+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Cryo-EM study of start codon selection during archaeal translation initiation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 7, Page 13366, Year 2016 |
| Publish date | Nov 7, 2016 |
 Authors Authors | Pierre-Damien Coureux / Christine Lazennec-Schurdevin / Auriane Monestier / Eric Larquet / Lionel Cladière / Bruno P Klaholz / Emmanuelle Schmitt / Yves Mechulam /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Eukaryotic and archaeal translation initiation complexes have a common structural core comprising e/aIF1, e/aIF1A, the ternary complex (TC, e/aIF2-GTP-Met-tRNA) and mRNA bound to the small ribosomal ...Eukaryotic and archaeal translation initiation complexes have a common structural core comprising e/aIF1, e/aIF1A, the ternary complex (TC, e/aIF2-GTP-Met-tRNA) and mRNA bound to the small ribosomal subunit. e/aIF2 plays a crucial role in this process but how this factor controls start codon selection remains unclear. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of the full archaeal 30S initiation complex showing two conformational states of the TC. In the first state, the TC is bound to the ribosome in a relaxed conformation with the tRNA oriented out of the P site. In the second state, the tRNA is accommodated within the peptidyl (P) site and the TC becomes constrained. This constraint is compensated by codon/anticodon base pairing, whereas in the absence of a start codon, aIF2 contributes to swing out the tRNA. This spring force concept highlights a mechanism of codon/anticodon probing by the initiator tRNA directly assisted by aIF2. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:27819266 / PubMed:27819266 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 5.34 Å |
| Structure data | |
| Chemicals | 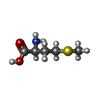 ChemComp-MET:  ChemComp-MG: 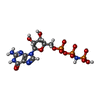 ChemComp-GNP:  ChemComp-ZN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSLATION / TRANSCRIPTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers







 pyrococcus abyssi ge5 (archaea)
pyrococcus abyssi ge5 (archaea)
