+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural basis of phosphate export by human XPR1. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 16, Issue 1, Page 683, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Jan 15, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Qixian He / Ran Zhang / Sandrine Tury / Valérie Courgnaud / Fenglian Liu / Jean-Luc Battini / Baobin Li / Qingfeng Chen /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Phosphorus in crucial for all living organisms. In vertebrate, cellular phosphate homeostasis is partly controlled by XPR1, a poorly characterized inositol pyrophosphate-dependent phosphate exporter. ...Phosphorus in crucial for all living organisms. In vertebrate, cellular phosphate homeostasis is partly controlled by XPR1, a poorly characterized inositol pyrophosphate-dependent phosphate exporter. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of human XPR1, which forms a loose dimer with 10 transmembrane helices (TM) in each protomer. The structure consists of a scaffold domain (TM1, TM3-4) and a core domain (TM2, TM5-10) structurally related to ion-translocating rhodopsins. Bound phosphate is observed in a tunnel within the core domain at a narrow point that separates the tunnel into intracellular and extracellular vestibules. This site contains a cluster of basic residues that coordinate phosphate and a conserved W573 essential for export function. Loss of inositol pyrophosphate binding is accompanied by structural movements in TM9 and the W573 sidechain, closing the extracellular vestibule and blocking phosphate export. These findings provide insight into XPR1 mechanism and pave the way for further in-depth XPR1 studies. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:39814721 / PubMed:39814721 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.64 - 2.91 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-60645, PDB-9ijy: EMDB-60646, PDB-9ijz: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-PO4:  ChemComp-6PL: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN TRANSPORT / Pi exporter / a key regulator of cellular Pi homeostasis |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




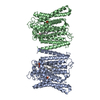

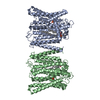
 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)