+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Passage of the HIV capsid cracks the nuclear pore. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Cell, Vol. 188, Issue 4, Page 930-943.e21, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Feb 20, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Jan Philipp Kreysing / Maziar Heidari / Vojtech Zila / Sergio Cruz-León / Agnieszka Obarska-Kosinska / Vibor Laketa / Lara Rohleder / Sonja Welsch / Jürgen Köfinger / Beata Turoňová / Gerhard Hummer / Hans-Georg Kräusslich / Martin Beck /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Upon infection, human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) releases its cone-shaped capsid into the cytoplasm of infected T cells and macrophages. The capsid enters the nuclear pore complex (NPC), ...Upon infection, human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) releases its cone-shaped capsid into the cytoplasm of infected T cells and macrophages. The capsid enters the nuclear pore complex (NPC), driven by interactions with numerous phenylalanine-glycine (FG)-repeat nucleoporins (FG-Nups). Whether NPCs structurally adapt to capsid passage and whether capsids are modified during passage remains unknown, however. Here, we combined super-resolution and correlative microscopy with cryoelectron tomography and molecular simulations to study the nuclear entry of HIV-1 capsids in primary human macrophages. Our data indicate that cytosolically bound cyclophilin A is stripped off capsids entering the NPC, and the capsid hexagonal lattice remains largely intact inside and beyond the central channel. Strikingly, the NPC scaffold rings frequently crack during capsid passage, consistent with computer simulations indicating the need for NPC widening. The unique cone shape of the HIV-1 capsid facilitates its entry into NPCs and helps to crack their rings. |
 External links External links |  Cell / Cell /  PubMed:39826544 PubMed:39826544 |
| Methods | EM (subtomogram averaging) |
| Resolution | 24.5 - 36.7 Å |
| Structure data | 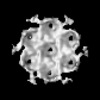 EMDB-51531: HIV-1 CA hexamer from capsids inside virions (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages) 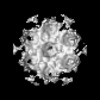 EMDB-51532: HIV-1 CA hexamer from cytoplasmic capsids (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages) 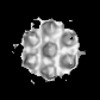 EMDB-51533: HIV-1 CA hexamer from capsids inside NPCs (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages) 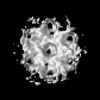 EMDB-51534: HIV-1 CA hexamer from nuclear capsids (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages)  EMDB-51535: HIV-1 CA pentamer from capsids inside virions (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages) 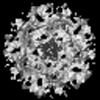 EMDB-51536: HIV-1 CA pentamer from cytoplasmic capsids (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages)  EMDB-51626: In situ human cytoplasmic ring subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages)  EMDB-51627: In situ human inner ring subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages)  EMDB-51628: In situ human nuclear ring subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages)  EMDB-51629: In situ human luminal ring subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages)  EMDB-51630: In situ human basket attachment to nuclear ring of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages)  EMDB-51631: In situ human asymmetric subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages)  EMDB-51632: In situ human symmetrized composite map of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of HIV infected macrophages)  EMDB-52138: In situ human cytoplasmic ring subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of mock infected macrophages) 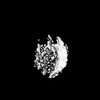 EMDB-52139: In situ human inner ring subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of mock infected macrophages) 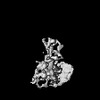 EMDB-52140: In situ human nuclear ring subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of mock infected macrophages)  EMDB-52141: In situ human luminal ring subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of mock infected macrophages)  EMDB-52142: In situ human basket attachment to nuclear ring of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of mock infected macrophages)  EMDB-52143: In situ human asymmetric subunit of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of mock infected macrophages)  EMDB-52144: In situ human symmetrized composite map of nuclear pore complex (FIB-lamella data of mock infected macrophages) |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



 Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human)