+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | A molecular ruler determines the repeat length in eukaryotic cilia and flagella. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Science, Vol. 346, Issue 6211, Page 857-860, Year 2014 |
| Publish date | Nov 14, 2014 |
 Authors Authors | Toshiyuki Oda / Haruaki Yanagisawa / Ritsu Kamiya / Masahide Kikkawa /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Existence of cellular structures with specific size raises a fundamental question in biology: How do cells measure length? One conceptual answer to this question is by a molecular ruler, but examples ...Existence of cellular structures with specific size raises a fundamental question in biology: How do cells measure length? One conceptual answer to this question is by a molecular ruler, but examples of such rulers in eukaryotes are lacking. In this work, we identified a molecular ruler in eukaryotic cilia and flagella. Using cryo-electron tomography, we found that FAP59 and FAP172 form a 96-nanometer (nm)-long complex in Chlamydomonas flagella and that the absence of the complex disrupted 96-nm repeats of axonemes. Furthermore, lengthening of the FAP59/172 complex by domain duplication resulted in extension of the repeats up to 128 nm, as well as duplication of specific axonemal components. Thus, the FAP59/172 complex is the molecular ruler that determines the 96-nm repeat length and arrangements of components in cilia and flagella. |
 External links External links |  Science / Science /  PubMed:25395538 PubMed:25395538 |
| Methods | EM (subtomogram averaging) |
| Resolution | 45.0 - 52.0 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-6108:  EMDB-6109: 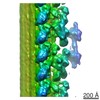 EMDB-6110: 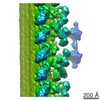 EMDB-6111:  EMDB-6112:  EMDB-6113:  EMDB-6114:  EMDB-6115:  EMDB-6116: 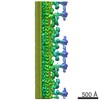 EMDB-6117: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




