dynamic microtubules EMDB-5897: Cryo EM density of microtubules stabilized by taxol  EMDB-5898:  EMDB-5899: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-GTP:  ChemComp-MG: 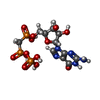 ChemComp-G2P:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-GDP:  ChemComp-TA1: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / microtubule / GmpCpp / GDP / dynamic / taxol |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers







 Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human)