+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural basis for PtdInsP-mediated human TRPML1 regulation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 9, Issue 1, Page 4192, Year 2018 |
| Publish date | Oct 10, 2018 |
 Authors Authors | Michael Fine / Philip Schmiege / Xiaochun Li /  |
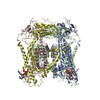
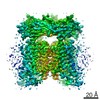
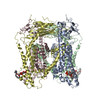
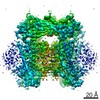
| PubMed Abstract | Transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1), a lysosomal channel, maintains the low pH and calcium levels for lysosomal function. Several small molecules modulate TRPML1 activity. ML-SA1, a ...Transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1), a lysosomal channel, maintains the low pH and calcium levels for lysosomal function. Several small molecules modulate TRPML1 activity. ML-SA1, a synthetic agonist, binds to the pore region and phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,5)P), a natural lipid, stimulates channel activity to a lesser extent than ML-SA1; moreover, PtdIns(4,5)P, another natural lipid, prevents TRPML1-mediated calcium release. Notably, PtdIns(3,5)P and ML-SA1 cooperate further increasing calcium efflux. Here we report the structures of human TRPML1 at pH 5.0 with PtdIns(3,5)P, PtdIns(4,5)P, or ML-SA1 and PtdIns(3,5)P, revealing a unique lipid-binding site. PtdIns(3,5)P and PtdIns(4,5)P bind to the extended helices of S1, S2, and S3. The phosphate group of PtdIns(3,5)P induces Y355 to form a π-cation interaction with R403, moving the S4-S5 linker, thus allosterically activating the channel. Our structures and electrophysiological characterizations reveal an allosteric site and provide molecular insight into how lipids regulate TRP channels. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:30305615 / PubMed:30305615 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.5 - 3.73 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-9000, PDB-6e7p: |
| Chemicals | 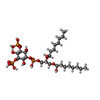 ChemComp-HZ7: 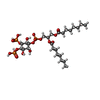 ChemComp-PIO: 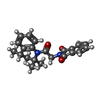 ChemComp-AQV: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / human TRPML1 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)