+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural and dynamic insights into the biased signaling mechanism of the human kappa opioid receptor. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 16, Issue 1, Page 9392, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Oct 28, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Chiyo Suno-Ikeda / Ryo Nishikawa / Riko Suzuki / Shun Yokoi / Seiya Iwata / Tomoyo Takai / Takaya Ogura / Mika Hirose / Akihisa Tokuda / Risako Katamoto / Akitoshi Inoue / Eri Asai / Ryoji Kise / Yukihiko Sugita / Takayuki Kato / Hiroshi Nagase / Ayori Mitsutake / Tsuyoshi Saitoh / Kota Katayama / Asuka Inoue / Hideki Kandori / Takuya Kobayashi / Ryoji Suno /  |
| PubMed Abstract | The κ-opioid receptor (KOR) is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, modulating cellular responses through transducers such as G proteins and β-arrestins. G-protein-biased KOR ...The κ-opioid receptor (KOR) is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, modulating cellular responses through transducers such as G proteins and β-arrestins. G-protein-biased KOR agonists aim to retain analgesic and antipruritic actions while limiting aversion and sedation. Aiming to inform G-biased KOR agonist design, we analyze signaling-relevant residues from structural and dynamic views. Here we show, using multiple complementary methods, shared residues that determine β-arrestin recruitment by nalfurafine and U-50,488H. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the KOR-G signaling complexes identify the ligand binding mode in the activated state. Vibrational spectroscopy reveals ligand-induced conformational changes. Cell-based mutant experiments pinpoint four amino acids (K227, C286, H291, and Y312; Ballesteros-Weinstein numbering is shown in superscript) that play crucial roles in β-arrestin recruitment. Furthermore, MD simulations revealed that the four mutants tend to adopt conformations with reduced β-arrestin recruitment activity. Our research findings provide a foundation for enhancing KOR-mediated therapeutic effects while minimizing unwanted side effects by targeting specific residues within the KOR ligand-binding pocket, including K227 and Y312, which have previously been implicated in biased signaling. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:41152269 / PubMed:41152269 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.76 - 2.9 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-64947: Cryo-EM structure of the human kappa opioid receptor signaling complex bound to compound A EMDB-65622, PDB-9w49: |
| Chemicals | 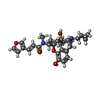 ChemComp-IVB:  PDB-1lwx: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / signal transduction / GPCR / G protein / opioid receptor / balanced agonist |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers







 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
