+検索条件
-Structure paper
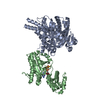
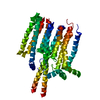
| タイトル | Structural insights into human adenylyl cyclase 9 in complex with Gαs by cryo-EM. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | J Struct Biol, Vol. 217, Issue 3, Page 108223, Year 2025 |
| 掲載日 | 2025年6月2日 |
 著者 著者 | Risa Nomura / Shota Suzuki / Koki Nishikawa / Hiroshi Suzuki / Yoshinori Fujiyoshi /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Adenylyl cyclase 9 (AC9) regulates many physiologic functions through the production of cAMP, an important second messenger that regulates downstream effectors. The activation of AC9 is highly ...Adenylyl cyclase 9 (AC9) regulates many physiologic functions through the production of cAMP, an important second messenger that regulates downstream effectors. The activation of AC9 is highly regulated by GPCR signaling. For example, AC9 is activated by the binding of Gαs, which, in turn, is activated by Gs-driven GPCRs. The structure of bovine AC9 (bAC9) was reported in 2019 using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). The structure of human AC9 (hAC9), however, has not been reported to date despite its potential benefit for drug development. Here, we analyzed the structures of hAC9 and hAC9 in complex with Gαs (hAC9-Gαs) using single-particle cryo-EM. The soluble domain of AC9-Gαs, the transmembrane (TM) domain of AC9-Gαs, and AC9 alone were analyzed at resolutions of 2.7 Å, 3.4 Å, and 3.2 Å, respectively. The results revealed three key aspects of the activation mechanism of hAC9 and its cAMP-generating function. First, a conformational change of the soluble domain was observed upon Gαs binding, resulting in a widely open catalytic site. Second, we analyzed the exact position of the C-terminus occluding the catalytic site in the hAC9-Gαs complex. Finally, we unexpectedly identified an elongated density suggestive of a single acyl chain in the TM domain. Consistent with recent reports on the allosteric regulation of AC by lipids, this finding suggests that the TM domain could serve as a potential drug target.These structural findings enhance our understanding of the structure and function of AC9 and other ACs and will provide a foundation for future AC-target drug discovery. |
 リンク リンク |  J Struct Biol / J Struct Biol /  PubMed:40466787 PubMed:40466787 |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.65 - 3.5 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-63823, PDB-9u3p: EMDB-63824, PDB-9u3q: EMDB-63825, PDB-9u3r: EMDB-63826, PDB-9u3s: EMDB-63827, PDB-9u3u: EMDB-63828, PDB-9u3v: |
| 化合物 | 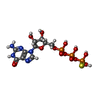 ChemComp-GSP:  ChemComp-MG: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / enzyme |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について












 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト) human respiratory syncytial virus (ウイルス)
human respiratory syncytial virus (ウイルス)